
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:e
E
D
Macmillan Learning
C
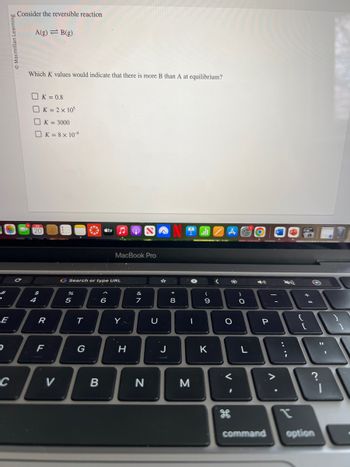
Consider the reversible reaction
A(g) B(g)
Which K values would indicate that there is more B than A at equilibrium?
20
$
4
K = 0.8
K = 2 x 105
K = 3000
K = 8 x 10-⁹
R
F
V
*
G Search or type URL
5
T
G
B
tv ♫
6
MacBook Pro
Y
H
&
7
N
U
☆
J
* 00
8
I
M
(
9
K
<
A Call
22
O
<
H
-O
)
O
L
P
Δ·
:
{
+
[
command option
11
3
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the reversible reaction A(g) rightleftharpoons B(g) Which K values would indicate that there is more B than A at equilibrium? K = 0.1 K = 4 * 10 ^ - 8 K = 4000 K = 5 * 10 ^ 7arrow_forwardConsider the following equilibrium reaction: 2NO (g) + Cl2 (g) 2 NOCl (g) K=12 At equilibrium, [NOCl] = 1.60 M and [NO] = 0.80 M. The [Cl2] isarrow_forwardDetermine the value of K for the following reaction. 2 SO2(g) + O2(g) = 2 SO3(g) The equilibrium concentrations are as follows. [SO2] = 0.6265 M [02] = 2.932 M [SO3] = 8.868 M Keep the answer with 2 decimal places.arrow_forward
- 4. For the reaction CH4(g) + 2 H2S(g) = CS2(g) + 4 H₂(g) Kc = 3.59 at 900 °C. For each of the following measured concentrations determine whether the reaction is at equilibrium. If not, in which direction will the reaction proceed to get to equilibrium? [CH] [H₂S] [CS₂] [H2] Expt 1 Expt 2 Expt 3 1.15 1.07 1.10 1.20 1.20 1.49 1.51 0.90 1.10 1.08 1.78 1.68arrow_forwardGiven the following reaction, the equilibrium constant, and the initial concentrations; answer the four bullet questions. 2 NO2 (g) - 2 NO (g) + O2 (g) Kc = 1.56 x 10-10 Initial Species Concentration (M) NO2 5.62 x 10-10 NO 3.99 x 10-16 O2 9.35 x 10-3 • Set up the equilibrium expression, and calculate the reaction quotient (Q). Note: ^ means "to the" Q = [ Select ] • How does Q compare to K? Q is [ Select]arrow_forwardConsider the following reaction where K = 77.5 at 600 K. CO(g) + Cl₂(g) 2 CoCl₂(g) A reaction mixture was found to contain 1.89×10-² moles of CO(g), 4.43×10-² moles of Cl₂(g) and 0.106 moles of COCI₂(g), in a 1.00 liter container. Is the reaction at equilibrium? If not, what direction must it run in order to reach equilibrium? The reaction quotient, Qc, equals The reaction A. must run in the forward direction to reach equilibrium. B. must run in the reverse direction to reach equilibrium. C. is at equilibrium.arrow_forward
- Q2arrow_forwardCan you please answer question 2arrow_forwardThe questions that follow are based on the reaction at equilibrium: C(s) + CO2(g) = 2C0(g) AH° = +172.5 kJ/mol %3D What would be the effect on the preceding reaction of adding 2.0 mol of CO? The composition of the system at equilibrium will not change. The reaction would shift to the product side. The reaction will shift to the reactant side. Additional information is needed to answer the question.arrow_forward
- Consider the following equilibrium: CO(g) + NO2(g) ↔ CO2(g) + NO(g) At a specific temperature the equilibrium concentrations where determined to be: [CO] = 0.0033M [NO2] = 0.021M [CO2] = 0.59M [NO] = 0.59M a- Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant b- Describe the position of the equilibriumarrow_forwardAn empty steel container is filled with 3.10 atm of H₂ and 3.10 atm of F2. The system is allowed to reach equilibrium. If Kp = 0.450 for the reaction below, what is the equilibrium partial pressure of HF? H₂ (g) + F₂ (g) → 2 HF (g)arrow_forwardConsider the following equilibrium system at 817 K. SO2 Cl2 (g) 2 SO2(g) + Cl2 (g) If an equilibrium mixture of the three gases at 817 K contains 1.60 x 10-3 M SO2 Cl2, 3.57 x 10-2 SO2, and 2.12 x 10-2 M Cl2, what is the value of the equilibrium constant К? M K =arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY