
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
I need an answer with a free body-diagram.
Show all work as quickly as possible.
Q:
A wooden plank of negligible mass and length L = 2.8 m is used to keep in balance, horizontally, a small cube of mass 20.0 kg when applying a force F of 80.0 N at one end of the board. The distance, in meters, between the support point of the board and the position where find the cube is:
a) 0.56
b) 0.80
c) 1.00
d) 1.12
e) 1.40
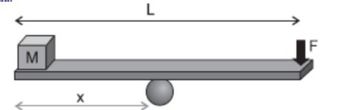
Transcribed Image Text:M
X
L
F
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 4. please solve for marrow_forwardA) Acceleration of mass M2 B) Speed of M2 after 4 seconds C) when M2 moves 4.6 m how far does M1 move. Thank youarrow_forwardQ3: As Engineer, you have been asked to calculate only the force in each members of the truss shown below (fig 3) after applying two forces on it (F1 and F2) which are (500 N and 0.8 kN) respectively. D -F1 4 m Fig 3 E F2 4 m A 5 marrow_forward
- You need to push a cupboard by applying a horizontal force F on its side. The cupboard width is L, height is H and mass is m. You are applying the force at a point that is a height h above the floor. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the dresser and the floor is u. The ground exerts upward normal forces of magnitudes Np and No at the two ends of the dresser. a) How much force do you need to apply for the cupboard to move with constant velocity? b) What are the magnitudes of normal forces Np and Na if the cupboard legs are separated by a distance L? c) What is the maximum height h where you can push the cupboard before it tips over? F H Pl Np N.arrow_forwardQ2: You ride your bike along a straight line from your house to a store (1000 m) away. On your way back, you stop at a friend's house which is halfway between your house and the store. Find: a. What is your displacement? b. What is the distance you have traveled?arrow_forwardSpring is hung vertically, and an object of mass (m) is attached to its lower end. The spring stretches a distance (d) from its equilibrium position-How much work is done by the spring on the object as it stretches through this distance?arrow_forward
- 6.2 In class we noted that the potential energy of a spring is given by Vsp (2) and k the spring constant. Now consider an object of mass m (not attached to the spring) that drops from rest, from a height z; > z0; onto the spring (which is initially in equilibrium at its rest length). Both the gravitational force and the spring force now contribute to the potential energy, initial final k(z – zo)²/2, where zo is the spring's equilibrium point E Zo Z=0 Vgrav Vgrav + Vsp if z z0 V (2) = (1) (a) Sketch (by hand, but carefully) a potential energy diagram for V(2) as a function of height z. (b) Include (and mark) the object's initial energy in the sketch of part (a), then include a horizontal line for the object's conserved total energy E. Also mark the turning point zf for z < zO. (c) Calculate the turning point position zf where the object momentarily comes to rest." (d) Your graph of part (a) should have an equilibrium point. Mark this equilibrium point in your graph, then calculate its…arrow_forwardPlease don't copy wrong solution ,Strictly use paper sheet to solve. Mechanical engineering: Thermodynamics. Q1:- A vertical hydraulic cylinder has a 125-mm diameter piston with hydraulic fluid inside the cylinder and an ambient pressure of 1 bar. Assuming standard gravity, find the piston mass that will create a pressure inside of 1500 kPa.arrow_forward£1,7 0:-11 | ZAY O K/s Figure below shows a rod that is free to rotate about its center of mass. A force F, = 15 N is applied at d, = 4 m from the COM and another force F, = 17 N is applied at d, = 7 m from the COM, as shown. The magnitude of the total torque about the axis of rotation is: F1 600 COM 300 F2arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY