
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
A bullet of mass m and speed
v passes completely through a pendulum
bob of mass M as shown in
Figure P6.64. The bullet emerges
with a speed of v/2. The pendulum
bob is suspended by a stiff rod of
length , and negligible mass. What
is the minimum value of v such that
the bob will barely swing through a
complete vertical circle?
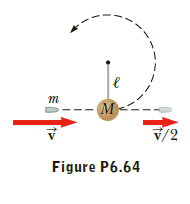
Transcribed Image Text:M-
v/2
Figure P6.64
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The conservation of momentum tellsus that the momentum of a system ofinteracting particles must remain constant ifthere are no outside forces. However, whentwo cars collide head-on, they can almostinstantly come to rest (and crumpleunfortunately). This system is essentiallyisolated since the only important interactionsare between the two cars. How can youreconcile these two observations?arrow_forwardRock A of mass M and another rock B of mass 2M are released from a height h above the ground. Upon impact which relationship correctly states the momenta of rocks A and B?arrow_forwardA pendulum consists of a smallobject called a bob hanging froma light cord of fixed length, withthe top end of the cord fixed, asrepresented in Figure CQ7.5. Thebob moves without friction, swingingequally high on both sides. Itmoves from its turning point Athrough point B and reaches itsmaximum speed at point C. (a) Atwhat point does the bob have nonzeroradial acceleration and zero tangential acceleration?What is the direction of its total acceleration at this point?(b) At what point does the bob have nonzero tangentialacceleration and zero radial acceleration? What is thedirection of its total acceleration at this point? (c) At whatpoint does the bob have both nonzero tangential and radialacceleration? What is the direction of its total accelerationat this point?arrow_forward
- question 59 pleasearrow_forwardWe have two spheres (m and M) that are separated by a small distance; m is to the left of M. A sphere of mass m (identical to one of the two initial spheres) is moving towards m at a speed V0. Show that when M is smaller than or equal to m, there will be 2 collisions and calculate the final speeds. Show that when M is larger than m, there will be three collisions and calculate the final velocities.arrow_forward. What is the initial kinetic energy in joules of the bullet in problem 1? What is the final kinetic energy of the combined bullet/pendulum?arrow_forward
- In the figure, two satellites, A and B, both of mass m = 36.1 kg, move in the same circular orbit of radius r = 7240 km around Earth (mass ME = 5.98×1024 kg) but in opposite senses of rotation and therefore on a collision course. (a) Find the total mechanical energy Е+ ЕÅ of the two satellites + Earth system before the collision. (b) If the collision is completely inelastic so that the wreckage remains as one piece of tangled material (mass = 2m), find the total mechanical energy immediately after the collision. (c) Just after the collision, is the wreckage falling directly toward Earth's center or orbiting around Earth? (a) Number Units (b) Number (c) Units A B Eartharrow_forwardBallistic Pendulum7. A mass of 15 g traveling at a rate of 250 m/s imbeds itself into a stationary lump of clayof mass 5 kg. What is the maximum height the combined mass of clay and bullet willrise to? (The book will have an illustration of a ballistic pendulum.) Find the resultingvelocity of combined mass and then use conservation of energy to find height.arrow_forwardA simple pendulum is given an initial tangential velocity such that it swings in acomplete circle around its fulcrum. Assume:● The string is 32 meters long● The bob has mass M Determine: (A) The minimum velocity atthe top ofthe loop. Now assume the mass passesthrough the top of the loop with theminimum found in part (a), above; Determine: (B) the velocity at an angle of 30 degrees from the vertical(i.e.: at 30 degrees up from a position fully at the bottom of the loop).arrow_forward
- > A crew Capsule is returning from the ISS, whose orbit is circular with radius Ro + 400 km. Prior to re-entry, the capsule will insert into a 200 km Coplanar parking orbit to validate a new safety. system. The crew execute a Hohmann transfer to change their orbit from that of the ISS to that of the parking orbit. Compute the phase angle Do at the time of Impulse 1. State answer in degrees.arrow_forwardPlease asaparrow_forwardLet's put a circle of 10 m radius and constant density. At 5 m from the center, I make a hole of 3 m radius. Where will be the center of mass of this system? I put this disk vertically on a horizontal table, but the hole at the bottom. What happens? Nature always goes to the state of minimum energy....!arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON