
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
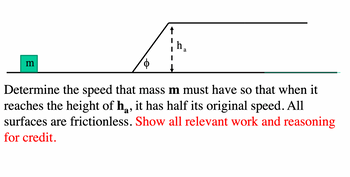
Transcribed Image Text:m
↑
h₁
a
Determine the speed that mass m must have so that when it
reaches the height of h, it has half its original speed. All
surfaces are frictionless. Show all relevant work and reasoning
for credit.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Given
speed that mass m must have so that when it reaches the height of ha , it has half its original speed. All surfaces are frictionless.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A box of 10 kg mass is sliding down a ramp with 60 degree inclination for 5 meters. The kinematic coefficient of friction is 0.3. What is the magnitude of work done by the friction force, in Newtons? Use g = 10 m/s2. Neglect the sign when entering your answer.arrow_forwardA 7.80-g bullet moving at 690 m/s penetrates a tree trunk to a depth of 5.10 cm. (a) Use work and energy considerations to find the average frictional force that stops the bullet.N(b) Assuming the frictional force is constant, determine how much time elapses between the moment the bullet enters the tree and the moment it stops moving.sarrow_forwardF A 2.3 kg block is moved at constant speed over a surface for which the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.26. The displacement is 6 m. It is pushed by a force directed at 34 degrees below the horizontal as shown in the figure above. Find the work done on the block by: a) the force; a) friction; a) gravity.arrow_forward
- e A grandfather clock is powered by thedescent of a 4.35-kg weight. (a) If the weight descends through adistance of 0.760 m in 3.25 days, how much power does it deliverto the clock? (b) To increase the power delivered to the clock,should the time it takes for the mass to descend be increased ordecreased? Explainarrow_forwardSolution to HW problem with all work and explanation, please.arrow_forwardPls help ASAParrow_forward
- A 2,200-kg pile driver is used to drive a steel I-beam into the ground. The pile driver falls 4.60 m before coming into contact with the top of the beam, and it drives the beam 15.0 cm farther into the ground as it comes to rest. Using energy considerations, calculate the average force the beam exerts on the pile driver while the pile driver is brought to rest. 588925.42 magnitude Write an expression for the work done by all of the forces acting on the beam as it moves into the ground and relate that work to the change in energy of the pile driver in order to find the force that the beam exerts on the pile driver. Narrow_forwardYou are a member of an Alpine Rescue Team. You must project a box of supplies up an incline of constant slope angle a so that it reaches a stranded skier who is a vertical distance h above the bottom of the incline. The incline is slippery, but there is some friction present, with kinetic friction coefficient mk. Use the work–energy theorem to calculate the minimum speed you must give the box at the bottom of the incline so that it will reach the skier. Express your answer in terms of g, h, mk, and a.arrow_forwardAn object of mass m can only move on the +z axis. It is subjected to a force in the +z direction given by F(x) = the origin. a. How much work does this force do if the object moves from z = a b. If at a the block had an initial velocity of magnitude vo in the +z direction, what is its velocity at b if no other force is acting on the object? am where a is a constant and z is the distance from to z = b?arrow_forward
- A child of mass m = 16 kg slides down a slide of height h = 2.7 m without friction. Let gravitational potential energy be zero at ground level. a)Write an expression for the child's total mechanical energy, E, at the top of the slide, in terms of the variables in the problem and the acceleration due to gravity g. b)Calculate the change in the child's potential energy, ΔU in joules, from the top to the bottom of the slide at ground level (i.e. ΔU = Uground - Utop). c)What is the child's final speed, vf in m/s?arrow_forwardACTIVITY 4: DECODE THE MESSAGE Directions: Determine the work done by the force on a given system in the following problems. Then, decode the message. A E How much work is done How much work is done by a shopper in pushing her distance of 7.9 m under the by the force? grocery cart by a force of action of a constant force of 32.0 N through a distance of 5.6 N. How much work is JA 4.0 kg object moves a 4.5 m? done on the object? Diplacement ( E You pull your bag with a MA crate is being lifted M You must exert a force of force of 30 N parallel to the into a truck. If it is moved 4.5 N on a book to slide it ground classroom 20 m away. How 3650 J of work is done, then J of work in the process, much work will you do on how far is the crate being how far have you moved the your bag? towards your with a 2470 N force and across a table. If you do 2.7 lifted? book? S A porter pulls a 10-kg luggage along a level road for 5 m by exerting a force of 20 N at angle of 30° with the horizontal…arrow_forwardYou stand at the top of a cliff and lower a first aid kit (attached to a rope) down the cliff to an injured hiker at a constant speed. What can you say about the work done by the rope and the work done by gravity on the kit as it is lowered? O The work done by the rope is positive and the work done by gravity is positive. The work done by the rope is negative and the work done by gravity is negative. O The work done by the rope is positive and the work done by gravity is negative. O The work done by the rope is zero and the work done by gravity is zero. O The work done by the rope is negative and the work done by gravity is positive.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON