
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
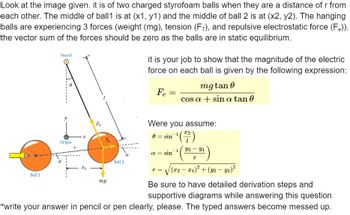
Transcribed Image Text:Look at the image given. it is of two charged styrofoam balls when they are a distance of r from
each other. The middle of ball1 is at (x1, y1) and the middle of ball 2 is at (x2, y2). The hanging
balls are experiencing 3 forces (weight (mg), tension (F+), and repulsive electrostatic force (F.)).
the vector sum of the forces should be zero as the balls are in static equilibrium.
Ball 1
Pencil
Origin
·x
Fr
mg
Ball 2
it is your job to show that the magnitude of the electric
force on each ball is given by the following expression:
Fe
=
Were you assume:
in-¹ (²/²7)
= sin
mgtan 0
cos a + sin a tan 0
a = sin
32 – 31
1 (9-³)
T
T
• = √(x2 − x₁)² + (y2 − y₁)²
Be sure to have detailed derivation steps and
supportive diagrams while answering this question
*write your answer in pencil or pen clearly, please. The typed answers become messed up.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A wracking ball is suspended below two cables each at an angle with the horizontal. The left cable has tension T1 and angle 37 degrees with the horizontal. The right cable has tension T2 and angle 22 degrees with the horizontal. The Wracking ball has mass 180 kg. Find the magnitude of tension T2.arrow_forwardtv wil The following forces are acting on the bracket below. The bracket has a width w of 2 inches and a height h of 3 inches. The bracket is in equilibrium (not accelerating). Determine F3y knowing F1x-98 lbf and F1y-166 lbf. For this question, what is F3y in Ibf? Note that the y-direction is pointing up, so if the force is pushing down on the bracket, it has a negative magnitude. h 3,arrow_forwardDraw the FBDs for the following system with its distributed loads simplified to their equivalentloads.Draw the FBD where the system is the bar. You can find the system in the image with all the details.arrow_forward
- See image for question. Thanks.arrow_forwardA hand exerts a force of 125 N on a scale at 30 cm from the joint center at the elbow. If the triceps attaches to the ulna at a 90° angle and at a distance of 3.5 cm from the elbow joint center, and if the weight of the forearm and hand is 45 N with the hand/ forearm CG located 15 cm from the elbow joint center, how much force is being exerted by the triceps?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY