
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Solve and draw shear and bending moment diagrams.
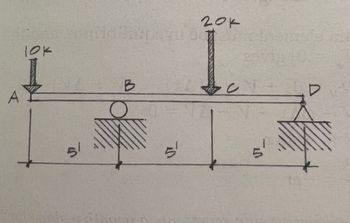
Transcribed Image Text:### Structural Beam Diagram
The diagram represents a structural beam subjected to different forces and constraints:
1. **Beam Description**:
- The beam is horizontal and segmented into parts labeled A, B, C, and D.
2. **Forces**:
- At point A, there is a downward force labeled "10k" (presumably representing 10,000 units of force).
- At point C, there is another downward force labeled "20k" (presumably 20,000 units).
3. **Supports**:
- Point B has a roller-type support, allowing for vertical movement but not horizontal (denoted by a small circle on a hatched surface).
- Point D is supported by a pin, restricting both vertical and horizontal movement, indicated by a triangle on a hatched surface.
4. **Distances**:
- The section of the beam from A to B is 5 feet.
- Another 5 feet from B to C.
- From C to D is also 5 feet.
This diagram serves as a fundamental representation useful for understanding concepts in physics and engineering, particularly in static equilibrium analysis.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Solve the problem and answer the questions that follow. - If the supports were swapped such that the left support were a roller and the right support a pin, how would your solution change? - If the value of “w” were doubled, what would be the bending moment at the left most point of the beam?arrow_forwardKindly write the full solution on a piece of paper rounded off to 4 decimal places, much appreciatedarrow_forward
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning