
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
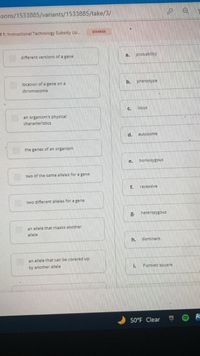
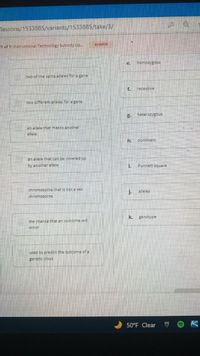
Match each vocabulary term to its definition
Transcribed Image Text:ssons/1533885/variants/1533885/take/3/
f1: Instructional Technology Subsidy Up.
DISMISS
different versions of a gene
a.
probability
location of a gene on a
b.
phenotype
chromosome
C.
locus
an organism's physical
characteristics
d.
autosome
the genes of an organism
e.
homozygous
two of the same alleles for a gene
f.
recessive
two different alleles for a gene
g.
heterozygous
an allele that masks another
allele
h.
dominant
an allele that can be covered up
by another allele
i.
Punnett square
EFC
50°F Clear
Transcribed Image Text:lessons/1533885/variants/1533885/take/3/
DISMISS
1 of 1: Instructional Technology Subsidy Up.
e.
homozygous
two of the same alleles for a gene
f.
recessive
two ditferent alleles for a gene
heterozygous
an allele that masks another
allele
h.
dominant
an allele that can be covered up
by another allele
i.
Punnett square
chromosome that is not a sex
j-
alleles
chromosome
k.
genotype
the chance that an outcome will
Occur
used to predict the outcome of a
gehetic cross
EFC
50°F Clear
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Biological macromolecules are massive molecules that are required for live organisms' survival and growth. Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids are the four major biological macromolecules with distinct activities. Nucleic acids are huge molecules that store and transport genetic information from one creature to another, as well as to conduct other processes such as protein production. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribose nucleic acid (RNA) are the two forms of nucleic acids (RNA). Genes are DNA-based and are found in the chromosomes of the nucleus inside the cells.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- State a random nonscientific question and explain why it is not a scientific questionarrow_forward'Organism' A 'Organism' B 2. Use the values given in Figure 7.4 to work out the surface area, volume and surface area-to- volume ratio (surface area ÷ volume) for 'Organism' A and 'Organism' B. (Remember: Surface area of each of the sides = length of the side x breadth of the side. Volume = length x breadth x height of the shape.) 3. Copy and complete the table. Use the values calculated in step 2. 2 cm 3 cm 6 cm 1 cm Fig. 7.4 Arrangement of cubes to represent two organisms Organism Surface area (cm²) Volume (cm³) Surface area: volume ratio A B Questions 1. Which arrangement of books would best represent a) a flatworm and b) an earthworm, which has a tubular shape? 3. (2) 2. Which 'organism' (A or B) has the largest surface area-to-volume ratio? (1) If a flatworm and an earthworm have the same volume, which worm would have the largest surface area-to-volume ratio? 4. Do you think that a flatworm and an earthworm could rely on diffusion across their body surfaces to meet their needs for…arrow_forwardhow do you make a graph to plot and record data after a a experiment?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education