
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question

Transcribed Image Text:6. LO 7: Using the symmetry of the arrangement, determine the direction of the force on q in the figure below,
given that qa=qb=7.5 µC qc=qd=-7.50μC.
a.
Draw a free body diagram of q.
b. Due to symmetry the direction of the net force is
A.
B.
C.
D.
In the +x direction
In the -x direction
In the +y direction.
In the -y direction.
Hint: For each force draw the x and y components. Some will add and some will cancel.
c. Calculate the magnitude of the force on the charge q, given that the square is 10.0 cm on a
side and q = 2.00 μC.
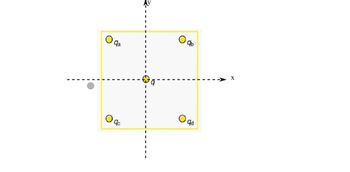
Transcribed Image Text:qa
O
qc
b.
qb
O qd
X
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Using the symmetry of the arrangement, determine the direction of the force on + q in the figure below, given that: Case 1. 9₂=9= +7.5 μC and qc = 9d = +7.5 μC. F net qa (a) In your notebook, draw the forces on q due to 9¹ 9² 9² and 9d. a' (b) Due to symmetry the direction of the net force is = O N qc Hint: For each force draw the x and y components. Some will add and some will cancel. (c) Calculate the magnitude of the force on the charge q, given that the square is 10.0 cm on a side and q = 2.2 μC. O qd Xarrow_forwardPlease answer the following question. Please specify the correct equations that you use in your answer. Please put a box and LABEL each equation that you plan to use for each element of the problem. Please label every variable with an explanation. Please make sure to label and give a full explanation to every variable in the problem. Please make sure to double check your work. Please confirm the answer is correct before submitting your response. Please do not skip any steps.arrow_forwardItem 14 Rutherford's Planetary Model of the Atom In 1911, Ernest Rutherford developed a planetary model of the atom, in which a small positively charged nucleus is orbited by electrons. The model was motivated by an experiment carried out by Rutherford and his graduate students, Geiger and Marsden. In this experiment, they fired alpha particles with an initial speed of 1.30 x 107m/s at a thin sheet of gold. (Alpha particles are obtained from certain radioactive decays. They have a charge of +2e and a mass of 6.64 × 10-27 kg.) Part A r = How close can the alpha particles get to a gold nucleus (charge = +79e), assuming the nucleus remains stationary? (This calculation sets an upper limit on the size of the gold nucleus. See Chapter 31 of the textbook for further details.) —| ΑΣΦ Submit Request Answer ? 14 of 15 m Reviewarrow_forward
- İt is just a question on study plan so it isn't effective for the grades of Physics-2 so if you can solve it will be perfect. Thanks in advance.arrow_forwardPart A A small metal bead, labeled A, has a charge of 25 nC. It is touched to metal bead B, initially neutral, so that the two beads share the 25 nC charge, but not necessarily equally. When the two beads are then placed 5.0 cm apart, the force between them is 4.4x10-4 N. Assume that A has a greater charge. What is the charge q4 and qB on the beads? Express your answers in nanocoulombs separated by a comma. IA: ¶B = 15 • 10~°,10 • 10-9 nC Submit X Incorrect; Try Again; 2 attempts remainingarrow_forwardPlease Asaparrow_forward
- A sphere with a radius of 1.5cm hangs by an insulating thread. The sphere is attracted to a positively charged rod held near the sphere. a) If the ball is made of an insulating material, what can you say about the charge on the sphere? Be specific and explain your answer. b) If the ball is made of a conducting material, what can you say about the charge on the sphere? Be specific and explain your answer.arrow_forwardr -e Physical constants (A) What is the radius of the orbit with n = 4? (B) What is the speed of the orbit with n = 4? The old Bohr model of the hydrogen atom was based on... (1) the assumption that the electron travels on a circle h = 6.626 x 10-34 Js; -28 (A) (in m) Bohr Model mv² r mvr = n and obeys Newton's second law, and (2) the hypothsis that angular momentum is quantized. For the Bohr model, Ke² = 2.307 x 107 Jm; 31 m9.11 x 10 kg. (B) (in m/s) Ke² 12. (1) (2) OA: 2.034x10-10 OB: 2.706x10-10OC: 3.598x10-10 OD: 4.786x10-10 OE: 6.365x10-10 OF: 8.466x10-10 OG: 1.126x109 OH: 1.497x109 OA: 8.533x104 OB: 1.237x105 OC: 1.794x105 OD: 2.601x105 OE: 3.772x105 OF: 5.470x105 OG: 7.931x105 OH: 1.150x106arrow_forwardB1arrow_forward
- Newer automobiles have filters that remove fine particles from exhaust gases. This is done by charging the particles and separating them with a strong electric field. Consider a positively charged particle +4.7 µC that enters an electric field with strength 2 x 105 N/C. The particle is traveling at 17 m/s and has a mass of 10-9 g. Tw What is the acceleration of the particle? (Enter the magnitude only.) m/s² What is the direction of the acceleration of the particle relative to the electric field? O It is in the same direction as the electric field. O It is 90° to the left of the electric field. It is 90° to the right of the electric field. It is in the opposite direction of the electric field.arrow_forwardConsider the point charges shown below. What will be the magnitude and direction of the force on the 1.0μC charge if the −2.0μC and −3.0μC charges are held in place?arrow_forwardItem 7 When two identical ions are separated by a distance of 8.4×10-10 m, the electrostatic force each exerts on the other is 5.2×10-9 N. Part A How many electrons are missing from each ion? Express your answer as an integer. ► View Available Hint(s) N₂ = Submit Provide Feedback ΠΑΣΦ ?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON