
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Identify test statistic
Identify p-value
Construct a confidence interval suitable for testing the claim that the two samples are from populations with the same mean.__<μ1−μ2<__(Round to three decimal places as needed.)

Transcribed Image Text:### Educational Text on Hypothesis Testing
**Context:**
Listed in the data table are IQ scores for a random sample of subjects with medium lead levels in their blood. Also included are statistics from a study on IQ scores for a random sample of subjects with high lead levels. Assume that the two samples are independent simple random samples from normally distributed populations. Do not assume that the population standard deviations are equal. Complete parts (a) and (b) below.
**Instructions:**
**a. Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim:**
The mean IQ score for subjects with medium lead levels is higher than the mean score for subjects with high lead levels.
**Determine the null and alternative hypotheses:**
Assume that:
- Population 1 consists of subjects with medium lead levels.
- Population 2 consists of subjects with high lead levels.
**Hypothesis Options:**
- **A.**
\( H_0: \mu_1 = \mu_2 \)
\( H_1: \mu_1 \neq \mu_2 \)
- **B.**
\( H_0: \mu_1 = \mu_2 \)
\( H_1: \mu_1 > \mu_2 \)
- **C.**
\( H_0: \mu_1 \neq \mu_2 \)
\( H_1: \mu_1 = \mu_2 \)
- **D.**
\( H_0: \mu_1 \leq \mu_2 \)
\( H_1: \mu_1 > \mu_2 \)
**Correct Answer:**
**B.**
\( H_0: \mu_1 = \mu_2 \)
\( H_1: \mu_1 > \mu_2 \)
**Note:**
- The null hypothesis (\( H_0 \)) suggests no difference in means.
- The alternative hypothesis (\( H_1 \)) suggests that the mean IQ score for subjects with medium lead levels is greater than for those with high lead levels.
**Test Statistic:**
Calculate the test statistic. (Round to two decimal places as needed.)
**Visual Element:**
- The image includes options for indicating null and alternative hypotheses, with option B being correctly marked. There is also a placeholder for calculating the
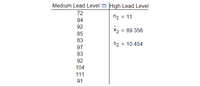
Transcribed Image Text:### Data on Lead Levels
#### Medium Lead Level Measurements:
- 72
- 94
- 92
- 85
- 83
- 97
- 83
- 92
- 104
- 111
- 91
#### High Lead Level Statistics:
- Sample size (\( n_2 \)): 11
- Mean (\( \bar{x}_2 \)): 89.356
- Standard deviation (\( s_2 \)): 10.454
This table presents measurements and statistical data for lead levels categorized into medium and high levels. The "Medium Lead Level" column lists individual measurements, while the "High Lead Level" section provides summary statistics.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Claim: The average career length for an NFL quarter back is 4.5 years. À random sample of 13 revealed a mean of 4.84 years and a sample standard deviation of 0.59. Use the traditional method at a 2.5% significance level to test the claim. Critical Value = 土 [three decimal accuracy] Test Statistic = [three decimal accuracy] Conclusion O Reject Ho Fail to Reject Hoarrow_forwardHow do I do this? Please helparrow_forwardWhat is the estimated standard deviation of the difference scores? (four decimals)arrow_forward
- Estimated Speed Smashed into hit n = 16 n = 16 M = 40 M = 34 SS = 510 SS = 414 Use a one-tailed test with α = .01. The t-statistic isarrow_forwardTest the claim that for the population of statistics final exams, the mean score is 7676 using alternative hypothesis that the mean score is different from 76.76. Sample statistics include ?=21,n=21, ?⎯⎯⎯=78,x¯=78, and ?=11.s=11. Use a significance level of ?=0.05.α=0.05. (Assume normally distributed population.) The test statistic is The positive critical value is The negative critical value is The conclusion is A. There is sufficient evidence to reject the claim that the mean score is equal to 76. B. There is not sufficient evidence to reject the claim that the mean score is equal to 76.arrow_forwardTest a claim that the mean amount of lead in the air in U.S. cities is less than 0.036 microgram per cubic meter. It was found that the mean amount of lead in the air for the random sample o 57 U.S. cities is 0.039 microgram per cubic meter and the standard deviation is 0.069 microgram per cubic meter. At α=0.10, can the claim be supported? Complete parts (a) through (e) below. Assume the population is normally distributed.arrow_forward
- Impact of the Population Standard Deviation on SE Compute the standard error for sample means from populations all with mean μ = 80 and with standard deviations o and o = 75 using a sample size of n = 90. Round your answers to two decimal places, if necessary. Standard Deviation o = 11: o = 40: o = 75: HI Standard Error = 11, o = 40,arrow_forwardTest the claim that the mean GPA of night students is significantly different than 2.8 at the 0.1 significance level. Based on a sample of 70 people, the sample mean GPA was 2.81 with a standard deviation of 0.03 The positive critical value is: (to 2 decimals)arrow_forward78 Answer was incorrectarrow_forward
- Pls show working Thank uarrow_forwardUsing Symmetry and the Empirical Rule A standardized test is approximately normally distributed with a mean score of 7272 and a standard deviation of 55. Use the symmetry of the normal curve and apply the Empirical rule to answer the questions. Make a sketch of the curve to help you determine the areas.Note: You must use the Empirical Rule values 68%68%, 95%95%, and 99.7%99.7% in your computations. The computer calculator will not give you the correct answer. What percent of students scored greater than 7272?____ % What percent of students scored between 7272 and 7777?_______ % What percent of students scored between 6767 and 7777? ______% What percent of students scored between 5757 and 6262? _____%arrow_forwardn=10, x=10.3, s=4.4, 95% confidence use the given degree of confidence and sample data to construct a confidence interval for the population mean u. assume that the population has a normal distributionarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman