
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
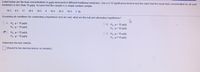
Transcribed Image Text:Listed below are the lead concentrations in µg/g measured in different traditional medicines. Use a 0.10 significance level to test the claim that the mean lead concentration for all such
medicines is less than 18 µg/g. Assume that the sample is a simple random sample.
19.5 8.5 17 20.5
19.5
4
16.5
20.5
10.5
Assuming all conditions for conducting a hypothesis test are met, what are the null and alternative hypotheses?
O A. Ho > 18 ug/g
H,p< 18 µg/g
O B. Ho: u= 18 µg/g
H u> 18 µg/g
C. Ho:u= 18 ug/g
O D. Ho: u= 18 µug/g
H,: µt 18 µg/g
H, u< 18 ug/g
Determine the test statistic,
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)

Transcribed Image Text:In a test of the effectiveness of garlic for lowering cholesterol, 49 subjects were treated with raw garlic. Cholesterol levels were measured before and after the treatment. The changes
(before minus after) in their levels of LDL cholesterol (in mg/dL) have a mean of 0.7 and a standard deviation of 2.37. Use a 0.05 significance level to test the claim that with garlic
treatment, the mean change in LDL cholesterol is greater than 0. What do the results suggest about the effectiveness of the garlic treatrnent? Assume that a simple random sample has
been selected. Identify the null and alternative hypotheses, test statistic, P-value, and state the final conclusion that addresses the original claim.
What are the null and alternative hypotheses?
O A. Ho: u>0 mg/dL
H,:u<0 mg/dL
B. Ho: µ=0 mg/dL
H,: u>0 mg/dL
O C. Ho: µ= 0 mg/dL
H,: µ#0 mg/dL
O D. Ho: µ=0 mg/dL.
H,iµ<0 mg/dL
Determine the test statistic.
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- To investigate the fluid mechanics of swimming, twenty swimmers each swam a specified distance in a water-filled pool and in a pool where the water was thickened with food grade guar gum to create a syrup-like consistency. Velocity, in meters per second, was recorded and the results are given in the table below. Velocity (m/s) Swimmer Water Guar Syrup 1 0.90 0.91 2 0.92 0.99 3 1.00 0.95 4 1.10 1.12 1.20 1.21 6. 1.25 1.21 7 1.25 1.29 8 1.30 1.30 9. 1.35 1.34 10 1.40 1.42 11 1.40 1.44 1.50 1.51 13 1.65 1.58 14 1.70 1.70 15 1.75 1.80 16 1.80 1.79 17 1.80 1.84 5,359 61 12arrow_forwardListed below are the lead concentrations in ug/g measured in different traditional medicines. Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim that the mean lead concentration for all such medicines is less than 16 ug/g. Assume that the sample is a simple random sample. 20.5 12.5 12.5 4.5 4.5 19 18 18.5 9. 16 O Assuming all conditions for conducting a hypothesis test are met, what are the null and alternative hypotheses? Ο Α. Ηo μ> 16 μgg Ο Β. H μ= 16 μglg H1>16 ug/g H,: p< 16 pg/g O C. H μ= 16 μgg ΟD. Ho μ= 16 μgg H: p<16 ug/g H: p#16 pg/garrow_forwardListed below are the lead concentrations in µg/g measured in different traditional medicines. Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim that the mean lead concentration for all such medicines is less than 15 pg/g. Assume that the sample is a simple random sample. 7 5 3 10.5 15 21.5 22 10 4.5 Assuming all conditions for conducting a hypothesis test are met, what are the null and alternative hypotheses? O B. Ho: H= 15 µg/g Ο Α. H0 μ= 15 μαα H, p# 15 µg/g H1: µ> 15 µg/g O D. H, µ> 15 µg/g O C. Ho H= 15 µg/g H:µ< 15 µg/g H7: µ< 15 µg/g Determine the test statistic. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Determine the P-value. (Round to three decimal places as needed.) State the final conclusion that addresses the original claim. 15 μg/g Ho. There is evidence to conclude that the mean lead concentration for all such medicines isarrow_forward
- Use a y2-test to test the claim o 45 Ha: 0245 O D. Ho: o245 O C. Ho: o>45 Ha:o545 Hai o<45 Identify the test statistic. (Round to three decimal places as needed.) Identify the critical value(s). (Round to three decimal places as needed. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.) Choose the correct conclusion below Click to select your answer(s).arrow_forwardListed below are the lead concentrations in µg/g measured in different traditional medicines. Use a 0.05 significance level to test the claim that the mean lead concentration for all such medicines is less than 16 µg/g. Assume that the sample is a simple random sample. 17.5 17 9 22.5 7.5 6 8.5 7.5 21.5 15.5 Assuming all conditions for conducting a hypothesis test are met, what are the null and alternative hypotheses? O A. Ho: μ16 µg/g H₁: μ16 μg/g OC. Ho: μ16 µg/g H₁: μ 16 µg/g H₁: μ 16 µg/g ✔ evidence to conclude that the mean lead concentration for all such medicines is 16 μg/g.arrow_forwardA sample is selected from a normal population, and resulting data are as follows: 45.2, 51.5, 49.4, 48.9, 52.4, 40.0 Does this data suggest that the population mean is greater than 50? Use a = 0.05. a. State the appropriate hypotheses.. b. Calculate the value of the test statistic. c. Determine the rejection region. d. What is your conclusion? Interpret your conclusion.arrow_forward
- Listed below are the lead concentrations in µg/g measured in different traditional medicines. Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim that the mean lead concentration for all such medicines is less than 16 µg/g. Assume that the sample is a simple random sample. 13.5 17.5 3.5 14.5 14.5 14 16 11 12 16.5 D Assuming all conditions for conducting a hypothesis test are met, what are the null and alternative hypotheses? OA. Ho = 16 µg/g OB. Ho: μ> 16 µg/g H,:μ 16 μg/g - O C. Ho : 4 = 16 pg/g OD. Ho: H=16 µg/g H₁ μ< 16 μg/g H₁ μ#16 μg/g Determine the test statistic. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Determine the P-value. (Round to three decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardListed below are the lead concentrations in ug/g measured in different traditional medicines. Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim that the mean lead concentration for all such medicines is less than 18 µg/g. Assume that the sample is a simple random sample. 19 7.5 3 14 8 15 6 22.5 22.5 21.5 O Assuming all conditions for conducting a hypothesis test are met, what are the null and alternative hypotheses? Ο Α. Η0: μ= 18 μαg Ο Β. Η μ= 18 μgg H1: µ> 18 µg/g H: µ# 18 µg/g OC. Ho: H= 18 µg/g Ο D. Ho: μ> 18 μgg H,: µ< 18 µg/g H,: µ< 18 µg/g Determine the test statistic. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Determine the P-value. (Round to three decimal places as needed.) State the final conclusion that addresses the original claim. V Ho. There is V evidence to conclude that the mean lead concentration for all such medicines is 18 μgg. Reject Fail to rejectarrow_forwardAssume that a simple random sample has been selected and test the given claim. Use the diastolic blood pressure measurements (in mm Hg) for adult females listed in the accompanying data table and test the claim that the adult female population has a mean diastolic blood pressure level less than 90mm Hg. Suppose a diastolic blood pressure above 90 is considered to be hypertension. Use a 0.10 significance level. Based on the result, can we conclude that none of the adult females in the sample have hypertension? 699679657181595074886958716464885583726370728972666772837489617175928662798177847559657660666452677262717865866095577575587964914646677157726873706673647157578271726565835476745291568383786871618957777689637181437274447187806867717965976770636768756169525568677475407354697865736368549470658553 Identify the value of the test statistic. Identify the P-value.arrow_forward
- Listed below are the lead concentrations in ug/g measured in different traditional medicines. Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim that the mean lead concentration for all such medicines is less than 16 ug/g. Assume that the sample is a simple random sample. 20.5 12.5 12.5 4.5 4.5 19 18 18.5 16 Assuming all conditions for conducting a hypothesis test are met, what are the null and alternative hypotheses? O A. Ho p> 16 pg/g H p 16 ug/g %3D O C. Ho p= 16 pg/g H p#16 pg/g D. Ho =16 pg/g H1:p<16 ug/g Determine the test statistic. - 1.42 (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Determine the P-value. (Round to three decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardUse the pulse rates in beats per minute (bpm) of a random sample of adult females listed in the data set available below to test the claim that the mean is less than 67bpm. Use a 0.01 significance level. Assuming all conditions for conducting a hypothesis test are met, what are the null and alternative hypotheses? A. H0:μ>67bpm H1:μ<67bpm B. H0:μ=67bpm H1:μ<67bpm C. H0:μ=67bpm H1:μ>67bpm D. H0:μ=67bpm H1:μ≠67bpm Determine the test statistic. ______________ (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Determine the P-value. ______________ (Round to three decimal places as needed.) State the final conclusion that addresses the original claim. (1) ______________H0. There is (2) ____________evidence to conclude that the mean of the population of pulse rates for adult females is (3) ________________67bpm. 1: Pulse Rate Data Pulse Rate (bpm) 94 54 76 40…arrow_forwardUse a y-test to test the claim o 40 Hg:o5 40 H3: o> 40 Identify the test statistic. (Round to three decimal places as needed.) Identify the critical value(s). (Round to three decimal places as needed. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.) Choose the correct conclusion below. O A. Reject Ho. There is not enough evidence at the 10% level of significance to support the claim. O B. Reject Ho. There is enough evidence at the 10% level of significance to support the claim. O C. Fail to reject Ho. There is enough evidence at the 10% level of significance to support the claim. Fail to reject Ho. There is not enough evidence at the 10% level of significance to support the claim. Click to select your answer(s). MacBook Air esc F2 F3 F4 F1 @ 23 $4 % 2 4arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman