
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
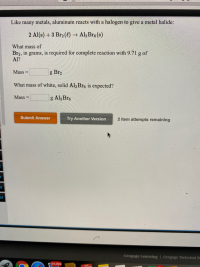
Transcribed Image Text:Like many metals, aluminum reacts with a halogen to give a metal halide:
2 Al(s) +3 Br2 (4) → Al,Bre (s)
What mass of
Br2, in grams, is required for complete reaction with 9.71 g of
Al?
Mass
g Br2
%3D
What mass of white, solid Al2Bre is expected?
Mass =
g Al2 Bre
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the chemical reaction that takes place between solid copper and oxygen gas. Complete the balanced molecular chemical equation for the reaction below. If no reaction occurs, write NR after the reaction arrow. Cu(s) + O2(g) → 3C2 2- Reset 1 3 4 6 7 8. 9. -> (s) (1) (g) (aq) H Cu NR • x H20 LOarrow_forwardBased on the balanced reaction: 2 Al + 3 Cl2→ 2 AlCl3, what is the maximum number of moles of AlCl3 that could be made by the reaction of (2.11x10^1) mol of Al and (1.990x10^1) mol of Cl2?arrow_forwardWhen 1.5173 g of an organic iron compound containingFe, C, H, and O was burned in O₂, 2.838 g of CO₂ and 0.8122 g of H₂O were produced. In a separate experiment to determinethe mass % of iron, 0.3355 g of the compound yielded 0.0758 gof Fe₂O₃. What is the empirical formula of the compound?arrow_forward
- 4. When a 19.34 gram piece of lithium is placed in a sample of water, how many grams of hydrogen gas are? 2 Li ( + 2 H,O → 2 LİOH(aq) + H«e) (s) 2(g)arrow_forwardHow many grams of oxygen react with iron to make 13.8 g of iron(III) oxide (rust)? 2Fe (s) + 3O₂ (g) → Fe₂O₃ (s) A) 2.77 g B) 2.07 g C) 8.30 g D) 1.84 g E) 4.15 garrow_forward8.229 X 1025 molecules of phosphine (PH3) reacts with 2.00 kg of O2 to produce phosphoric acid. Find: Limiting Reagent Moles of each reactant leftover Mass of each product madearrow_forward
- Consider the following unbalanced equation: Ca3(PO4)2 (s) + H2SO4(aq) → CaSO4(s) + H3PO4(aq) What masses of calcium sulfate and phosphoric acid can be produced from the reaction of 1.0 kg calcium phosphate with 1.0 kg concentrated sulphuric acid (98% H2SO4 by mass)?arrow_forwardA sample of limestone and other soil materials was heated, and the limestone decomposed to give calcium oxide and carbon dioxide. CACO3 (s) → Ca0(s) + CO2 (g) A 5.483 g sample of limestone-containing material gave 2.14 g of CO2, in addition to CaO, after being heated at a high temperature. What was the mass percent of CACO3 in the original sample? %arrow_forwardWhat mass of cobalt (III) sulfide is produced from the reaction of 0.750 g of sulfur with 3.50 g of cobalt? Co (s) + S (s) → Co₂S, (s) garrow_forward
- A student investigated the stoichiometry of the reaction of zinc (Zn) with HCI solution and reported the following data: When 0.2158 g of Zn reacted with 10.00 mL of 1.000M HCI, 82.062 g of water was displaced. A total of 36.00 mL of 9.501 x 102M NaOH solution was required to titrate the HCI remaining in the reaction mixture at the end of the reaction. The room temperature was 27.0°C and the barometric pressure was 777 torr. The gram atomic mass of Zn is 65.38 g mol The density of water at 27.0 °C is 0.9965 g mLand its vapor pressure is 27.0 torr. R = 8.21 X 10 - -1 atm K-1 mol 1 Calculate the number of millimoles of Zn reactingarrow_forwardwhat's the net ionic equation of Ag + Pb(NO3)2 =arrow_forwardCan anyone explain step by step (in details)how did we get the balanced equation?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY