
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781133104261
Author: Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
thumb_up100%
With Bernoulli's principle, is there any other reason as to why the pressure of the fluid decreases with an increased velocity other than using the equation and conservation of energy? Why does the fluid pressure decrease? With an airplane wing, how does the air above the wing move faster and therefore provide less pressure, and why does this result in lift?
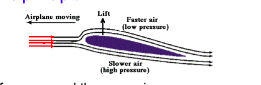
Transcribed Image Text:Lift
Airplane moving
Faster air
(low pressure
Slower air
high pressurs)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Some chimney pipes have a T-shape, with a crosspiece on top that helps draw up gases whenever there is even a slight breeze. Explain how this works in terms of Bernoulli’s principle.arrow_forwardA pressure cooker contains water and steam in equilibrium at a pressure greater than atmospheric pressure. How does this greater pressure increase cooking speed?arrow_forwardYou can squirt water from a garden hose a considerably greater distance by partially covering the opening with your thumb. Explain this works.arrow_forward
- What does it mean to say that two systems are in thermal equilibrium?arrow_forwardA scuba diver makes a slow descent into the depths of the ocean. His vertical position with respect to a boat on the surface changes several times. He makes the first stop 9.0 m from the boat but has a problem with equalizing the pressure, so he ascends 3.0 m and then continues descending for another 12.0 m to the second stop. From there, he ascends 4 m and then descends for 18.0 m, ascends again for 7 m and descends again for 24.0 m, where he makes a stop, waiting for his buddy. Assuming the positive direction up to the surface, express his net vertical displacement vector in terms of the unit vector. What is his distance to the boat?arrow_forwardA pressure cooker contains water and steam in equilibrium at a pressure greater than atmospheric pressure. How does this greater pressure increase cooking speed?arrow_forward
- In ballet, dancing en pointe (on the tips of the toes) is much harder on the toes normal dancing or walking. Explain why, in terms of pressure.arrow_forwardAn airplane passenger has 100 cm3 of air in his stomach just before the plane takes off from a sea-level airport. What volume will the air have at cruising altitude if cabin pressure drops to 7.50104N/m2 ?arrow_forwardWhen a glass bottle full of vinegar warms up, both the vinegar and the glass expand, but the vinegar expands significantly more with temperature than does the glass. The bottle will break if it is filled up to its very tight cap. Explain why and how a pocket of air above the vinegar prevents the bottle from breaking.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

An Introduction to Physical Science
Physics
ISBN:9781305079137
Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning