
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

Transcribed Image Text:(c) Let X1,..., Xn be a random sample from the Pareto distribution given above.
(i) Find the Method of Moments Estimator (MME) for 0.
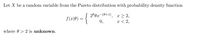
Transcribed Image Text:Let X be a random variable from the Pareto distribution with probability density function
2º 0x-(0+1),
0,
x > 2,
x < 2,
f(x|0) =
where 0 > 2 is unknown.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The average wait time to get seated at a popular restaurant in the city on a Friday night is 9 minutes. Is the mean wait time different for men who wear a tie? Wait times for 13 randomly selected men who were wearing a tie are shown below. Assume that the distribution of the population is normal. 7, 8, 9, 10, 10, 8, 10, 9, 10, 8, 11, 11, 9 What can be concluded at the the αα = 0.01 level of significance level of significance? For this study, we should use The null and alternative hypotheses would be: H0:H0: H1:H1: The test statistic = (please show your answer to 3 decimal places.) The p-value = (Please show your answer to 4 decimal places.) The p-value is αα Based on this, we should the null hypothesis. Thus, the final conclusion is that ... The data suggest the population mean is not significantly different from 9 at αα = 0.01, so there is statistically insignificant evidence to conclude that the population mean wait time for…arrow_forwardThe U.S. Geological Survey compiled historical data about Old Faithful Geyser (Yellowstone National Park) from 1870 to 1987. Let x1 be a random variable that represents the time interval (in minutes) between Old Faithful eruptions for the years 1948 to 1952. Based on 9180 observations, the sample mean interval was x1 = 62.6 minutes. Let x2 be a random variable that represents the time interval in minutes between Old Faithful eruptions for the years 1983 to 1987. Based on 24,872 observations, the sample mean time interval was x2 = 70.0 minutes. Historical data suggest that σ1 = 8.91 minutes and σ2 = 11.78 minutes. Let μ1 be the population mean of x1 and let μ2 be the population mean of x2. (a) Compute a 95% confidence interval for μ1 – μ2. (Use 2 decimal places.) lower limit upper limit (b) Comment on the meaning of the confidence interval in the context of this problem. Does the interval consist of positive numbers only? negative numbers only? a mix of positive and…arrow_forwardthe value used in the equation for the t-test for independent means that approximates the sample size is known as thearrow_forward
- Suppose the random variable, X, follows a geometric distribution with parameter (0< 0 <1). Let X₁, X₂, X, be a random sample of size n from the population of X. (d) Find the method of moments estimator (mme) of 0. (e) Show how the mle of 0 is related to its mme. Explain if it is always true. (f) Verify if X, is a sufficient statistic for 8 or not. (g) Justify if = is an unbiased estimator for 6.arrow_forwardIt has been determined experimentally that steel wires of a certain length have strength with a mean value of 1 kip and a coefficient of variation of 16%. What is the probability that the strength of such a wire is less than 0.7 kips? Try Type I and Type III asymptotic distributions of extremes and compare the results.arrow_forwardLet X₁, X₂, ..., Xn be a random sample of size n from a geometric distribution for which p is the probabil- ity of success. (a) Use the method of moments to find a point estimate for p. (b) Explain intuitively why your estimate makes good sense.arrow_forward
- For 50 randomly selected speed dates, attractiveness ratings by males of their female date partnerS (x) are recorded along with the attractiveness ratings by females of their male date partners (y); the ratings range from 1 to 10. The 50 paired ratings yield *= 6.3, y = 6.1. r= - 0.283, P.value = 0.046, and g = 8.39 - 0.369x. Find the best predicted value of y (attractiveness rating by female of male) for a date in which the attractiveness rating by the male of the female is x= 4. Use a 0.01 significance level. see score The best predicted value of g when x= 4 is 7. (Round to one decimal place as needed.)arrow_forwardLet X1, X2, X3, ..., X, be a random sample from a distribution with known variance Var(X,) = o², and unknown mean EX, = 0. Find a (1 – a) confidence interval for 0. Assume that n is large.arrow_forwardThe U.S. Geological Survey compiled historical data about Old Faithful Geyser (Yellowstone National Park) from 1870 to 1987. Let x1 be a random variable that represents the time interval (in minutes) between Old Faithful eruptions for the years 1948 to 1952. Based on 9520 observations, the sample mean interval was x1 = 62.8 minutes. Let x2 be a random variable that represents the time interval in minutes between Old Faithful eruptions for the years 1983 to 1987. Based on 23,117 observations, the sample mean time interval was x2 = 73.0 minutes. Historical data suggest that ?1 = 8.98 minutes and ?2 = 12.83 minutes. Let ?1 be the population mean of x1 and let ?2 be the population mean of x2. (a) Compute a 90% confidence interval for ?1 – ?2. (Use 2 decimal places.) lower limit upper limit (b) Comment on the meaning of the confidence interval in the context of this problem. Does the interval consist of positive numbers only? negative numbers only? a mix of positive and…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman