
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780134753119
Author: Sheldon Ross
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
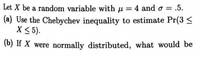
Transcribed Image Text:Let X be a random variable with u = 4 and o = .5.
(a) Use the Chebychev inequality to estimate Pr(3 <
X < 5).
%3D
(b) If X were normally distributed, what would be
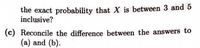
Transcribed Image Text:the exact probability that X is between 3 and 5
inclusive?
(c) Reconcile the difference between the answers to
(a) and (b).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, probability and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Let Y be a Poisson random variable with mean λ = 2. (a) Find P(Y ≥ 2). (b) Find P(Y ≥ 4|Y ≥ 2).arrow_forwardWith reference to Definition 4, show that μ0 = 1and that μ1 = 0 for any random variable for whichE(X) exists.arrow_forwardWe have a random variable X and Y that jave the joint pdf f(x) = {1 0<x<1, 0<y<1} {0 otherwise} Let U = Y - X2. What is the support for the random variable U? Are there critical points? If U = Y/X. What is the support for the random variable U? Are there critical points?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)ProbabilityISBN:9780134753119Author:Sheldon RossPublisher:PEARSON
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)ProbabilityISBN:9780134753119Author:Sheldon RossPublisher:PEARSON

A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Probability
ISBN:9780134753119
Author:Sheldon Ross
Publisher:PEARSON
