
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
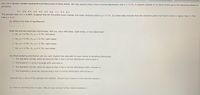
Transcribed Image Text:Let x be a random variable representing dividend yield of bank stocks. We may assume that x has a normal distribution with o = 3.1%. A random sample of 10 bank stocks gave the following yields (in
percents).
5.7
4.8
6.0
4.9
4.0
3.4
6.5
7.1
5.3
6.1
The sample mean is x =
5.38%. Suppose that for the entire stock market, the mean dividend yleld isu = 4.7%. Do these data indicate that the dividend yield of all bank stocks is higher than 4.7%?
Use a = 0.01.
(a) What is the level of significance?
State the null and alternate hypotheses. Will you use a left-tailed, right-talled, or two-tailed test?
O Ho: H = 4.7%, H1: H < 4.7%; left-tailed
O Ho: H > 4.7%; H1: H = 4.7%; right-tailed
O Ho: H = 4.7%; H1: H > 4.7%; right-tailed
O Ho: H = 4.7%; H1: µ # 4.7%; two-tailed
(b) What sampling distribution will you use? Explain the rationale for your choice of sampling distribution.
O The standard normal, since we assume that x has a normal distribution with known o.
O The Student's t, sincen is large with unknown o.
O The standard normal, since we assume that x has a normal distribution with unknown o.
O The Student's t, since we assume that x has a normal distribution with known o.
Compute the z value of the sample test statistic. (Round your answer to two decimal places.)
(c) Find (or estimate) the P-value. (Round your answer to four decimal places.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 6.2 The Standard Normal Distribution Table: Z-score and Probability A company produces steel rods. The lengths of the steel rods are normally distributed with a mean of 164.7 cm and a standard deviation of 2.5 cm. Find the probability that the length of a randomly selected steel rod is greater than 167.7 cm. Probability -arrow_forwardAllen's hummingbird (Selasphorus sasin) has been studied by zoologist Bill Alther.† Suppose a small group of 13 Allen's hummingbirds has been under study in Arizona. The average weight for these birds is x = 3.15 grams. Based on previous studies, we can assume that the weights of Allen's hummingbirds have a normal distribution, with ? = 0.20 gram. (d) Find the sample size necessary for an 80% confidence level with a maximal margin of error E = 0.06 for the mean weights of the hummingbirds. (Round up to the nearest whole number.) ____________ hummingbirdsarrow_forwardLet x be a random variable representing dividend yield of Australian bank stocks. We may assume that x has a normal distribution with s.d.= 2.3% . A random sample of 12 Australian bank stocks has a sample mean of x=6.16% . For the entire Australian stock market, the mean dividend yield is 7.2%. Do these data indicate that the dividend yield of all Australian bank stocks is higher than 7.2%? Find (or estimate) the P-value. Round your answer to three decimal places.arrow_forward
- Suppose a professor uses a normal distribution to assign grades in her math class. • She assigns an A to students scoring more than 1.9 standard deviations above the mean. • She assigns an F to students scoring more than 2.2 standard deviations below the mean. She assigns a B to students who Score between 1 and 1.9 standard deviations above the mean. • She assigns a D to students who Score between 1.2 and 2.2 standard deviations below the mean. • All other students get a C. Use the Cumulative Z-Score Table to answer the following questions. The Z-Score Table can be found below by selecting "Read". Write your answer as a percent using 2 decimal places. What percent of the class receives each grade assuming the scores are normally distributed? Hint % will recieve an A % will recieve a B % will recieve a C % will recieve a D % will recieve an Farrow_forwardThe Office of Student Services at a large western state university maintains information on the study habits of its full-time students. Their studies indicate that the mean amount of time undergraduate students study per week is 20 hours. The hours studied follows the normal distribution with a population standard deviation of 12 hours. Suppose we select a random sample of 100 current students. What is the standard error of the mean? 1.20 12 .95 2.70arrow_forwardBhuro.0p0arrow_forward
- Assume all populations are normally distributed. A travel analyst claims that the mean price of a round trip flight from New York City to Los Angeles is less than $507. In a random sample of 55 round trip flights from NYC to LA, the mean price is $502. Assume the population standard deviation is $111. At α = 0.05, is there enough evidence to support the travel analyst’s claim?arrow_forwardA magazine claims that the mean amount spent by a customer at Burger Stop is greater than the mean amount spent by a customer at Fry World. The results for samples of customer transactions for the two fast food restaurants are shown below. At x = 0.01, can you support the magazine's claim? Assume the population variances are equal. Assume the samples are random and independent, and the populations are normally distributed. Complete parts (a) through (e) below. Burger Stop Fry World X₁ = $11.22 X₂ = $10.59 $₁ = $0.79 $2 = $0.64 n₂ = 10 n₁ = 12 (a) Identify the claim and state Ho and H₂. Which is the correct claim below? O A. "The mean amount spent by a customer at Burger Stop is greater than the mean amount spent by a customer at Fry World." OB. "The mean amount spent by a customer at Burger Stop is equal to the mean amount spent by a customer at Fry World." O c. "The mean amount spent by a customer at Burger Stop is not equal to the mean amount spent by a customer at Fry World." O D.…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman