
Database System Concepts
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780078022159
Author: Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
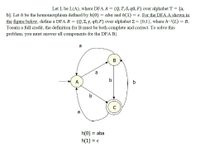
Transcribed Image Text:Let L be L(A), where DFA A = (Q,T, 8, q0, F) over alphabet T = {a,
b}. Let h be the homomorphism defined by h(0) = aba and h(1) = €. For the DFA A shown in
the figure below, define a DFA B = (Q,E, Y, q0, F) over alphabet E = {0,1}, where h-1(L) = B.
Toearn a full credit, the definition for B must be both complete and correct. To solve this
problem, you must answer all components for the DFA B.
a
В
A
b
a
h(0) = aba
h(1) = €
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Pick the option that is correct for A, B, C, D (A) Element defintion or Hypothesis (B) Exsistential generaliztion 1, 2 or Exsistential instantaion 1, 2 or Universal generaliztion 1, 2 or Universal instantaion 1, 2 (C) Q(b) ^ R(b) or Q(b) ∨ R(b) or Q(x) ^ R(x) or Q(x) ∨ R(x) (D) ∀Q(x) or ∀¬Q(x) or ∃Q(x) or ∃¬Q(x)arrow_forwardLet A = {a, b, c, d} and R = {(a, a), (b, b), (c, c), (d, d), (a, d), (d, a), (b, c), (c, b)} an equivalence relation on A. Select the following sets that are equivalence classes of R {a, b} {a} {a,b,c} O{c, b} O{a, d} {a,b,c,d} {d} {c, d}arrow_forwardUse the Pumping Lemma to show that the the following language over {a,b,c}* is not CF {wct | t ∈ {a,b}* ∧ w is a substring of t}arrow_forward
- Consider the following language: {x ∈ {a, b}∗ |#a(x) ≤ 2#b(x)} (a) Give a CFG for this set.(b) Prove that the given CFG is correctarrow_forwardComputer Science Suppose L ⊆{a, b}∗ is defined as follows: Λ∈L; for every x and y in L, the strings axb, bxa, and x yare in L. Show that L =AEqB , the language of all strings x in {a, b}∗ satisfying n_a (x) =n_b (x).arrow_forwardMathematical Logic First-order or predicate logic. Show that the sum relation, {(m,n,p)|p=m+n}, is not definable on (N; ∙). Hint: Consider an automorphism of (N; ∙) that interchanges two primes. Where N is the set of natural numbers. Please be as clear as possible. Show and explain all the steps. Thank you very much.arrow_forward
- Discrete Structurearrow_forwardLet regular language L1 recognized by DFA (Q1,Σ,δ1,s1,F1) and regular language L2 recognized by DFA (Q2,Σ,δ2,s2,F2). We will construct a product DFA as the quintuple (Q,Σ,δ,s,F) where: •Q=Q1×Q2•For allx∈Σ and (q1,q2)∈Q1×Q2,δ((q1,q2),x) = (δ1(q1,x),δ2(q2,x))•s= (s1,s2) DetermineFso that the product DFA recognizes: (i)L1∪L2(ii)L1∩L2(iii)L1\L2Based on your choice for F, for each case, provide a detailed proof why the product DFA recognizes each of the mentioned languages. Conclude that in-tersection of two regular languages is a regular language and set-theoretic dif-ference of two regular languages is regular.arrow_forwardWrite python Code for classifier QMi=1 p(yi|X, α)arrow_forward
- Prove that the following languages are not regular using the Pumping lemma and/or closure properties. Note: Do not use other methods. a. L1 = {w ∈ {a, b}∗: na(w) + nb(w) = 3 · nb(w)} (na (w) is used to denote the number of a's in the string w) b. L2 = {anbmck: n, m, k ∈ ℕ, n < m or n < k}arrow_forwardThe format P(X) represents as a power set of given "X", (of all X's subsets) Now, assume there are two sets A= {q, w, e, r} and B = {w, r, f}. (a) What are the elements of P(A) ∩P(B )?(b) What is the cardinality of P(A ∪B )?(c) What is |P(A) ∪P(B )|?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780134444321
Author:Tony Gaddis
Publisher:PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780132737968
Author:Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780133976892
Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337627900
Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education