
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:<Homework 6
Exercise 8.27 - Enhanced - with Solution
Two ice skaters, Daniel (mass 65.0 kg) and Rebecca (mass
45.0 kg), are practicing. Daniel stops to tie his shoelace and,
while at rest, is struck by Rebecca, who is moving at 14.0 m/s
before she collides with him. After the collision, Rebecca has a
velocity of magnitude 7.00 m/s at an angle of 55.1° from her
initial direction. Both skaters move on the frictionless, horizontal
surface of the rink.
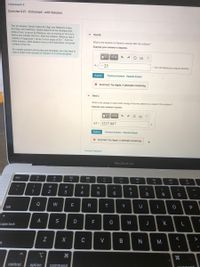
Part B
What is the direction of Daniel's velocity after the collision?
Express your answer in degrees.
For related problem-solving tips and strategies, you may want to
view a Video Tutor Solution of Collision in a horizontal plane.
- 25
from the Rebecca's original direction
Submit
Previous Answers Request Answer
X Incorrect; Try Again; 4 attempts remaining
Part C
What is the change in total kinetic energy of the two skaters as a result of the collision?
Express
answer in joules.
Vol AEd
AK = 1237.887
J
Submit
Previous Answers Request Answer
X Incorrect; Try Again; 5 attempts remaining
Provide Feedback
MacBook Air
esc
80
88
F2
DII
DD
F6
F7
FB
F9
23
2$
&
1
2
3.
4
6.
7
8.
Q
W
E
R
T
Y
tab
|
P
A
S
F
G
つ
K
caps lock
C
V
く
t
control
option
command
エ
リ
Transcribed Image Text:Exercise 8.27 - Enhanced - with Solution
Two ice skaters, Daniel (mass 65.0 kg) and Rebecca (mass
45.0 kg), are practicing. Daniel stops to tie his shoelace and,
while at rest, is struck by Rebecca, who is moving at 14.0 m/s
before she collides with him, After the collision, Rebecca has a
velocity of magnitude 7.00 m/s at an angle of 55.1° from her
initial direction. Both skaters move on the frictionless, horizontal
surface of the rink.
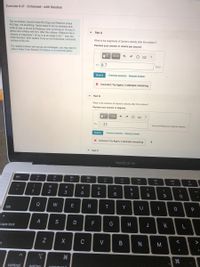
Part A
What is the magnitude of Daniel's velocity after the collision?
Express your answer in meters per second.
For related problem-solving tips and strategies, you may want to
view a Video Tutor Solution of Collision in a horizontal plane.
ΠνΠ ΑΣφ
v = 8.7
m/s
Submit
Previous Answers Request Answer
X Incorrect; Try Again; 4 attempts remaining
Part B
Vhat is the direction of Daniel's velocity after the collision?
Express your answer in degrees.
25
from the Rebecca's original direction
Submit
Previous Answers Request Answer
X Incorrect; Try Again; 4 attempts remaining
Part C
MacBook Air
80
888
esc
DII
DD
F3
F2
F4
F5
F6
F7
E9
@
#3
2$
1
3
6.
7
Q
W
E
R
T
Y
U
tab
A
S
F
G
H
J
K
caps lock
C
V
control
option
B
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Concept Simulation 7.1 illustrates the physics principles in this problem. An astronaut in his space suit and with a propulsion unit (empty of its gas propellant) strapped to his back has a mass of 146 kg. The astronaut begins a space walk at rest, with a completely filled propulsion unit. During the space walk, the unit ejects some gas with a velocity of +32 m/s. As a result, the astronaut recoils with a velocity of -0.39 m/s. After the gas is ejected, the mass of the astronaut (now wearing a partially empty propulsion unit) is 165 kg. What percentage of the gas propellant was ejected from the completely filled propulsion unit? Percent depleted = Number i Unitsarrow_forwardI need help pleasearrow_forwardA1arrow_forward
- A two dimensional collision between a green and a purple ball, where the purple ball strikes the green. If the data for both objects' velocities (x and y components) versus time are provided, and the mass of the balls are identical, what is a way to determine if the momentum of the system conserved? Explain your methodology. Green ball: vx = 0 m/s from t = 0 s to t = 0.4 s vx = 17.42 m/s from t = 0.5 s to t = 5 s vy = 0 m/s from t = 0 s to t = 0.4 s vy = -8.01 m/s from t = 0.5 s to t = 5 s Purple ball: vx = 22.3 m/s from t = 0 s to t = 0.4 s vx = 4.878 m/s from t = 0.5 s to t = 5 s vy = 2.6 m/s from t = 0 s to t = 0.4 s vy = 10.61 m/s from t = 0.5 s to t = 5 sarrow_forwardPhysics homework assignment, I don't know how to do this question. There's three parts but it's all one question. Thanks for the help!arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON