Question
Lenz’s Law, AC, DC and RLC (Resistor-Inductor-Capacitor) Circuits: A constant magnetic field is directed into the page in the shaded rectangular region. What happens to the induced emf and current in the copper ring that slides through the region from positions 1 to position 5?
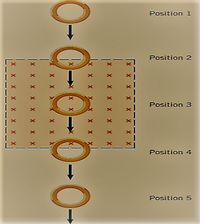
Transcribed Image Text:Position 1
Position 2
Position 3
Position 4
Position 5
0-
0-0
x x x X X x x X
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A 250-ohm resistor, a 0.450 H inductor, and a 6.45 µF capacitor are connected in series across an emf with a 36.0 volt amplitude and an angular frequency of 260 rad/s. What is the impedance? What is the current amplitude? What is the phase angle between the voltage and current? Does the voltage lag or lead? a. b. с.arrow_forwardWhich of the following statements are true? Choose all that apply. A changing magnetic field will always induce a voltage. As current through an inductor decreases, the inductance remains constant. For an LR circuit, as R increases, & decreases. Transformers can simultaneously decrease voltage & decrease current. Generators transform electrical energy (electricity) into kinetic energy. The mks units for inductance are Wb.arrow_forwardFaradey’s law states that the EMF induced by a change in magnetic flux depends on the change in magnetic flux with respect to time and number of turns of coils. Mathematically it is defined like the figure. Why do we use ds in the line integral of Faradey’s law to calculate the electric field? Don,t copy from anywhere. Do all calculation step by step .Answer Must be correct.Read question all step.arrow_forward
- A series RL circuit is built with 110 2 resistor and a 5.0-cm-long, 1.0-cm-diameter solenoid with 800 turns of wire. What is the peak magnetic flux through the solenoid if the circuit is driven by a 20 V, 5.0 kHz source? ΕΧΕΙ ΑΣΦ VAΣ ? mWbarrow_forwardPlease answer it within 30 minutes. I will upvote!arrow_forwardJust after the switch is closed, what is the magnitude of the potential difference vabvab across the resistor R1? What is the magnitude of the potential difference vcdvcd across the inductor L? The switch is left closed a long time and then opened. Just after the switch is opened, what is the magnitude of the potential difference vabvab across the resistor R1? What is the magnitude of the potential difference vcdvcd across the inductor L?arrow_forward
- c1. What is the magnitude of the induced emf at t = 0 s? c2. What is the magnitude of the induced emf after a long time has passed? d. After the current in the RL circuit has reached its final value (as in b2. above) the positions of the switches are reversed, with S1 open and S2.How long does it take for the current to reach a tenth of its initial value?arrow_forwardYour RL circuit has a characteristic time constant of 21.5 ns, and a resistance of 5.40 MΩ. A. What is the inductance (in H) of the circuit? B. What resistance (in MΩ) should you use (instead of the 5.40 MΩ resistor) to obtain a 1.00 ns time constant, perhaps needed for quick response in an oscilloscope?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios