
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
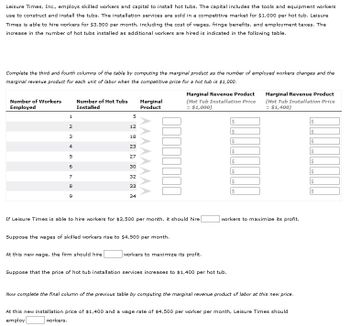
Transcribed Image Text:Leisure Times, Inc., employs skilled workers and capital to install hot tubs. The capital includes the tools and equipment workers
use to construct and install the tubs. The installation services are sold in a competitive market for $1,000 per hot tub. Leisure
Times is able to hire workers for $3,500 per month, including the cost of wages, fringe benefits, and employment taxes. The
increase in the number of hot tubs installed as additional workers are hired is indicated in the following table.
Complete the third and fourth columns of the table by computing the marginal product as the number of employed workers changes and the
marginal revenue product for each unit of labor when the competitive price for a hot tub is $1,000.
Number of Workers
Employed
1
2
3
4
10
5
6
7
8
9
Number of Hot Tubs
Installed
5
12
At this new wage, the firm should hire
18
23
27
30
32
33
34
Marginal
Product
If Leisure Times is able to hire workers for $3,500 per month, it should hire
Suppose the wages of skilled workers rise to $4,500 per month.
Marginal Revenue Product
(Hot Tub Installation Price
= $1,000)
workers to maximize its profit.
$
$
$
$
$
$
$
Suppose that the price of hot tub installation services increases to $1,400 per hot tub.
Marginal Revenue Product
(Hot Tub Installation Price
= $1,400)
workers to maximize its profit.
Now complete the final column of the previous table by comput the marginal revenue product of labor at this new price.
At this new installation price of $1,400 and a wage rate of $4,500 per worker per month, Leisure Times should
employ
workers.
$
00000⁰
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Since the early 1970’s, the U.S. government has had a program called the Earned Income Tax Credit. A simplified version of this program works as follows: The government subsidizes your wages by paying you 50% in addition to what your employer paid you but the subsidy applies only to the first $60 (per day) you receive from your employer. If you earn more than $60 per day, the government gives you only the subsidy for the first $60 earned but nothing for anything additional you earn. For instance, if you earn $100 per day, the government would give you 50% of the first $60 you earned — or $30. Suppose you consider workers 1 and 2. Both can work up to 10 hours per day at a wage of $10 per hour, and after the policy is put in place you observe that worker 1 works 7 hours per day while worker 2 works 5 hours per day. Assume throughout that Leisure is a normal good. (a) Illustrate these workers’ budget constraints with and without the program. (b) Can you tell whether the program has…arrow_forwardWhat is the significance of resource pricing?Explain how the factors determining resource demand differ from those determining product demand. Explain the meaning and significance of the fact that the demand for a resource is a derived demand. Why do resource demand curves slope downward? What factors determine the elasticity of resource demand? What effect will each of the following have on the elasticity or the location of the demand for resource C, which is being used to produce commodity X? Where there is any uncertainty as to the outcome, specify the causes of that uncertainty.arrow_forwardDetermine whether there is a specific market price above which demand is zero or price per unit is unbounded. Write the maximum possible market price, using dollars per unit as the units of measure for input. (If the price per unit is unbounded, enter UNBOUNDED.) D(p) = 3.6p-0 -0.3 p = units dollars per unitarrow_forward
- From 2016 to 2026, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics expects that there will be a fall in demand for Multiple Choice occupational therapy assistants. commercial drivers. physical therapists. Saved word processors and typists.arrow_forwardSuppose the supply of apple pickers in Southwest Michigan can be expressed by the equation Qs=2/15(W-10) . An apple farmer advertises a wage of $100 per day to pick apples; however, when the day of the harvest arrives the farmer tells those assembled at the orchard that only 10 pickers are needed, and, as more than 10 pickers showed up looking for work, the wage will fall to the equilibrium. How many pickers showed up to work the apple harvest? What is the equilibrium wage offered by the farmer? Graph the supply of and demand for labor at the orchard, indicating the equilibrium price. Calculate the pickers’ total producer surplus, including the surplus lost by the pickers who were available to work but were not hired.arrow_forwardExercise 2. Suppose that Government is currently evaluating a project, which is going to hire native language teachers and requires in total 5000 hours of teaching. Let's denote the hour taught by native language teacher by letter L. Thus, the project's demand for teaching hours by native language teachers is described by the demand function La project = 5000. Suppose that the following is known about the current (pre-project) market for native language teachers: - there is no involuntary unemployment among the native language teachers - the Government does not apply any taxes or subsidies in this particular labour market; - the current (pre-project) demand for teaching hours by native language teachers is described by the demand function La = 30000 – 300Wa, where La denotes the quantity of teaching hours (by native language teachers) demanded and Wa denotes the demander price per teaching hour; - the current (pre-project) supply of teaching hours by native language teachers is given…arrow_forward
- Rubber for erasers is produced in the market. There are equations for the Supply and Inverse Demand of eraser rubber that model its Supply and Demand graph. These equations are (for supply), P = 20 + Qs, and (for Inverse Demand), P = 80 - Qd. With that said, the government realizes that it is not turning out enough revenue from the market. As a result, it places a per-unit sales tax of $10. (Part I) Draw the market equilibrium with the government intervention (Q**, PD**, and PS**) of the sales tax. Please label the graph for slopes, equilibrium points, sales tax, etc. (Part II) What is the market equilibrium without the intervention of the government? (Part III) The government once again realizes that the previous tax was not sufficient, and the government is still not making enough money. So, it increases the sales from $10 to $20. Consequently, what is the new market equilibrium point (Q**, PD**, and PS**) with this new intervention? It is not necessary to label this point on the…arrow_forwardnd 35. AVERAGE SUPPLY A manufacturer supplies S(p) = 0.5p² + 3p + 7 hundred units of a Sie per certain commodity to the market when the price is p dollars per unit. Find the average supply as the price varies from p = $2 to p = $5. 6 43. Earrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education