
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
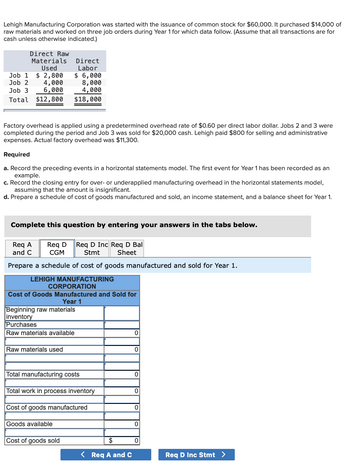
Transcribed Image Text:**Lehigh Manufacturing Corporation Case Study**
Lehigh Manufacturing Corporation began operations with the issuance of common stock for $60,000. It purchased raw materials costing $14,000 and worked on three jobs during Year 1.
**Direct Costs:**
- **Job 1**:
- Raw Materials Used: $2,800
- Direct Labor: $6,000
- **Job 2**:
- Raw Materials Used: $4,000
- Direct Labor: $8,000
- **Job 3**:
- Raw Materials Used: $6,000
- Direct Labor: $4,000
**Total:**
- Raw Materials Used: $12,800
- Direct Labor: $18,000
Factory overhead is applied using a predetermined overhead rate of $0.60 per direct labor dollar. Jobs 2 and 3 were completed, and Job 3 was sold for $20,000 in cash. Lehigh incurred $800 in selling and administrative expenses. Actual factory overhead was $11,300.
**Required Tasks:**
- **Task a**: Record events in a horizontal statements model. An example of Year 1's first event is provided.
- **Task b**: Record closing entry for over- or underapplied manufacturing overhead, assuming it's insignificant.
- **Task c**: Prepare a schedule of the cost of goods manufactured and sold, an income statement, and a balance sheet for Year 1.
---
**Schedule of Cost of Goods Manufactured and Sold for Year 1:**
- **Beginning raw materials inventory**
- **Purchases**
- **Raw materials available**
- **Raw materials used**
- **Total manufacturing costs**
- **Total work in process inventory**
- **Cost of goods manufactured**
- **Goods available**
- **Cost of goods sold**
Note: The fields for amounts are placeholders (set to zero initially).
This exercise guides students through applying basic accounting concepts in manufacturing, including cost accounting and financial statement preparation.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.]Information on Kwon Manufacturing’s activities for its first month of operations follows: Purchased $101,700 of raw materials on credit. Materials requisitions show the following materials used for the month. Job 201 $ 49,900 Job 202 25,300 Total direct materials 75,200 Indirect materials 10,320 Total materials used $ 85,520 Time tickets show the following labor used for the month. Job 201 $ 40,900 Job 202 14,300 Total direct labor 55,200 Indirect labor 25,900 Total labor used $ 81,100 Applied overhead to Job 201 and to Job 202 using a predetermined overhead rate is 80% of direct materials cost. Transferred Job 201 to Finished Goods Inventory. (1) Sold Job 201 for $168,860 on credit. (2) Record cost of goods sold for Job 201. Incurred the following actual other overhead costs for the month. Depreciation of factory equipment $ 33,700 Rent on factory building (payable)…arrow_forwardPrimare Corporation has provided the following data concerning last month’s manufacturing operations. Purchases of raw materials $ 31,000 Indirect materials used in production $ 4,740 Direct labor $ 58,800 Manufacturing overhead applied to work in process $ 87,200 Underapplied overhead $ 4,180 Inventories Beginning Ending Raw materials $ 10,700 $ 19,500 Work in process $ 55,900 $ 65,700 Finished goods $ 34,600 $ 44,000 Required: 1. Prepare a schedule of cost of goods manufactured for the month. 2. Prepare a schedule of cost of goods sold for the month. Assume the underapplied or overapplied overhead is closed to Cost of Goods Sold.arrow_forwardA company produces washers and dryers in an assembly-line process. Labor costs incurred during a recent period were: corporate executives, $500,000; assembly-line workers, $209,000; security guards, $45,000; and plant supervisor, $110,000. The total of company's direct labor cost was: Select one: O a. $754,000 O b. $319,000 O c. $203,000 O d. $209,000 O e. $864,000arrow_forward
- The following costs relate to one month's activity in Martin Company: Indirect materials $ 300 Rent on factory building $ 500 Maintenance of equipment $ 50 Direct material used $1,200 Utilities on factory $ 250 Direct labour $1,500 Selling expense $ 500 Administrative expense $ 300 Work-in-process inventory, beginning $ 600 Work-in-process inventory, ending $ 800 Finished goods inventory, beginning $ 500 Finished goods inventory, ending $ 250 Required: (a.) Prepare a schedule of cost of goods manufactured in good form. (b.) Determine the cost of goods sold.arrow_forwardZachary Manufacturing Corporation was started with the issuance of common stock for $70,000. It purchased $7,600 of raw materials and worked on three job orders during Year 1 for which data follow. (Assume that all transactions are for cash unless otherwise indicated.) Direct Raw Materials Used Direct Labor Job 1 $ 1,100 $ 2,100 Job 2 2,000 3,700 Job 3 3,400 2,100 Total $ 6,500 $ 7,900 Factory overhead is applied using a predetermined overhead rate of $0.70 per direct labor dollar. Jobs 2 and 3 were completed during the period and Job 3 was sold for $11,070 cash. Zachary paid $700 for selling and administrative expenses. Actual factory overhead was $6,130. Required a. Record the preceding events in a horizontal statements model. The first event for Year 1 has been recorded as an example.arrow_forwardLarned Corporation recorded the following transactions for the just completed month. a. $86,000 in raw materials were purchased on account. b. $84,000 in raw materials were used in production. Of this amount, $72,000 was for direct materials and the remainder was for indirect materials. c. Total labor wages of $120,500 were paid in cash. Of this amount, $100,500 was for direct labor and the remainder was for indirect labor. d. Depreciation of $197,000 was incurred on factory equipment. Required: Record the above transactions in journal entries. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field.) View transaction list Journal entry worksheet 1 23 4 $86,000 in raw materials were purchased on account. Note: Enter debits before credits. Transaction General Journal a. Record entry Clear entry Debit Credit View general journalarrow_forward
- Primare Corporation has provided the following data concerning last month’s manufacturing operations. Purchases of raw materials $ 30,000 Indirect materials used in production $ 5,000 Direct labor $ 58,000 Manufacturing overhead applied to work in process $ 87,000 Underapplied overhead $ 4,000 Inventories Beginning Ending Raw materials $ 12,000 $ 18,000 Work in process $ 56,000 $ 65,000 Finished goods $ 35,000 $ 42,000 Required: 1. Prepare a schedule of cost of goods manufactured for the month (see picture below for reference). 2. Prepare a schedule of cost of goods sold for the month. Assume the underapplied or overapplied overhead is closed to Cost of Goods Sold.arrow_forwardPrimare Corporation has provided the following data concerning last month’s manufacturing operations. Purchases of raw materials $ 30,000 Indirect materials used in production $ 5,000 Direct labor $ 58,000 Manufacturing overhead applied to work in process $ 87,000 Underapplied overhead $ 4,000 Inventories Beginning Ending Raw materials $ 12,000 $ 18,000 Work in process $ 56,000 $ 65,000 Finished goods $ 35,000 $ 42,000 Can you please help me to do the following: Prepare a schedule of cost of goods manufactured for the month as well as prepare a schedule of cost of goods sold for the month. Assume the underapplied or overapplied overhead is closed to Cost of Goods Sold.arrow_forwardA partial listing of costs incurred during December at Gagnier Corporation appears below: Factory supplies $8,000 Administrative wages and salaries $105,000 Direct materials $153,000 Sales staff salaries $68,000 Factory depreciation $49,000 Corporate headquarters building rent $34,000. Indirect labor Marketing Direct labor $32,000 $103,000 $83,000 The total of the period costs listed above for December is a. 89,000 b. $310,000 c. $325,000 d. $399,000arrow_forward
- Please read the picture below and complete.arrow_forwardPrimare Corporation has provided the following data concerning last month’s manufacturing operations. Purchases of raw materials $ 30,000 Indirect materials used in production $ 4,580 Direct labor $ 59,700 Manufacturing overhead applied to work in process $ 88,000 Underapplied overhead $ 4,200 Inventories Beginning Ending Raw materials $ 11,800 $ 19,200 Work in process $ 55,500 $ 66,300 Finished goods $ 33,600 $ 42,900 Required: 1. Prepare a schedule of cost of goods manufactured for the month. 2. Prepare a schedule of cost of goods sold for the month. Assume the underapplied or overapplied overhead is closed to Cost of Goods Sold.arrow_forwardNewcomb Manufacturing Company was started on January 1, Year 1, when it acquired $3,900 cash from the issue of common stock. During the first year of operation, $2,700 of direct raw materials was purchased with cash, and $1,550 of the materials was used to make products. Direct labor costs of $2,900 were paid in cash. Newcomb applied $830 of overhead cost to the Work in Process account. Cash payments of $830 were were made for actual overhead costs. The company completed products that cost $3,500 and sold goods that had cost $2,720 for $3,900 cash. Selling and administrative expenses of $670 were paid in cash. Required a. Prepare T - accounts and record the events affecting Newcomb Manufacturing. Include closing entries. b1. Prepare a schedule of cost of goods manufactured and sold. b2. Prepare an income statement. b3. Prepare a balance sheet.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education