
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
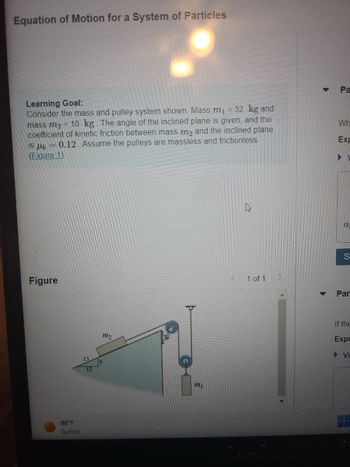
Transcribed Image Text:Equation of Motion for a System of Particles
Learning Goal:
Consider the mass and pulley system shown. Mass m₁ = 32 kg and
mass m₂ = 10 kg. The angle of the inclined plane is given, and the
coefficient of kinetic friction between mass me and the inclined plane
is μ = 0.12. Assume the pulleys are massless and frictionless.
(Figure 1)
Figure
1 of 1
98°F
Sunny
m₂
mi
▼
Pa
Wh
Exp
V
a
Si
Par
If the
Expr
▶ Vi
Transcribed Image Text:and
the
ane
Submit
Part B - Finding the speed of the mass moving up the ramp after a given time
If the system is released from rest, what is the speed of mass m₂ after 4 s?
Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.
View Available Hint(s)
v(4 s) =
Value
Units
Submit
▼
Part C- Finding the distance moved by the hanging mass
ramp how far downward does mass m₁ move?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- (1) A 50 kg block rests on a 20° incline plane, as shown in Figure 1. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the plane is 0.4. Determine the maximum horizontal force P that can be applied to the block without causing it to slide. P 50 kg H, = 0.40 20° Figure 1arrow_forwardA carnival ride has people stand inside a vertical cylinder with their backs to the wall. The cylinder starts spinning and the riders find that they are “stuck” to the wall and don’t slide down, even if the floor is removed. The ride has a radius of r. The person has a mass of m and is moving with a constant speed of v. The coefficient of static friction between the person and the wall is μs , and kinetic friction μk. The person is only touching the wall, not touching the floor. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the person? In what direction does it point? The speed is constant. Why is the acceleration not zero? Briefly explain. No equations!arrow_forwardPlease answer and show how you got it You are on an elevator fixed to a wall that can move up and down freely while you pull with a force of 150 N on a massless rope (the orange line in the diagram below) with length L. This rope is connected to one end of a beam with the same length, L, and mass m=20 kg. The left end of the beam is in contact with the same wall the elevator is on and the coefficient of static friction =0.2 between the beam and the wall. See diagram below for a representation of the situation and note that free fall acceleration points directly downward 0 L Part A) Label all the forces acting on the beam and discuss the direction of any torques exerted on the beam about the contact point between the beam and the wall Part B) What is the maximum angle the beam can subtend with respect to the horizontal _m such that it will just begin to slip? Potentially useful trig identities are sin(2x)=2sin(x)cos, sin(180-x)=sin(x), sin(90+x)=cos(x)arrow_forward
- You construct a version of the cart and bucket, but with a slope whose angle can be adjusted. You use a cart of mass 167 kg and a bucket of mass 57.0 kg. The cable has negligible mass, and there is no friction. What must be the angle of the slope so that the cart moves downhill at a constant speed and the bucket moves upward at the same constant speed? With this choice of angle, what will be the tension in the cable?arrow_forwardSolve it correctly please. I will rate accordingly.arrow_forward2) After playing a game of pinball, you decide to do some calculations on the launching mechanism. The pinball and the plunger have a mass of 0.30 kg and 0.50 kg respectively. The spring coefficient in the pinball machine is 300 N/m. The original length of the spring is 100 mm and the compressed length is 35 mm. If the coefficient of friction between the ball and the surface is 0.15, calculate the velocity of the ball right before it loses contact with the plunger (in m/s). Note that the plunger is never in contact with the ground and assume the ball slides without rolling. [Ans. to check: 1.23 m/s] HO wwwarrow_forward
- Blocks A and B have a masses of 150 kg and 280 kg, respectively. (Figure 2) The coefficient of static friction between A and B and between B and C is 0.290. The coefficient of static friction between the rope and peg E is 0.570. Pulley D rotates freely, and P = 27.0 N. If \theta = 60.0 degrees, what is the smallest magnitude, T, of tension, T, that causes block B to move? P A B E Tarrow_forwardV-belt calculationarrow_forwardCan you help me with that?arrow_forward
- Needs Complete typed solution with 100 % accuracy.arrow_forward3.2 Sliding blocks with friction* Mass MA = 4kg rests on top of mass Mg = 5 kg that rests on a fric- tionless table. The coefficient of friction between the two blocks is such that the blocks just start to slip when the horizontal force F applied to the lower block is 27 N. Suppose that now a horizontal force is applied to the upper block. What is its maximum value for the blocks to slide without slipping relative to each other?arrow_forwardDear, Can you please give me the solution to this question and provide it with side drawings and explanations to understand the solution better? Thank you in advance!!arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY