
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
6th Edition
ISBN: 9780134463216
Author: Robert F. Blitzer
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:EF
SC
myEFSC
→ C
A
Z
Select Your School
Lesson 5.4 Certify Mode QX
o Mail - Paige A - Outlook
X
X
Calendar
learn.hawkeslearning.com/Portal/Lesson/lesson_certify#!
- Save & Exit Certify Lesson: 5.4 Applications of Percent
PAIGE ABENDROTH
7
Question 7 of 12, Step 1 of 1
6/15
Correct
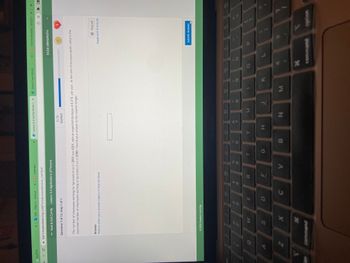
The number of employees working for Sprockets R Us in 2005 was 8261, with an expected decrease of 4.3 % per year. At the rate of decrease given, what is the
expected number of employees working at Sprockets R Us in 2006? Round your answer to the nearest integer.
Keypad
Answer
How to enter your answer (opens in new window)
Keyboard Shortcuts
Submit Answer
© 2022 Hawkes Learning
MacBook Air
$3
300
20
F3
ABA
2
3
W
E
R
S
X
H
command
C
%
25
V
G
X
B
Y
H
87
F7
C
N
8
30
FB
M
K
FO
O
Course Modules: 202220-1 X +
36
P
command
29
$12
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- For some data, we know the range R of the data is 12 and its median is 6. Find Estimated Lowest Number, and Estimated Highest Number for this data. Give you answers in the same order asked.arrow_forwardChoose the best statement to summarize the association shown between hat size and IQ in the scatterplot below. Hat Size O The scatterplot does not show a trend that would indicate an association between hat size and IQ scores. O As hat size increases, IQ scores tend to decrease. O As hat size increases, IQ scores tend to increase. Hat size causes IQ to increase.arrow_forwardThe data in the relative frequency bar graph below represents the number of stars earned by 140 performers in a talent competition. 35 30 25 20 15 10 1 Number of Stars How many performers earned exactly 3 stars? Be careful - compare the question wording to the scale on the y-axis of the graph. Notice it says "percentage of performers" Percentage of Performers (N = 140) N 寸arrow_forward
- A survey was conducted two years ago asking college students their top motivations for using a credit card. You think this distribution has changed. You randomly select 425 college students and ask each one what the top motivation is for using a credit card. Can you conclude that there has been a change in the distribution? Use a = 0.025. Complete parts (a) through (d). Response Old Survey % 29% New Survey Frequency, f Rewards 110 Low rates Cash back Discounts 23% 96 21% 109 7% 46 Other 20% 64 O B. The distribution of motivations is 110 rewards, 96 low rate, 109 cash back, 46 discounts, and 64 other. O C. The distribution of motivations is 29% rewards, 23% low rate, 21% cash back, 7% discounts, and 20% other. Which hypothesis is the claim? o Ho (b) Determine the critical value, Yo, and the rejection region. X = 11.143 (Round to three decimal places as needed.) Choose the correct rejection region below. Oc. Xarrow_forwardOnly round final answer (to 2 decimal places). Please report proportion as a decimal number, and not a percentagearrow_forwardThe data in the relative frequency bar graph below represents the number of stars earned by 140 performers in a talent competition.How many performers earned exactly 5 stars? Be careful - compare the question wording to the scale on the y-axis of the graph. Notice it says "percentage of performers"arrow_forwardRound every calculation to 2 decimal points unless the specific question asks for something different. Show answers as decimals and not percents or fractions.arrow_forwardPlease helparrow_forwardThe data represent the time, in minutes, spent reading a political blog in a day. Construct a frequency distribution using 5 classes. In the table, include the midpoints, relative frequencies, and cumulative frequencies. Which class has the greatest frequency and which has the least frequency? C Complete the table, starting with the lowest class limit. (Simplify your answers.) Class Frequency Midpoint 17 "" Which class has the greatest frequency? The class with the greatest frequency is from to Which class has the least frequency? The class with the least frequency is from to 32 3 32 6 Relative Frequency 28 39 5 25 11 9 8 27 15 8 38 30 24 17 0 30 Cumulative Frequency Qarrow_forwardPlease graph the answer (Solve p =, z =, etc)arrow_forwardyour car is more crowded than you think. table 5.8 reports results from a 1969 personal transportation survey on "home-to-work" trips in metropolitan areas. The survey stated that the average car occupancy was 1.4 people. check that calculation.arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosarrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Algebra
ISBN:9780134463216
Author:Robert F. Blitzer
Publisher:PEARSON

Contemporary Abstract Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:9781305657960
Author:Joseph Gallian
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)
Algebra
ISBN:9780135163078
Author:Michael Sullivan
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth Edition
Algebra
ISBN:9780980232776
Author:Gilbert Strang
Publisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press

College Algebra (Collegiate Math)
Algebra
ISBN:9780077836344
Author:Julie Miller, Donna Gerken
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education