
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
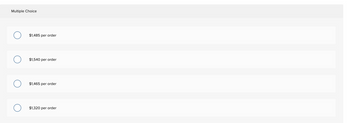
Transcribed Image Text:Multiple Choice
O
O
O
$1,485 per order
$1,540 per order
$1,465 per order
$1,320 per order
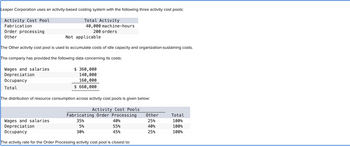
Transcribed Image Text:Leaper Corporation uses an activity-based costing system with the following three activity cost pools:
Activity Cost Pool
Total Activity
Fabrication
40,000 machine-hours
200 orders
Order processing
Other
Not applicable
The Other activity cost pool is used to accumulate costs of idle capacity and organization-sustaining costs.
The company has provided the following data concerning its costs:
Wages and salaries
Depreciation
Occupancy
Total
$360,000
140,000
160,000
$ 660,000
The distribution of resource consumption across activity cost pools is given below:
Activity Cost Pools
Fabricating Order Processing Other
35%
25%
5%
40%
30%
25%
Wages and salaries
Depreciation
Occupancy
The activity rate for the Order Processing activity cost pool is closest to:
40%
55%
45%
Total
100%
100%
100%
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- hekov Company has two support departments, Human Resources and General Factory, and two producing departments, Fabricating and Assembly. Support Departments Producing Departments HumanResources GeneralFactory Fabricating Assembly Direct costs $170,000 $330,000 $114,200 $94,000 Normal activity: Number of employees — 60 45 80 Square footage 1,500 — 6,000 14,000 The costs of the Human Resources Department are allocated on the basis of number of employees, and the costs of General Factory are allocated on the basis of square footage. Chekov Company uses the direct method of support department cost allocation. Required: 1. Calculate the allocation ratios for the four departments using the direct method. If an amount is zero, enter "0". Round your answer to the nearest cent. Proportion of Driver Used by Human Resources General Factory Fabricating Assembly Human Resources fill in the blank 1 fill in the blank 2 fill in the blank 3 fill in the blank 4…arrow_forwardMultiple Choice $6.49 $5.63 $3.92 $5.20arrow_forwardLarner Corporation is a diversified manufacturer of industrial goods. The company's activity-based costing system contains the following six activity cost pools and activity rates: Activity Rates $8.00 per direct labor-hour Activity Cost Pool Labor-related Machine-related Machine setups Production orders Shipments $9.00 per machine-hour $ 50.00 per setup $100.00 per order $ 180.00 per shipment General factory $9.00 per direct labor-hour Cost and activity data have been supplied for the following products: Direct materials cost per unit Direct labor cost per unit Number of units produced per year Direct labor-hours Machine-hours Machine setups Production orders Shipments Unit product cost Total Expected Activity J76 379 900 2,900 4 8 12 852 50 20 B52 4 Required: Compute the unit product cost of each product listed above. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to 2 decimal places.) 378 $ 4.50 $ 4.75 4,000 852 $ 45.00 $10.00. 500arrow_forward
- Gutknecht Corporation uses an activity-based costing system with three activity cost pools. The company has provided the following data concerning its costs and its activity-based costing system: Costs: Wages and salaries Depreciation Utilities Total Distribution of resource consumption: $ 300,000 180,000 240,000 $ 720,000 Wages and salaries Depreciation Utilities Activity Cost Pools Assembly 35% Setting Up Other Total 40% 25% 100% 5% 10% 60% 35% 100% 60% 30% 100% How much cost, in total, would be allocated in the first-stage allocation to the Other activity cost pool? O Multiple Choice $180,000 $216,000 $210,000 $138,000arrow_forwardGadubhaiarrow_forwardA company which uses activity-based costing has two products: A and B. The annual production and sales of Product A is 12,000 units and of Product B is 10,500 units. There are three activity cost pools, with total cost and total activity as follows: Total Activity Product Product A Activity Cost Pool Total Cost Total Activity 1 Activity 2 Activity 3 52-54 $25,420 130 490 620 $38,400 $122,670 890 310 1,200 820 3,410 4,230 The activity-based costing cost per unit of Product A is closest to: (Round your intermediate calculations to 2 decimal places.) Multiple Choice $10.79 $1.60 $4.80 $3.10arrow_forward
- Aarrow_forwardKlumper Corporation is a diversified manufacturer of industrial goods. The company's activity-based costing system contains the following six activity cost pools and activity rates: Activity Cost Pool Activity Rates Supporting direct labor $ 8 per direct labor-hour Machine processing $ 4 per machine - hour Machine setups $ 40 per setup Production orders $ 150 per order Shipments $ 120 per shipment Product sustaining $ 900 per product Activity data have been supplied for the following two products: Total Expected Activity K425 -M67 Number of units produced per year 200 2,000 Direct labor-hours 925 40 Machine - hours 2, 600 30 Machine setups 11 1 Production orders 11 1 Shipments 22 1 Product sustaining 1 1arrow_forwardKlumper Corporation is a diversified manufacturer of industrial goods. The company's activity-based costing system contains the following six activity cost pools and activity rates: Activity Cost Pool Supporting direct labor Machine processing Machine setups Activity Rate $7 per direct labor-hour $4 per machine-hour $ 45 per setup Production orders. $ 160 per order Shipments $ 130 per shipment Product sustaining $ 900 per product Activity data have been supplied for the following two products: Number of units produced per year Direct labor-hours Machine-hours Machine setups Production orders Shipments Product sustaining Activity Cost Pool Supporting direct labor Machine processing Machine setups Production orders Shipments Product sustaining Total overhead cost $ K425 Total Expected Activity K425 M67 2,000 0 $ 200 1,000 3,000 5 5 Required: How much total overhead cost would be assigned to K425 and M67 using the activity-based costing system? M67 10 1 30 20 1 1 0 1 1arrow_forward
- Rabia Company has two support departments, Human Resources and Maintenance, and two producing departments, Fabrication and Assembly Support Departments Producing Departments Human Resources Maintenance Fabrication Assembly Budgeted overhead Direct labor hours Machine hours Number of employees $40,000 $72,000 $140,000 $160,000 2,000 2,500 8,000 10,000 12,000 8,000 4 5 15 25 The company only had mixed cost. Human Resource costs are allocated based on the number of employees, and maintenance costs are allocated based on machine hours. Predetermined overhead rates for fabrication and assembly are based on direct labor hours. Required: 1. Calculate the allocation ratios. 2. Using the direct method, allocate the costs of the Human Resources and Maintenance deportments to the Fabrication and Assembly departments. Also write the final cost of both the production departments. 3. What if the Maintenance Department had 50 employees? How would that affect the allocation of Human Resources…arrow_forwardGive me answerarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education