
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781337093347
Author: Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Transcribed Image Text:L'avionnaire
30 in
+
3
M
- 20 in
1 KIP
2
D
-20in
1 KIP
ED
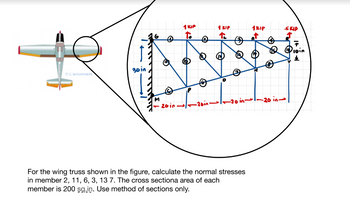
For the wing truss shown in the figure, calculate the normal stresses
in member 2, 11, 6, 3, 13 7. The cross sectiona area of each
member is 200 sq.in. Use method of sections only.
1KIP
50
✪
.SKIP
in-
7
Ploin
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A capped cast-iron pipe is compressed by a brass rod, as shown. The mil is turned until it is just snug, then add an additional quarter turn to pre-compress the cast-iron pipe. The pitch of the threads of the bolt ap = 52 mils (a mil is one-thousandth of an inch). Use the numerical properties provided. (a) What stresses a and arwill be produced in the cast-iron pipe and brass rod. respectively, by the additional quarter turn of the nut? (b) Find the bearing stress ahbeneath the washer and the shear stress t(in the steel cap.arrow_forwardWhile drilling a hole with a brace and bit, you exert a downward force P = 25 lb on the handle of the brace (see figure). The diameter of the crank arm is d = 7/16 in. and it s lateral offset is b = 4-7/8 in. Determine the maximum tensile and compressive stresses e1, and e2respectively, in the crank.arrow_forwardA sign is supported by a pipe (see figure) having an outer diameter 110 mm and inner diameter 90 mm. The dimensions of the sign are 2.0 m X 1.0 m, and its lower edge is 3.0 m above the base. Note that the center of gravity of the sign is 1.05 m from the axis of the pipe. The wind pressure against the sign is 1.5 kPa. Determine the maximum in-plane shear stresses due to the wind pressure on the sign at points /I, B, and C, located on the outer surface at the base of the pipe.arrow_forward
- Repeat the previous problem using ? = 50° and stresses on the rotated element: sy1= 70 MPa, ??y1=-82 MPa, and tx1y1=-35 MPa.arrow_forwardContinuous cable ADS runs over a small Frictionless pulley at D to support beam OABC that is part of an entrance canopy Tor a building (see figure}. Assume that the canopy segment has a weight it' = 1700 lb. (a) Find the required cross-sectional area of cable ADB if the allowable stress is 18 ksi. (b) Determine the required diameter of the pins at O. A, R and D if the allowable stress in shear is 12 ksi.arrow_forwardA gondola on a ski lift is supported by two bent arms, as shown in the figure. Each arm is offset by the distance b = ISO mm from the line of action of the weight force W. The allowable stresses in the arms are 100 MPa in tension and 50 MPa in shear. If the loaded gondola weighs 12 kN, what is the minimum diameter roof the arms?arrow_forward
- A circle of a diameter d = 200 mm is etched on a brass plate (see figure). The plate has dimensions of 400 x 400 x 20 mm. Forces are applied to the plate, producing uniformly distributed normal stressescr^ =59 MPaander^ = —17 MPa. Calculate the following quantities: (a) the change in length Aac of diameter at: (b) the change in length Abd of diameter bd; (c) the change At in the thickness of the plate; (d) the change AV in the volume of the plate; (e) the strain energy U stored in the plate; (f) the maximum permissible thickness of the plate when strain energy £/must be at least 784 J; and (g) the maximum permissible value of normal stress axwhen the change in volume of the plate cannot exceed 0.015% of the original volume. (Assume E = 100 GPa and v = 0.34arrow_forwardSolve the preceding problem for a W 200 × 41,7 shape with h = 166 mm, h = 205 mm. rw = 7.24 mm, tE= ILS mm,andV = 38 kN.arrow_forwardA fire extinguisher tank is designed for an internal pressure of 825 psi. The tank has an outer diameter of 4.5 in. and thickness of O.OS in. Calculate the longitudinal stress, the circumferential stress, and the maximum shear stresses (out-of-plane and in-plane) at the outer surface of the tank.arrow_forward
- A solid circular bar is fixed at point A. The bar is subjected to transverse load V = 70 lb and torque T = 300 lb-in. at point B. The bar has a length L = 60 in. and diameter d = 3 in. Calculate the principal normal stresses and the maximum shear stress at clement 1 located on the bottom surface of the bar at fixed end A (see figure), Assume that element 1 is a sufficient distance from support A so that stress concentration effects are negligiblearrow_forwardA ship's spar is attached at the base of a mast by a pin connection (see figure). The spar is a steel tube of outer diameter d2= 3.5 in. and inner diameter d1= 2.8 in. The steel pin has a diameter d = 1 in., and the two plates connecting the spar to the pin have a thickness t = 0.5 in. The allowable stresses are compressive stress in the spar. 10 ksi: shear stress in the pi n, 6.5 ksi: and bearing stress between t he pin and t he connecting plates, 16 ksi. Determine the allowable compressive force Pallowin the spar.arrow_forwardA short column with a wide-flange shape is subjected to a compressive load that produces a resultant force P = 55 kN acting at the midpoint of one flange (see figure). Determine the maximum tensile and compressive stresses asand o^., respectively, in the column, Locate the neutral axis under this loading condition. Recompute maximum tensile and compressive stresses if a 120 mm X 10 mm cover plate is added to one flange as shown.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning