
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Experiment 4
Name
Potentiometric Analysis of Acid in Soft Drinks: Cola vs. Uncola
Purpose
Calculations
A.
Standardization of NaOH
Mean conc. NaOH solution:
M
Standard deviation:
M
Relative standard deviation (%RSD):
%
B.
Data for titration of cola and uncola with NaOH
Using Excel or a similar program, make a table with the following columns:
Vol. NaOH
Added
pH
V2 - V1
pH2 − pH
(V1+V2)/2 pH2 - pH₁
V2 - V1
C.
Results
Cola:
pH of soda after boiling:
Volume NaOH required to reach first end point:
±
ml; pH:
Volume NaOH required to reach second end point:
±
ml; pH:
H3PO4 concentration:
H2PO4 concentration:
M
%RSD:
M
%RSD:
Uncola:
pH of soda after boiling:
Volume NaOH required to reach the end point:
±
_ml; pH: _
Citric acid concentration:
±
M
%RSD:
Include all information from the Calculations/Questions section as well as sample
calculations; answer all questions. Check your calculations carefully! Don't forget to include
copies of your lab notebook pages for this experiment.
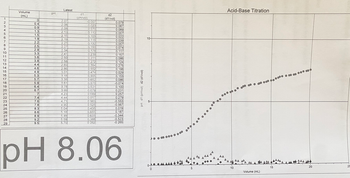
Transcribed Image Text:Latest
Volume
pH
d1
d2
(mL)
123
(pH/vol)
(d1/vol)
0
2.07
-0.007
0.079
0.4
2.06
0.023
0.087
0.9
2.08
0070
0.089
4
1.3
2.13
0.110
0.057
5
1.5
2.15
0.103
0.022
6
10-
1.9
2.19
0.115
0.039
7
2.2
2.23
0.132
0.057
8
2.5
2.27
0.150
0.074
9
2.9
2.34
0.179
0.117
10
3.3
2.41
0.239
0.157
11
3.6
2.50
0.311
0.086
12
3.8
2.58
0.272
0.124
13
4.4
2.69
0 364
0.275
14
4.6
2.86
0.552
0.198
15
4.9
3.01
0.474
0.029
16
5.3
3.18
0.505
0.153
17
5.7
3.38
0.652
0.086
18
5.9
3.61
0.570
-0.074
19
6.4
3.78
0.531
0.100
20
6.7
3.99
0.679
0.231
21
7
4.23
0.689
0.257
22
7.4
4.44
0.817
0.279
23
7.6
4.71
0 983
-0.553
24
7.8
4.90
0.525
-0.567
pH d1 (pH/vol) d2 (d1/vol)
5-
25
8.3
5.04
0.435
0.019
26
8.6
5.18
0.655
0.187
27
8.9
5.49
0.633
-0.344
28
9.2
5.59
0.388
-0.523
29
9.5
5.70
0 262
-0.265
pH 8.06
Acid-Base Titration
0
5
10
15
20
-0
Volume (mL)
25
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 1) Using the measured pH, calculate the concentration of H3O+ and OH- at the equivalence point. 2) If the theoretical pKa of KHP is 5.4, calculate the percent error using your experimental pKa value.arrow_forward9-10. (a) Find the pH of a solution prepared by dissolving 1.00 g of glycine amide hydrochloride plus 1.00 g of glycine amide in 0.100 L. + Cl- H3N H2N. NH2 NH2 Glycine amide hydrochloride (BH†) FM 110.54, pK, = 8.20 Glycine amide (B) FM 74.08 (b) How many grams of glycine amide should be added to 1.00 g of glycine amide hydrochloride to give 100 mL of solu- tion with pH 8.00? (c) What would be the pH if the solution in (a) is mixed with 5.00 mL of 0.100 M HC1? (d) What would be the pH if the solution in (c) is mixed with 10.00 mL of 0.100 M NaOH?arrow_forwardA student performed three aqueous layer titrations in Part 1 using a standard sodium thiosulfate solution with a concentration of 0.01155 M. They reported the following measurements: Final Aqueous Layer Burette Reading Initial Aqueous Layer Burette Reading Final Thiosulfate Burette Reading Initial Thiosulfate Burette Reading Determination #1 16.33 m 6.50 mL 31.98 mL 0.76 mL Determination #2 26.76 mL 16.33 mL 33.62 mL 0.88 mL Determination #3 36.95 mL 26.76 mL 32.22 ML 0.41 mL What is the concentration of reducible iodine (in mol/L) in the aqueous phase based on the data from their second titration (ie. their second determination)? Report your answer to the correct number of significant figures and only report the numerical value (no units).arrow_forward
- I dont know if I’m doing it rightarrow_forwardX ch b Answered: Determine the pH du X + agage.com/static/nb/u/evo/index.html?deploymentid=55750823468596024212874980&eISBN=9781305657571&snapshop=30540668d-155276463... 2 req 2 req 2 req 2 req 2 req R MindTap-Cengage Learning X Back F4 shown below. Design a buffer that has a pH of 7.19 using one of the weak base/conjugate acid systems Weak Base CH3NH2 C6H1503N C5H5N $1 5 6. Prepare Buffers by Direct Addition: This is group attempt 1 of 5 Si grams weak base How many grams of the bromide salt of the conjugate acid must be combined with how many grams of the weak base, to produce 1.00 L of a buffer that is 1.00 M in the weak base? grams bromide salt of conjugate acid = 96 T F5 Kb 4.2×10-4 5.9x10-7 STE Conjugate Acid Ka CH3NH3 2.4×10-11 C6H1503NH+ 1.7×10-8 1.5x10-9 CsH5NH+ 6.7x10-6 F6 6 = Y X + F7 & 7 + Autosaved at 10:38 PM W F8 8 X F9 019 ( pka 10.62 7.77 5.17 9 F10 ☀- ) F11 0 @ F12 Regenerate Group (4) @ 1 Insert Next 10:38 11/3/2 PrtScarrow_forward▪ True or false: the internal standard behaves chemically just like the analyte, and it is not found in the sample(it is added) ▪ True or false: In analysis of blood alcohols, lead is a much better IS than n-propanolarrow_forward
- A titration was done to determine the concentration of a sample of HCl. The volume of the acid sample used in each titration trial was 10.00 mL. The following data also was collected: a. What was the average volume of Ca(OH)2 used? b. Calculate the concentration of the HCl sample.arrow_forwardA student performed three aqueous layer titrations in Part 1 and they reported the following measurements: Final Burette Reading Initial Burette Reading Volume of Aqueous Aliquot Final Burette Reading Initial Burette Reading Volume of Sodium Thiosulfate Determination #1 16.33 mL 6.50 mL 9.83 m 31.98 mL 0.76 mL 31.22 mL Determination #2 Determination #3 26.76 mL 16.33 mL 10.43 mL 33.62 mL 0.88 mL 32.74 mL 36.95 mL 26.76 mL 10.19 mL 32.22 mL 0.41 mL 31.81 mL Which determinations were the student's 'best two'? Calculate the percent difference for the 'best two' and show the complete calculation. Note that the concentration of standard sodium thiosulfate, which the student used, is unknown.arrow_forwardHow are you supposed to answer this question if no values are given besides the Kb of the possible analytes?arrow_forward
- Procedure: Mix 0.01M KMNO4 and 2 drops of 6M H2SO4 with several drops of 1.0M K2C2O4. Observation: A slight color peach begins to appear. 5K2C2O4(aq) + 2KMnO4(aq)+ 8H2SO4(aq) → 2MnSO4(aq) + 10CO2(aq) + 6K2SO4(aq) + 8H2O(l) Has oxidation and reduction occurred? If oxidation and reduction has occurred? If oxidation and reduction has occurred define the change in oxidation numbers for the following atoms and define what is undergoing oxidation and reduction: Mn[ ? ] → Mn[ ? ] C[ ? ] → C[ ? ]arrow_forwardBUFFER CAPACITY EXPERIMENT Part 1: Preparation and pH Meter Calibration Prepare 50 mL of 0.5 M acetic acid from a concentrated stock. Prepare 50 mL of 0.5 M sodium hydroxide from a solid. Part 2: Buffer Capacity Transfer 20 mL of 0.5 M acetic acid (Ka is 1.75*10-5), stir at a slow setting and measure the pH reading is stabilized. Add 1.0 mL of 0.5 M NaOH and measure the pH. Continue adding 0.5 M NaOH in 0.5 - 1.0 mL increments until a major spike in pH occurs. After the spike, add another two 0.5 – 1.0 mL increments of 0.5 M NaOH. Create a pH vs. Volume graph to determine the range of the buffer’s capacity. Compare the actual data (nonstandard conditions) with the theoretical data under standard conditions. I NEED HELP WITH CALCULATIONS AN SMALL RESULT INTERPRETATION DESCRIPTION PLEASE TO UNDERSTAND WHAT I DID AND WHY THANKSarrow_forwardNeed help with 6a-6earrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY