
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
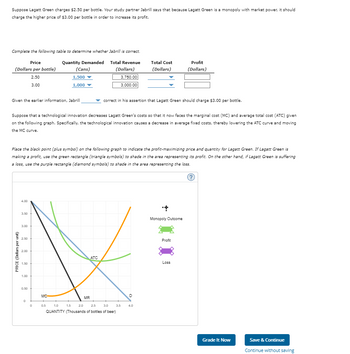
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose Lagatt Green charges $2.50 per bottle. Your study partner Jabrill says that because Lagatt Green is a monopoly with market power, it should
charge the higher price of $3.00 per bottle in order to increase its profit.
Complete the following table to determine whether Jabrill is correct.
Price
(Dollars per bottle)
Quantity Demanded
(Cans)
Total Revenue
(Dollars)
2.50
1,500
3,750.00
3.00
1,000
3,000.00
Given the earlier information, Jabrill
PRICE (Dollars per unit)
Suppose that a technological innovation decreases Lagatt Green's costs so that it now faces the marginal cost (MC) and average total cost (ATC) given
on the following graph. Specifically, the technological innovation causes a decrease in average fixed costs, thereby lowering the ATC curve and moving
the MC curve.
4.00
Place the black point (plus symbol) on the following graph to indicate the profit-maximizing price and quantity for Lagatt Green. If Lagatt Green is
making a profit, use the green rectangle (triangle symbols) to shade in the area representing its profit. On the other hand, if Lagatt Green is suffering
a loss, use the purple rectangle (diamond symbols) to shade in the area representing the loss.
?
3.50
3.00
2.50
2.00
1.50
1.00
0.50
0
0
MC
MR
0.5
ATC
correct in his assertion that Lagatt Green should charge $3.00 per bottle.
1.0
1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0
QUANTITY (Thousands of bottles of beer)
Total Cost
(Dollars)
3.5
D
4.0
Profit
(Dollars)
Monopoly Outcome
Profit
Loss
Grade It Now
Save & Continue
Continue without saving
Transcribed Image Text:Back to Assignment
Attempts
1. Profit maximization and loss minimization
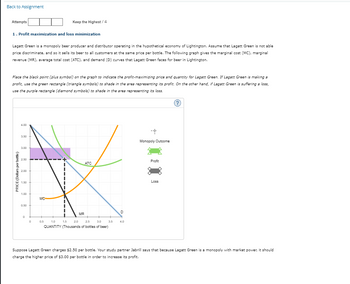
Lagatt Green is a monopoly beer producer and distributor operating in the hypothetical economy of Lightington. Assume that Lagatt Green is not able
price discriminate, and so it sells its beer to all customers at the same price per bottle. The following graph gives the marginal cost (MC), marginal
revenue (MR), average total cost (ATC), and demand (D) curves that Lagatt Green faces for beer in Lightington.
Place the black point (plus symbol) on the graph to indicate the profit-maximizing price and quantity for Lagatt Green. If Lagatt Green is making a
profit, use the green rectangle (triangle symbols) to shade in the area representing its profit. On the other hand, if Lagatt Green is suffering a loss,
use the purple rectangle (diamond symbols) to shade in the area representing its loss.
PRICE (Dollars per bottle)
4.00
3.50
3.00
2.50
2.00
1.50
1.00
0.50
0
0
Keep the Highest/4
MC
0.5
1.5
ATC
1.0
2.0 2.5 3.0
QUANTITY (Thousands of bottles of beer)
MR
3.5
D
4.0
Monopoly Outcome
Profit
Loss
Suppose Lagatt Green charges $2.50 per bottle. Your study partner Jabrill says that because Lagatt Green is a monopoly with market power, it should
charge the higher price of $3.00 per bottle in order to increase its profit.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Saltanat has a monopoly on ginger (имбирный) cookies in Almaty. The inverse demand function for the cookies is P = 100 – Q, where P denotes price and Q denotes quantity. The marginal cost is zero. a)Calculate P, Q and profits, if Saltanat maximizes profits. b) Now suppose instead that the ginger-cookie industry is competitive. Calculate P, Q and profits.arrow_forwardKalamazoo Competition-Free Concrete (KCC) is a local monopolist of ready-mix concrete. Its annual demand function is Q* = 10,000 – 200P, where Pis the price, in dollars, of a cubic yard of concrete and Qis the number of cubic yards sold per year. Suppose that Kalamazoo's marginal cost is $20 per cubic yard and fixed costs are sunk. Instructions: Round your answers to 2 decimal places. a. What is the deadweight loss from monopoly pricing? b. Now suppose that fixed costs are avoidable and large enough such that the monopolist elects not to produce. What is the deadweight loss from the monopoly not producing? %24arrow_forwardBlue INK is the only cabel service provider in Gazipur. The diagram below depicts the price, output and costs incurred by Blue INK. Use the graph to answer the following questions: 1. What is the Total revenue generated by Blue INK at the profit maximizing level of output? 2. If the Cable Service Market turns into a Perfectly Competitive Market, what will be the total ammount of the service provided? 3. If the market turns into a Monopoly market again, what will be the total deadweight loss created?arrow_forward
- Help me pleasearrow_forwardThe graph below shows the Market conditions of Honey’s Laundry service, which is the only laundry in Arizon Residential Area. Considering the shop as a Monopoly market, answer the following questions: (a)In order to maximize profit, how many clothes does the shop clean?[Answer in numerical value only without any unit] (b)If the opening of five new laundries turns it into a perfectly competitive market, what should be the price Sunny’s laundry be charging now?[Answer in numerical value only without any unit] (c)Compute the change in total revenue between part a and part b.[Answer in numerical value only without any unit] Note: Bartleby does not accept more than 3 sub-parts, and here are no more than 3. Please solve all parts to get a 'like'. Thanksarrow_forwardExercise A.4. A company operating in a market of monopolistic competition has an inverse demand curve for its product: P=315-3q, where q is the number of units produced of the good and P its price. The total cost of production of this company is given by: TC(q)=q²+75q+4000. a) To maximize profits, how many units of the good should you sell? b) What price should I charge? (c) What benefits would it reap? (d) Given the above information, how much would you have to reduce fixed costs for longterm equilibrium to occur? Represent graphicallyarrow_forward
- Questión 7 óf 18 Suppose that the corresponding graph relates to a firm that is able to engage in perfect price discrimination. What is this firm's profit? Price/Cost $50 45 40 profit = $ 35 30 25 Marginal cost = Average total cost 15 10 5 Demand 10 20 30 40 50 60 80 90 100 Quantity 70 20arrow_forwardA patent gave Sony a legal monopoly to produce a robot dog called Aibo. The Chihuahua-size pooch robot can sit, chase balls, dance, and play an electronic tune. When Sony started selling the toy in July 1999, it announced that it would sell 3,000 Aibo robots in Japan for about $2,000 each and a limited litter of in the United States for $2,500 each. Suppose that Sony's marginal cost of producing Aibos is $500.Its inverse demand curve is Pj= 3500−0.5Qj in Japan and Pa =4500−Qa Solve for the equilibrium prices and quantities (assuming that U.S. customers cannot buy robots from Japan). The equilibrium quantity in Japan is ____and the price, Pj is $____arrow_forwardThe following diagram illustrates the demand curve facing a monopoly in an industry with no economies or diseconomies of scale and no fixed costs. In the short and long run, MC = ATC. 1.) Using the point drawing tool, indicate the monopoly output and monopoly price (Monopoly) in the figure to the right. Attach the appropriate provided label. 2.) Using the rectangle drawing tool, shade in monopoly profits (Profit). Attach the appropriate provided label. 3.) Using the triangle drawing tool, shade in the "excess burden" or "welfare costs" of the monopoly (Excess burden). Attach the appropriate provided label. Note: Carefully follow the instructions above and only draw the required objects. The monopoly creates excess burden because O A. it produces where price equals marginal cost. B. it produces an inefficiently large amount of output. O C. it charges a price that is too low. D. it produces where marginal cost is positive. E. it produces where price is above marginal cost. MR Output, Q…arrow_forward
- Le Jouet is a French firm, and it is the only seller of toy trains in France and Russia. Suppose that when the price of toy trains increases, Russian children more readily replace them with toy airplanes than French children. Thus, the demand for toy trains in Russia is more elastic than in France. The following graphs show the demand curves for toy trains in France (Dr) and Russia (DR) and marginal revenue curves in France (MRF) and Russia (MRR). Le Jouet's marginal cost of production (MC), depicted as the grey horizontal line in both graphs, is $12, and the resale of toy trains from Russia to France is prohibited. Assume there are no fixed costs in production, so marginal cost equals average total cost (ATC). PRICE (Dollars per toy train) 40 36 32 28 Total 24 20 16 12 8 4 0 Country France Russia France MR Price (Dollars per toy train) 20 20 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 QUANTITY (Millions of toy trains) N/A O True MC-ATC OF O False N/A (?) Single Price Quantity Sold (Millions of toy…arrow_forwardSuppose that a firm produces wooden train engines in a monopolistically competitive market. The following graph shows its demand curve, marginal revenue (MR) curve, marginal cost (MC) curve, and average total cost (ATC) curve: Place a black point (plus symbol) on the graph to indicate the long-run monopolistically competitive equilibrium price and quantity for this firm, Next, place a grey point (star symbol) to indicate the minimum average total cost the firm faces and the quantity associated with that cost.arrow_forwardThe following diagram illustrates the demand curve facing a monopoly in an industry with no economies or diseconomies of scale and no fixed costs. In the short and long run, MC = ATC. 1.) Using the point drawing tool, indicate the monopoly output and monopoly price (Monopoly) in the figure to the right. Attach the appropriate provided label. 2.) Using the rectangle drawing tool, shade in monopoly profits (Profit). Attach the appropriate provided label. 3.) Using the triangle drawing tool, shade in the "excess burden" or "welfare costs" of the monopoly (Excess burden). Attach the appropriate provided label. Note: Carefully follow the instructions above and only draw the required objects. The monopoly creates excess burden because A. it produces where marginal cost is positive. B. it produces where price equals marginal cost. OC. it produces an inefficiently large amount of output. D. it produces where price is above marginal cost. E. it charges a price that is too low. Click the graph,…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education