
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
In a laboratory experiment, students synthesized a new compound and found that when 10.92 grams of the compound were dissolved to make 188.0 mL of a benzene solution, the osmotic pressure generated was 5.22 atm at 298 K. The compound was also found to be nonvolatile and a non-electrolyte.
What is the molecular weight they determined for this compound?
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1 Formula
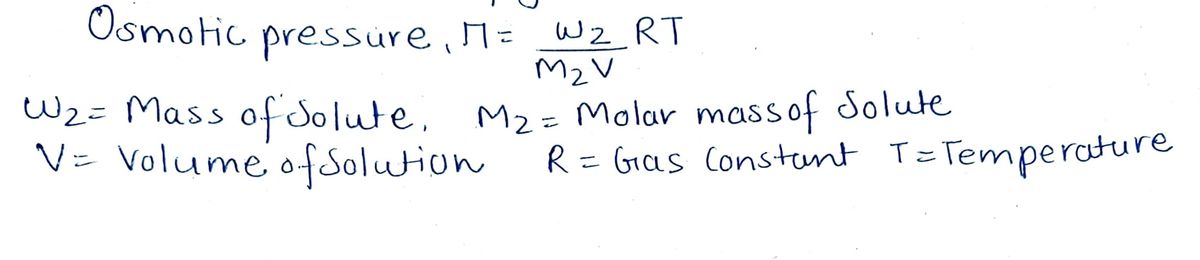
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- At what temperature (in °C) would a 0.00610 M solution of glucose in water exhibit an osmotic pressure of 0.150 atm?arrow_forwardAMoving to another question will S When 1.373 g of a nonelectrolytic substance was dissolved in enough benzene to make 0.166 L of solution, the osmotic pressure was found to be 1 torr at 21.3 °C. What is the molar mass (g mol) of this substance? (the answer should be entered with 3 significant figures; do not enter units; give answer in scientific notation--valid notation examples include 1.23e-8 and 1.23e8 and-1.23e-4 and 1.23e0) Questlen 28 EQuestion 28 of 29 A Moving to another question will save this response. 40 S80. & 60 2 24 4 %23 6 9 delete 7. E R Y enter S L K return ock V B N alt atrol option mand command optionarrow_forwardA 200.0 mL sample of an aqueous solution at 45°C contains 24.6 mg of an unknown nonelectrolyte compound. If the solution has an osmotic pressure of 7.48 torr, estimate the molar mass of the unknown compound. (1 atm = 760 torr, 1 g = 1000 mg)arrow_forward
- In a laboratory experiment, students synthesized a new compound and found that when 11.52 grams of the compound were dissolved to make 160.1 mL of a benzene solution, the osmotic pressure generated was 7.75 atm at 298 K. The compound was also found to be nonvolatile and a non-electrolyte. What is the molar mass they determined for this compound? g/molarrow_forwardAt what temperature (in °C) would a 0.00390 M solution of glucose in water exhibit an osmotic pressure of 0.150 atm?arrow_forwarda 7.45 Ml solution is made by dissolving a 0.00542 g of an unknown polypeptide in water. its osmotic pressure was measured to be 12.95mmHg at 25 C. What is the molar mass of the polypeptidearrow_forward
- Help with the following questionarrow_forwardAt what temperature (in °C) would a 0.00570 M solution of glucose in water exhibit an osmotic pressure of 0.150 atm?arrow_forwardA 0.13-g sample of a purified protein is dissolved in water to give 2.0 mL of solution. The osmotic pressure is found to be 17.0 torr at 25°C. Calculate the protein's molar mass. Molar mass = g/molarrow_forward
- 0.0471 kg of biphenyl (C12H10) is dissolve in benzene (C6H6) to create a solution with a total volume of 350.0 mL. (Assume the change in volume is negligible) What would be the osmotic pressure (in atm) of this solution at 40.0 °C? Assume the density of the solution is the same as benzene, 0.877 g/mL.arrow_forwardAt what temperature (in °C) would a 0.00510 M solution of glucose in water exhibit an osmotic pressure of 0.150 atm?arrow_forwardIn a laboratory experiment, students synthesized a new compound and found that when 11.40 grams of the compound were dissolved to make 160.5 mL of a ethanol solution, the osmotic pressure generated was 6.03 atm at 298 K. The compound was also found to be nonvolatile and a non-electrolyte. What is the molecular weight they determined for this compound?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY