
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
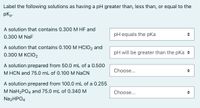
Transcribed Image Text:Label the following solutions as having a pH greater than, less than, or equal to the
pka-
A solution that contains 0.300 M HF and
pH equals the pKa
0.300 M NaF
A solution that contains 0.100 M HCIO2 and
0.300 М КСIO2
pH will be greater than the pka +
A solution prepared from 50.0 mL of a 0.500
M HCN and 75.0 mL of 0.100 M NaCN
Choose...
A solution prepared from 100.0 mL of a 0.255
M NaH2PO4 and 75.0 mL of 0.340 M
Choose...
Na2HPO4
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 11. Calculate the concentrations of all species, pH and % ionization for each of the following. a) 0.20 M HC2H3O2 (Ka = 1.75×105) b) 1.5 M HNO₂ c) 0.10 M NH3 d) 0.25 M HN3 (Ka = 7.10×105) (Kb = 1.75×105) (Ka = 2.20×105)arrow_forwardWhen 35.0 mL of 0.300 M hydrobromic acid and 35.0 mL of 0.300 M ammonia are combined, the pH of the resulting solution will be : A. Less than 7 B. Equal to 7 C. Greater than 7arrow_forwarda .1000 M solution of a weak acid, HA, is 3.0% dissociated. Determine the value of Ka for the weak acidarrow_forward
- If 25 mL of 0.750 M HCl are added to 100. mL of 0.352 M NaOH, what is the final pH? Select one: a. 13.12 b. 0.88 c. 13.45 d. 0.55 e.7.00arrow_forwardCalculate the pH of a buffer solution made by dissolving 50 g of NaHCO3 and 20 g of H2CO3 to make 100 mL of a buffer solution. Help! H2CO3 Ka1= 4.30 x 10^-7 a. 6.77 b. 6.63 c. 6.10 d. 6.37arrow_forwardQuestion is attached.arrow_forward
- The pH after adding 21.0 mL of 1.0 M NaOH to 25.0 mL of 1.0 M HCl is 0.087 0.16 0.80 1.1arrow_forwardEqual molar amounts of benzoic acid and sodium acetate are mixed together in water, is the resulting solution acid,basic, or neutral? Here are some Ka valuesarrow_forwardWhat combination of substances will give a buffered solution that has a pH of 5.05? (Assume each pair of substances is dissolved in 5.0 L of water.) (Kb for NH3 = 1.8 ´ 10–5; Kb for C5H5N = 1.7 ´ 10–9) a. 1.0 mole NH3 and 1.5 mole NH4Cl b. 1.5 mole NH3 and 1.0 mole NH4Cl c. 1.0 mole C5H5N and 1.5 mole C5H5NHCl d. 1.5 mole C5H5N and 1.0 mole C5H5NHCl e.none of thesearrow_forward
- Ka of acetic acid equals 1.8*10^-5 The buffer solution is 50 mL of 0.2 M CH3CO2H and 50 mL of 0.2 M NaCH3CO2together in a beaker. What is the theoretical pH of each soluton? a. 50 mL of boiled deionized water + 5 mL of 0.2 M HClb. 50 mL of boiled deionized water + 5 mL of 0.2 M NaOHc. 50 mL of buffer + 5 mL of 0.2 M HCld. 50 mL of buffer + 5 mL of 0.2 M NaOHarrow_forwardChange the top option to a Base and repeat the table for 0.001, 0.01, 0.1 and 1 for the base filling in the table below. Acid Base Initial pH Initial pH Concentration Concentration 0.001M 3.00 0.001M 11.00 0.01M 2.00 0.01M 12.03 0.1M 1.00 0.1M 13.00 1M 0.00 1M 14.00 If you were to use a calculator to do these calculations would you get the same answers? Try at least one on the acid side and one on the base side to confirm your answer.arrow_forwardClassify the salts according to strength and role in buffer system. Classifications are as follows: Strong Acid/Conjugate Base, Strong Base/Conjugate Acid, Weak Acid/Conjugate Base, or Weak Base/Conjugate Acid. Example: HCI - Strong Acid/Conjugate Base 1. CaCO3 2. Li2SO3 3. Na₂S 4. Na3PO4 5. KC1 5000000 6. KCN 7. BaClz 8. NSHCO3 9. NACOOCH3 10. N₂HsBr 11. AgNO3 12. KHSO4 13. NaOCI wwwwww 14. NaNO3 15. NaH₂PO4arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY