
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
The natural frequency ω of vibration of a mass M attached
to a rod, as in Fig. depends only on M and the stiffness EI and length L of the rod. Tests with a
2-kg mass attached to a 1040 carbon steel rod of diameter
12 mm and length 40 cm reveal a natural frequency of 0.9 Hz.
Use these data to predict the natural frequency of a 1-kg
mass attached to a 2024 aluminum alloy rod of the same
size.
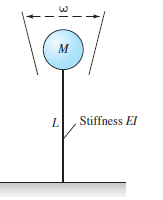
Transcribed Image Text:L.
Stiffness El
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- (b) A passenger car has a tyre spring rate of 18,900 N/m. The front suspension rate is 1,450 N/m and the rear is 1,050 N/m. Assume the front tyres are loaded to 10,000 N and rear tyres are at 7,900 N. (i) Solve the front suspension ride rate in N/m. (11) Evaluate the natural frequency at front suspension.arrow_forwardConsider the dynamic system shown below. Rod Pulley Rc Rod Pulley RA = 10 cm PIB 1A The following parameters are given for the system: m₂ = 1 kg RA mg mc 2 kg RB Rc 20 cm m₂ = 3 kg R₂ = 30 cm k = 1200 N/m Note that pulleys A and B are constrained to move together and pulleys C and D are constrained to move together. Useful note... a. Obtain the characteristic equation(s) for this system. b. The applied force is removed. Then, pulley A/B is turned 2 degrees and released from rest. Find the system response.arrow_forwardE IVP Consider a 3-element axial vibration model of a fixed-fixed bar. Use finite element analysis to determine the first two natural frequencies w1= a where and b are scalars, I is the length of the bar, E is Young's modulus and p is the density. Determine the value of b using 3 decimal places. and w2= b E = IV Parrow_forward
- A spring mass system with a natural frequency fn = 20 Hz is attached to a vibration table. Thetable is set to vibrate at 16 Hz, with a maximum acceleration 0.25 g. Answer the followingquestions. Justify your answers d. What is the maximum acceleration of the mass assuming the packaging can be modeled asa viscous damper with a damping ratio of 0.2?e. Is the motion of the mass in phase or out of phase with the motion of the table?arrow_forwardHi, Could you please help, thnksarrow_forwardGiven an oscillator of mass 2.0kg and spring constant of 180N/m, what is the period without damping? Use numerical methods to model this oscillator with an additional friction force equal to where c is a positive damping constant. Using c=5.0, what is the new period of oscillation. What about for c=10? Assume initial position is 0.2m and initial velocity is zero. Please find the period using the position versus time plot and use the first full cycle of the motion.arrow_forward
- is my sloution correct ?arrow_forwardA diving board has a mass of 7.8 kg and a stiffness of 4.4 N/m. Its length is 1.8 m. Determine the natural frequency of the board. Note: Give your answer in rad/s Answer: s page Nex Type here to search earrow_forwardHello Good Evening Sir,Permission, i have a question in my homework related Mechanics of material strength or mechanical engineering lesson. The following below is the questions. Please advice. Thank you so much Regards,Irfanarrow_forward
- A compact object with a mass of 8.80 kg oscillates at the end of a vertical spring with a spring constant of 1.60 ✕ 104 N/m. The motion is damped by air resistance, and the damping coefficient is b = 3.00 N · s/m. (a) What is the frequency (in Hz) of the damped oscillation? Hz (b) By what percentage does the amplitude of the oscillation decrease in each cycle? % (c) Over what time interval (in s) does the energy of the system drop to 5.00% of its initial value? s (d) What If? The atmosphere of Venus is 50 times thicker than that on Earth. If the effect of air resistance on Venus is represented by b = 150 N · s/m, recalculate the answers for parts (a) to (c) for this system if it is set in motion in the atmosphere of Venus. What is the frequency (in Hz) of the damped oscillations? Hz What is the percentage decrease in amplitude in each cycle? % What is the time interval (in s) for the energy to drop to 5.00% of its initial value? sarrow_forwardIn free vibration we experimentally determine the natural frequency of a mass-spring system to be f, = 120.2796 Hz. The results show that decreasing the stiffness of the system by Ak = 592880.1217 N/m, the natural frequency will be decreased by Af, = 31.6418HZ. What is thearrow_forwardAn undamped spring mass system has a mass of 10 kg and a spring stiffness of 2250 N/m. It is excited by a harmonic force having a sine function characteristic with amplitude of 100 N and an excitation frequency of 15 rad/s. The initial displacement and the velocity are 0.15 m and 1.5 m/s respectively. The Particular solution at t = 2s The frequency ratio is: Choose... Choose...arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY