
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
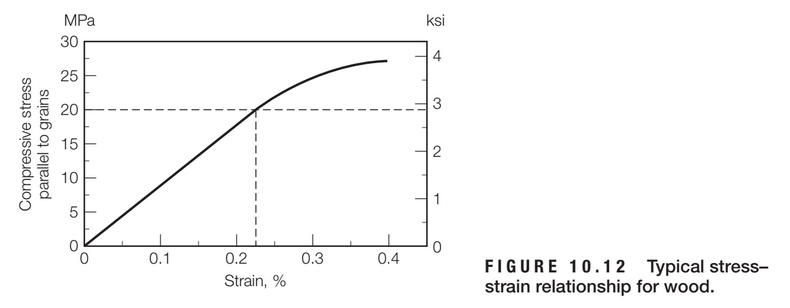
Compute the modulus of elasticity of the wood species whose stress–strain
relationship is shown in Figure 10.12, using both the SI and English units.
Compare the results with the typical values shown in Table 1.1 in Chapter 1
and comment about the results.
Transcribed Image Text:ksi
MPa
30
4
25
20
15
10
1
0.1
FIGURE 10.12 Typical stress-
strain relationship for wood.
0.2
0.3
0.4
Strain, %
4.
3.
2.
parallel to grains
Compressive stress
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please fill in all sectionsarrow_forwardCompare the benefits of engineered composites to those of timber. Give examplesof applications in which composites would be more beneficial compared totimber. Give additional examples of applications where the use of timber would bemore advantageous.arrow_forwardWhat will be the moment of resistance of the composite section shown in the figure below if the permissible stress in wood and steel is 70 N/mm² and 120 N/mm² respectively. Steel plate Wood -200 4150 400 10arrow_forward
- During laboratory testing of an 6-inch aluminum-alloy rod with a cross sectional area of 0.32in², a tensile load of 50,000 lbs.is applied. Ifthe cross sectional area decreases to 0.3188in? and lengthens to 6.022 inches, what is the Modulus of Elasticity and Poisson's Ratio? E = 6/ɛ V = = -E(lateral)/ɛ(axial)arrow_forwardUsing linear interpolation determine the DBTT of a given steel with the following Charpy tests results: 18 J at -18°C 28 J at -2°C 45 J at 5°C 60 J at 12°C -3.6°C -4.6°C -5.6°C -2.6°Carrow_forwardA No. 8 steel rebar is tested in tension. By monitoring the load reading of the testing machine, it was found that the specimen yielded at a load of 60,000 lbs and fractured at 75,000 lbs. Determine the following: a. Tensile stresses at yield and at fracture. b. Estimate how much increase in length would occur at 75% of the yield stress in a 16-in. gauge length.arrow_forward
- A wood beam reinforced by an aluminum channel section is shown in the figure. 150 mm 230 mm 38 mm 6.5 mm -163 mm- The beam has a cross section of dimensions 150 mm x 230 mm, and the channel has a uniform thickness of 6.5 mm. If the allowable stresses in the wood and aluminum are 8 MPa and 50 MPa, respectively, and if their moduli of elasticity are in the ratio 1 to 6, what is the maximum allowable bending moment for the beam? Enter the magnitude in kN · m. (Assume that the component parts of the beam are securely bonded by adhesives or connected by fasteners. Also, be sure to use the transformed-section method in the solution.) (No Response) 14.06 kN· marrow_forwardAn ASTM A615 grade 60 number 10 rebar with a gauge length of 8 in. was subjected to tension to fracture according to ASTM E-8 method. The load and deformation data were as shown in Table .Using a spreadsheet program, obtain the following:a. A plot of the stress–strain relationship. Label the axes and show units.b. A plot of the linear portion of the stress–strain relationship. Determine modulus of elasticity using the best-fit approach.c. Proportional limit.arrow_forwardPlease provide all necessary information, explanation, and solutions. Thank you!arrow_forward
- Which of the following options are correct for the section shown in figure? 40 mm 100 mm 100 mm Elastic section modulus Shape factor 40 mm 100 mm 100 mmarrow_forwardPlease find the following? Use standard table unitsarrow_forwardplease answer these two question 1.Explain the reason that flexural modulus of elasticity and compression test modulus of elasticity must be considered separately when both the flexural test and the parallel to grain compressive test caused normal stresses parallel to the grain of the wood. 2. Discuss the difference between isotropic and orthotropic materials for wood.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning