
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
The equation below represents a linear
all derivations in the spaces under the corresponding question.
l) Plot the demand function on the top set of axes: Qx = 80000 - 100P x . The
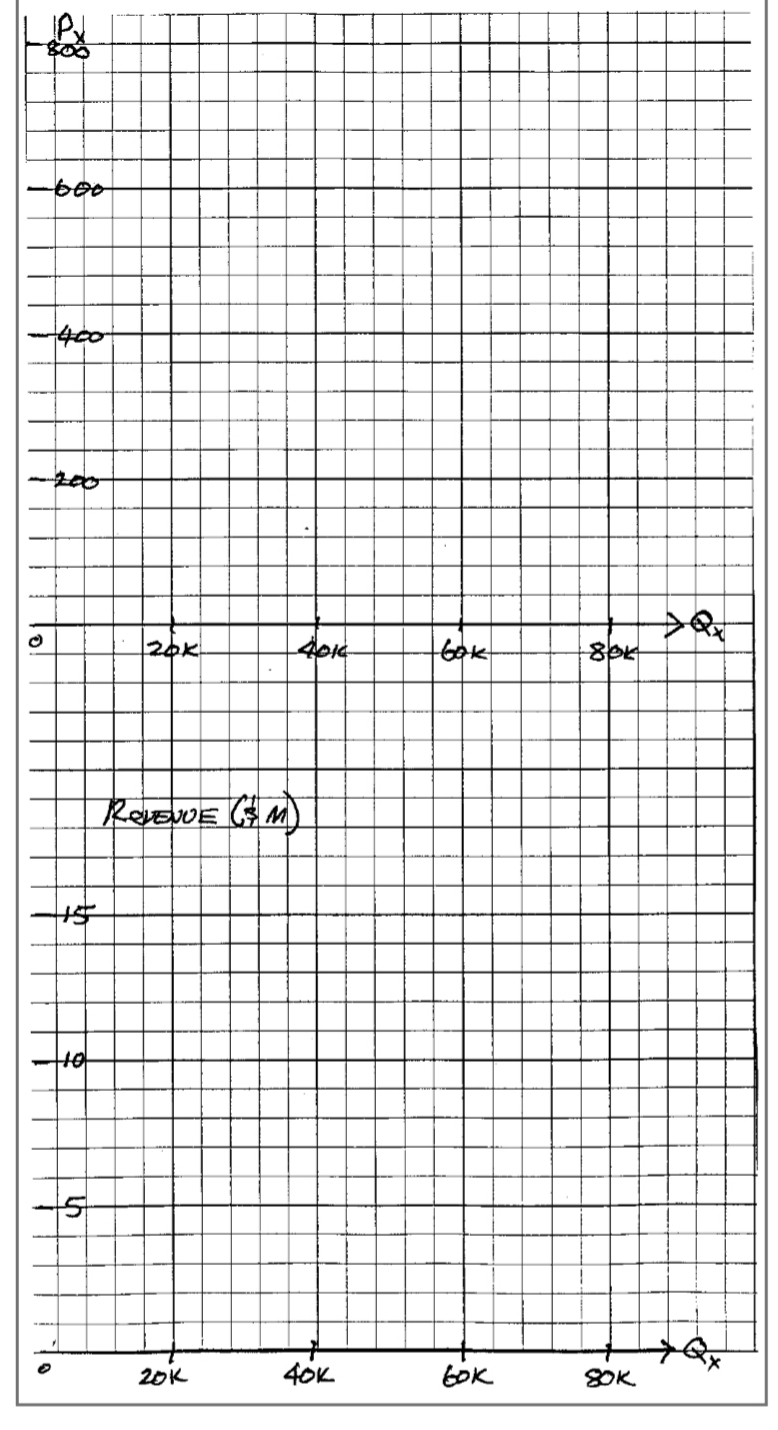
Transcribed Image Text:k<e
20K
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- I need help determining this onearrow_forwardIn the market for widgets supply and demand are estimated as follows : P= 20-1.8 Qd and P= 2+Qs. Graph these curves and solve for equillibrium price and quantityarrow_forwardUse the green rectangle (triangle symbols) to compute total revenue at various prices along the demand curve. Note: You will not be graded on any changes made to this graph. PRICE (Dollars per scooter) TOTAL REVENUE (Dollars) 195 180 165 910 150 1130 800 1020 090 135 580 120 470 105 360 On the following graph, use the green point (triangle symbol) to plot the weekly total revenue when the market price is $30, $45, $60, $75, $90, $105, and $120 per scooter. 250 75 140 60 45 30 15 0 Demand 03 6 9 12 15 18 21 24 27 30 33 36 39 QUANTITY (Scooters) 0 15 30 45 Total Revenue 60 75 90 105 120 125 150 165 180 195 PRICE (Dollars per scooter) A Total Revenue ? (?) According to the midpoint method, the price elasticity of demand between points A and B is approximately Suppose the price of scooters is currently $30 per scooter, shown as point B on the initial graph. Because the demand between points A and B is in total revenue per week. a $15-per-scooter increase in price will lead to In general,…arrow_forward
- Assume the demand curve for Pepsi passes through the following two points. Price per bottle of Pepsi $2.25 $1.75 Number of bottles of Pepsi sold 100,000 275,000 When plotting the demand curve (with price in dollars on the y-axis and quantity in bottles on the x-axis), when the y-value is $2.25, the x-value is the y-value is $1.75, the x-value is bottles. (Enter your responses as whole numbers.) bottles, and whenarrow_forwardSolve full question pleasearrow_forwardNote:- Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism. Answer completely. You will get up vote for sure.arrow_forward
- The following table shows worldwide sales of a certain type of cell phone and their average selling prices in 2012 and 2013. Year 2012 2013 Selling Price ($) Sales (millions) 928 1,144 375 335 (a) Use the data to obtain a linear demand function for this type of cell phone. (Let p be the price, and let q be the demand). q(p): -5.4p + 3185 X Use your demand equation to predict sales if the price is lowered to $255. 1808 x million phones (b) Fill in the blank. For every $1 increase in price, sales of this type of cell phone decrease by 5.4 million units.arrow_forwardPls answer it with step by step explanationarrow_forwardRevenue R from the sale of x units of a product is found by multiplying the price by the number of items sold. (a) Factor the right side of R = 200x - x². R = (b) What is the expression for the price of the item? The consumer expenditure, in dollars, for a commodity is the product of its market price, p, and the number of units demanded, x. Suppose that for a certain commodity, the consumer expenditure is given by 9,000p - 150p². (a) Factor this in order to find an expression for the number of units demanded. (Simplify your answer completely.) x = units (b) Use (a) to find the number of units demanded when the market price is $33. x = units A company's average cost per unit when x units are produced is defined to be Total cost Average cost = Χ Suppose a company's average costs are given by 6000 Average cost = +35+0.2x. X Express the average-cost formula as a single fraction. Average cost = 3arrow_forward
- Price A B Quantity Price D Quantity The market for BREAD is represented by the dark solid curves in the two graphs above (demand and supply are shown separately to make the diagram easier to read). Indicate which curve (or curves) we would move to with each of the following changes.arrow_forwardThe following table models the supply of a specialty coffee: \table[[Price per Pound, Pounds Supplied (in thousands)], [$ 8,8], [$9,9], [$10,11], [$11, 13]] A new supplier enters the market. As a result, the supply curve shifts by two pounds supplied for all prices. Graph the new supply curve. (Directions: Use the segment tool to select the first point and then click on the next point. For the following points, click on your previous point and then select your new point. This will draw a line between all your points.) (Directions: Use the segment tool to select the first point and then click on the next point. For the following points, click on your previous point and then select your new point. This will draw a line between all your points.) Segment Move Undo Redo Resetarrow_forwardThe Law of Demand states that as the price of a good increases, ceteris penbus, the The relationship that exists between these two variables can be described as decreases. This can be shown graphically with demand curve or numericaly in a table using a 0arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education