
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
An object and lens are positioned to form a well-focused image on a viewing screen. Then a piece of cardboard is lowered just in front of the lens to cover the top half of the lens. Using what you’ve learned from as shown, what happens to the image on the screen?
A. Nothing
B. The upper half of the image vanishes.
C. The lower half of the image vanishes.
D. The image becomes fuzzy and out of focus.
E. The image becomes dimmer but remains in focus.
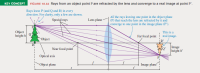
Transcribed Image Text:KEY CONCEPT
FIGURE 18.32 Rays from an object point P are refracted by the lens and converge to a real image at point P'.
Rays leave P (and Q and R) in every
direction. For clarity, only a few are shown.
Special rays
All the rays leaving one point in the object plane
(P) that reach the lens are refracted by it and
converge to one point in the image plane (P").
Lens plane
Object
height h
This is a
Far focal point
real image.
Object
R'
Image
height h'
Near focal point
Optical axis
Object plane
Image plane
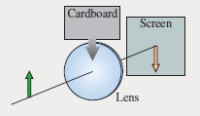
Transcribed Image Text:Cardboard
Screen
Lens
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Which of these are characteristics of real images? Select one or more: a. Light rays do not go through real images. b. Real images formed by single lenses or mirrors are always inverted. c. Real images formed by single lenses or mirrors are always upright. d. Light rays go through real images.arrow_forwardPlease answer these 2 questionsarrow_forwardTo view an insect, an entomologist places a converging lens with a focal length of 10 cm a distance of 8.0 cm from the insect. What will be the magnification of the insect's image? a. +5 b. +3 c. +4 d. +6 e. +7arrow_forward
- Two converging lenses with focal lengths of 50 cm and 21 cm are 10 cm apart. A 3.9- cm-tall object is 25 cm in front of the 50-cm -focal-length lens. A. Calculate the distance between the final image and 21-cm-focal-length lens. B. Calculate the image height.arrow_forward3. An object sits 23 cm in front of a diverging mirror. An image is formed 14 cm behind the mirror. What is the focal length of the mirror? a. b. What is the magnification of the image?arrow_forwardA bug is 3 cm to the left of a lens with f = -4.56 cm. Find the image distance from the lens. A second lens of f = 8 cm is placed 1.21 cm to the right of the first lens. Find the distance of the final image from the second lens. Use the image from the first lens as an "object" for the second lens. The final image is: A. Upright B. Inverted The final image is: A. Real B. Virtualarrow_forward
- A concave lens has a focal length of -45 cm. a) Find the image distance that results when an object is placed 32 cm in front of the lens. b) Find the magnification that results when an object is placed 32 cm in front of the lens.arrow_forwardA lens forms an image of an object. The object is 15.4 cm from the lens. The image is 11.7 cm from the lens on the same side as the object. a. What is the absolute value of the focal lens of the lens? cm b. Is the lens converging or diverging? converging diverging c. If the object is 8.48 mm tall, how tall is the image? mm d. Is the image upright or inverted? upright O inverted e. To receive full credit for this problem you will need to draw a principal ray diagram, including three principal rays. yes, got it - I will attach the diagram in Canvas with the rest of my work. no, I don't have a diagram to attach.arrow_forwardA doctor examines a mole on the patient with a 17.2 cm focal length magnifying glass held 11.2 cm from the mole. Describe the image the doctor sees. A.Real B. Virtual C. Inverted D. Upright E. Smaller than object F. Larger than objectarrow_forward
- Which of the following scenarios is a reasonable representation of a nearsighted person wearing proper corrective lenses? A.Light passes through a concave lens and then another concave lens. B. Light passes through a convex lens and then a concave lens C.Light passes through a concave lens and then a convex lens D. light passes through a convex lens and then another convex lensarrow_forwardWhich of the following statements for single optic devices are true? Choose all that apply. a. Any physicist worth their weight in garbanzo beans (not chick peas) knows that concave lenses will have a positive focal length. b. For virtual images, the image distance is positive and the object distance is negative. c. By convention, if the image height is positive then the image is upright. d. If an optic produces an image with a magnification of 0.6, then the image is diminished. e. Experiments have shown that convex mirrors can create real images. f. If an image has a magnification of -6, then the image is real.arrow_forward6. An object is 185 cm from a convex lens with a focal length of 25 cm. When an inverted image is 12 cm tall, how tall is the associated object? 7. What are the image height and orientation produced by the setup in the following figure? Object 5.0 cm – 10.0 cm - 15.0 cmarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON