
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Kenji sees a classified ad from Lucia offering a used digital camera for $30. On the opposite page, he sees a big color ad from a national electronics chain offering a new digital camera for $250. Kenji values a digital camera at $300 as long as it works, regardless of whether it is new or used.
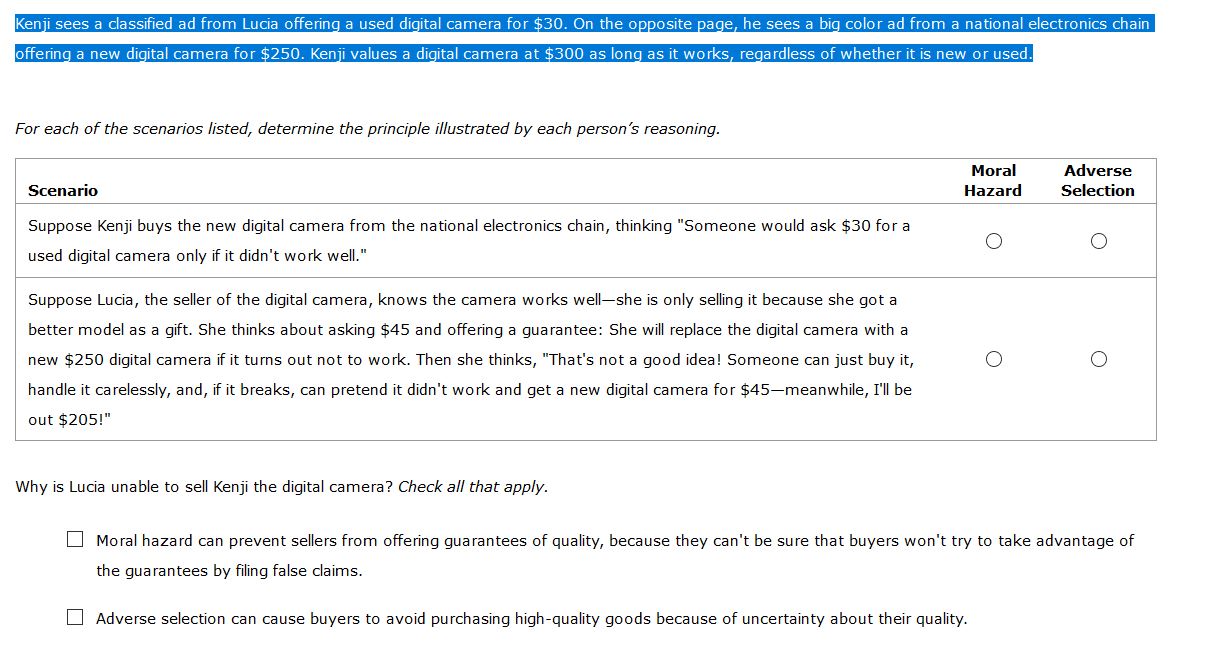
Transcribed Image Text:Kenji sees a classified ad from Lucia offering a used digital camera for $30. On the opposite page, he sees a big color ad from a national electronics chain
offering a new digital camera for $250. Kenji values a digital camera at $300 as long as it works, regardless of whether it is new or used.
For each of the scenarios listed, determine the principle illustrated by each person's reasoning.
Moral
Adverse
Scenario
Hazard
Selection
Suppose Kenji buys the new digital camera from the national electronics chain, thinking "Someone would ask $30 for a
used digital camera only if it didn't work well."
Suppose Lucia, the seller of the digital camera, knows the camera works well-she is only selling it because she got a
better model as a gift. She thinks about asking $45 and offering a guarantee: She will replace the digital camera with a
new $250 digital camera if it turns out not to work. Then she thinks, "That's not a good idea! Someone can just buy it,
handle it carelessly, and, if it breaks, can pretend it didn't work and get a new digital camera for $45-meanwhile, I'll be
out $205!"
Why is Lucia unable to sell Kenji the digital camera? Check all that apply.
O Moral hazard can prevent sellers from offering guarantees of quality, because they can't be sure that buyers won't try to take advantage of
the guarantees by filing false claims.
O Adverse selection can cause buyers to avoid purchasing high-quality goods because of uncertainty about their quality.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- #51arrow_forwardJenny is going to rent a truck for one day. There are two companies she can choose from, and they have the following prices. Company A charges $90 and allows unlimited mileage. Company B has an initial fee of $55 and charges an additional $0.70 for every mile driven.arrow_forwardwhat does this mean in terms of the interrelationship of supply, price, and demand on two items of your choice. Maybe it’s a Christmas that a child really wants but that most stores no longer have in stock. Or it might be a piece of clothing that you bought last year and now want to replace it but which is hard to find or twice as expensive as what it was last year.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education