
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Explain step by step
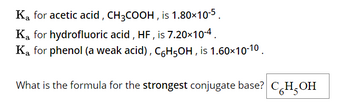
Transcribed Image Text:Ka for acetic acid, CH3COOH, is 1.80×10-5.
Ka for hydrofluoric acid, HF, is 7.20×10-4.
Ką for phenol (a weak acid), C6H5OH, is 1.60×10-10.
What is the formula for the strongest conjugate base? CH₂OH
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Given data :
Ka for acetic acid, CH3COOH, is 1.80×10-5
Ka for hydrofluoric acid, HF, is 7.20×10-4
Ka for phenol (a weak acid), C6H5OH, is 1.60×10-10
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 39arrow_forwardWhich of the following statements is the best explanation of how activation energy affects the rate of a chemical reaction? A. A high activation energy means molecules have less kinetic energy and hence rate of reaction will be slower. B. A high activation energy means molecules must have more kinetic energy to overcome it, and hence rate of reaction will be faster. C. A high activation energy means molecules have a lot of kinetic energy and hence rate of reaction will be faster. D. A high activation energy means molecules must have less kinetic energy to overcome it, and hence rate of reaction will be slower. E. A high activation energy means molecules must have more kinetic energy to overcome it, and hence rate of reaction will be slower.arrow_forwardB. Rates of reaction are typically measured as the change of concentration per unit time. Some typical units of concentration are: M, mM, pM, µM, nM. Some typical units of time are: years, days, hr, s, ms, ps, µs, and ns. For each reaction, suggest a reasonable unit of measure for the rate of reaction. a. The combustion of gasoline. b. The transformation of organic material into crude oil. Chemical change involved with memory in the human brain. с. d. The rusting of an iron nail. 9. Why would a scientist use nM/ps instead of M/s? - 112 -arrow_forward
- The change in temperature from 20°C to 10°C is found to halve the rate of a particular chemical reaction. How did the change in temperature affect the reaction? Periodic Table and Datasheet O The number of molecules colliding with sufficient energy to react increased. O The number of molecules colliding with sufficient energy to react decreased. O The activation energy increased. O The activation energy decreased.arrow_forwardReaction rate increases if reactant is added. O True O Falsearrow_forwardChemistry 2. The following experimental data are obtained for the decomposition of nitrogen dioxide: 2 NO2(g) → 2 NO(g) + O2(g) ⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯ Time, s [NO2], M ln[NO2], [NO2]-1, M-1 ⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯ 0 10.0 x 10-3 -4.605 1.00 x 102 60 6.83 x 10-3 -4.986 1.46 x 102 120 5.18 x 10-3 -5.263 1.93 x 102 180 4.18 x 10-3 -5.477 2.39 x 102 240 3.50 x 10-3 -5.655 2.86 x 102 300 3.01 x 10-3 -5.806 3.32 x 102 ⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯ Plot a graph of ln[NO2] versus t and 1/[NO2] versus t. Determine the decomposition of NO2 follows a first order or second order rate law with respect to [NO2].arrow_forward
- According to collision theory, the molecules must have enough energy when they collide to cause chemical bonds to break and form. In other words, for a reaction to happen. What do we call the minimum energy required to initiate a chemical reaction? Choose from the choices below: Activation energy Collision energy Heat energy Reaction energyarrow_forwardTypical Chemical Potential Energy (PE) Diagram for an Exothermic Reaction A catalyst provides an alternate pathway for a reaction to occur. The alternate pathway has a lower activation energy (AE), meaning that the reactant molecules do not need to collide with as much energy in order for a reaction to occur, so more collisions result in a reaction, so the reaction rate is faster. Chemical Potential Energy (Enthalpy) Note that adding a catalyst does not change the amount of energy released (AH) for the reaction. Activation Energy (AE) with a catalyst PE of Reactants AH PE of Products Rxn Progress What effect does a catalyst have on the stoichiometry of the reaction? What effect does the catalyst have on the mechanism of a reaction? AE wlo a catalystarrow_forwardHow does increasing temperature affect the rate of reaction? the activation energy increases so the reaction rate decreases the reactants have more kinetic energy so the frequency of the effective collisions increases the reactants have more kinetic energy so the frequency of the effective collisions decreases the activation energy increases so the reaction rate increasesarrow_forward
- 18. In an experiment, the data below was collected for this reaction: A + B - C + D Expérience initial speed [A] (mol/L) [B] (mol/L) (mol/L•s) 0,0299 1 0,0020 0,0030 0,0020 0,0060 0,0598 3 0.0040 0,0060 0,2392 Determine the equation for the law of reaction rate. Show reasoning.arrow_forwardReaction rate increased by an increase of surface area of a reactant. One way to increase surface area is to add catalyst crush solid reactant into smaller pieces increase reactant's temperature increase reactant's concentrationarrow_forwardFree Energy (kcal/mol) 25 20 15 10 B 5 сле C A D 0 Reaction progress Use the reaction energy diagram above to answer the following questions. Calculate the activation energy, AG *, for the step B to A. kcal/mol Calculate the overall energy change, AG°, for the process A to D. Which step is faster, (a) B to C or (b) D to C? @ kcal/molarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY