
Concept explainers
Prepare
Rate, Ending Balance of WIP, Finished Goods, and COGS
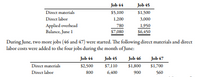
At the beginning of June, Rhone Company had two jobs in process, Job 44 and Job 45, with the
following accumulated cost information:
At the end of June, Jobs 44, 45, and 47 were completed. Only Job 45 was sold. On June 1, the
balance in Finished Goods was zero.
Required:
1. Calculate the overhead rate based on direct labor cost. (Note: Round to three decimal places.)
2. Prepare a brief job-order cost sheet for the four jobs. Show the balance as of June 1 as well
as direct materials and direct labor added in June. Apply overhead to the four jobs for the
month of June, and show the ending balances.
3. Calculate the ending balances of Work in Process and Finished Goods as of June 30.
4. Calculate the Cost of Goods Sold for June.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

- At the end of June, the job cost sheets at Ace Roofers show the following costs accumulated on three jobs. Job 7 $ 28,900 24,800 12,400 At June 30 Direct materials Direct labor Overhead applied Additional Information a. Job 5 was started in May, and the following costs were assigned to it in May: direct materials, $7,900; direct labor, $3,700; and applied overhead, $2,800. Job 5 was finished in June. b. Job 6 and Job 7 were started in June; Job 6 was finished in June, and Job 7 is to be completed in July. c. Overhead cost is applied with a predetermined rate based on direct labor cost. The predetermined overhead rate did not change across these months. Job 5 $ 18,800 11,800 5,900 Job 6 $ 34,900 18,000 9,000 Total transferred cost 4. What is the total cost transferred to Finished Goods Inventory in June?arrow_forwardXYZ Company uses a job costing system. The direct materials for Job Y were purchased in September and put into production in October. The job was not completed by the end of October. At the end of October, in what account would the direct materials cost assigned to Job Y be located? Select one: O a Work-in-Process Inventory. Ob. None of the given is correct. ON Finished Goods Inventory. Od. Raw Materials Inventory. O e. Cost of Goods Sold.arrow_forward1. What is the total cost of direct materials requistioned in June? 2. What is the total cost of direct labor used in June? ( please check plagiarism)arrow_forward
- Required information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] At the end of June, the job cost sheets at Ace Roofers show the following costs accumulated on three jobs. At June 30 Direct materials Direct labor Overhead applied Additional Information Job 5 $ 18,400 11, 400 5,700 Job 6 $ 34,700 17,600 8,800 Job 7 $ 28,700 24,400 12, 200 a. Job 5 was started in May, and the following costs were assigned to it in May: direct materials, $7,700; direct labor, $3,500; and applied overhead, $2,600. Job 5 was finished in June. b. Job 6 and Job 7 were started in June; Job 6 was finished in June, and Job 7 is to be completed in July. Total transferred cost c. Overhead cost is applied with a predetermined rate based on direct bor cost. The predetermined overhead rate did not change across these months. 4. What is the total cost transferred to Finished Goods Inventory in June?arrow_forwardRequired information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Caro Manufacturing has two production departments, Machining and Assembly, and two service departments, Maintenance and Cafeteria. Direct costs for each department and the proportion of service costs used by the various departments for the month of August follow: Department Machining Assembly Maintenance Cafeteria Job CM-22: Direct Costs $92,000 62,400 38,800 31,000 Job CM-23: Proportion of Services Used by Maintenance. Cafeteria Machining Machine-hours Labor-hours. Machine-hours. Labor-hours 0.8 Assume that both Machining and Assembly work on just two jobs during the month of August: CM-22 and CM-23. Costs are allocated to jobs based on machine-hours in Machining and labor-hours in Assembly. The number of labor- and machine-hours worked in each department are as follows: Machining 300 50 30 20 0.2 Assembly 40 36 20 150 Prev 0.6 0.1 S Assembly 0.2 0.1 2 of 13 HH Nextarrow_forwardJensen Fences uses job order costing. Manufacturing overhead is charged to individual jobs through the use of a predetermined overhead rate based on direct labor costs. The following information appears in the company's Work in Process Inventory account for the month of June: Debits to account: Balance, June 1 Direct materials Direct labor Manufacturing overhead (applied to jobs as 125% of direct labor cost) Total debits to account Credits to account: Transferred to Finished Goods Inventory account Balance, June 30 Required: $ 5,000 18,000 12,100 15,125 $ 50,225 44,000 $ 6,225 a. Assuming that the direct labor charged to the jobs still in process at June 30 amounts to $1,500, compute the amount of manufacturing overhead and the amount of direct materials that have been charged to these jobs as of June 30. b. Prepare general journal entries to summarize: 1. The manufacturing costs (direct materials, direct labor, and overhead) charged to production during June. 2. The transfer of…arrow_forward
- Ivanhoe Company begins operations on April 1. Information from job cost sheets shows the following: Manufacturing Costs Assigned Job Number April May June Month Completed 10 $6,700 $4,600 May 11 4,400 4,200 $3,200 June 12 1,400 April 13 4,900 3,500 June 14 5,600 3,600 Not complete Each job was sold for 25% above its cost in the month following completion. (a) Calculate the balance in Work in Process Inventory at the end of each month. Work in Process Inventory April 30 $enter a dollar amount May 31 $enter a dollar amount June 30 $enter a dollar amountarrow_forwardAssume it is the beginning of the month, using the estimates and a job-order costing system, what price would you recommend Lina quote for each of the above two jobs to ensure profitability in the long term? 2. Assume it is the end of the month, determine the amount of under- or over-applied overhead and recommend to Lina how the amount should be accounted for. 3. Prepare a schedule of cost of goods manufactured for the month - these were the only two jobs started and sold (zero beginning and ending work-in-process inventory). Assume that actual materials used and the labour rate/hours are the same as estimated. Hint: refer to Exhibit 5.11 on page 213 of text for suggested format.arrow_forwardLouisiana Metals uses a job costing system. The company applies manufacturing overhead using a predetermined rate based on direct labor cost. The following debits (credits) appeared in the Work-in-Process Inventory for June. June 1 For the month For the month For the month For the month Balance Direct labor Direct materials Manufacturing overhead To finished goods Beginning inventory ??? $ 33,000 43, 200 19,800 (78,700) Job LM-12, the only job still in production at the end of June, has been charged $13,200 in direct materials cost and $12,400 in direct labor cost. Required: What was the beginning balance in Work-in-Process Inventory?arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





