
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
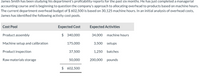
Transcribed Image Text:**Analysis of Overhead Costs by James Smith**
James Smith has been assessing the profitability reports of his department for the last six months. After completing a managerial accounting course, he is scrutinizing the company's method of allocating overhead to products based solely on machine hours. The department currently works with an overhead budget of $602,500, derived from 30,125 machine hours. In his preliminary analysis, James has identified distinct activity cost pools, as detailed below:
| **Cost Pool** | **Expected Cost** | **Expected Activities** |
|-------------------------------|-------------------|----------------------------|
| Product assembly | $340,000 | 34,000 machine hours |
| Machine setup and calibration | $175,000 | 3,500 setups |
| Product inspection | $37,500 | 1,250 batches |
| Raw materials storage | $50,000 | 200,000 pounds |
**Total**: **$602,500**
This table categorizes overhead costs into four primary areas and assigns expected costs and activities to each, offering a more nuanced view of how resources are utilized in production.
![**Overhead Rate Calculations**
(a) **Traditional Overhead Rate Calculation**
Calculate the company's traditional overhead rate based on machine hours.
- **Overhead rate:** $ [Input field] / MH
(b) **Activity-Based Costing Overhead Rates Calculation**
Calculate the company's overhead rates using the proposed activity-based costing pools. (Round answers to 2 decimal places, e.g., 15.25.)
- **Product assembly:** $ [Input field] / MH
- **Machine setup and calibration:** $ [Input field] / setup
- **Product inspection:** $ [Input field] / batch
- **Raw materials storage:** $ [Input field] / lb](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/8ad87420-52d2-4e34-815e-eb9bcb5c95c0/6c64ea92-d7ae-4a36-96ba-7537b6b342e1/qffgs6l_thumbnail.png)
Transcribed Image Text:**Overhead Rate Calculations**
(a) **Traditional Overhead Rate Calculation**
Calculate the company's traditional overhead rate based on machine hours.
- **Overhead rate:** $ [Input field] / MH
(b) **Activity-Based Costing Overhead Rates Calculation**
Calculate the company's overhead rates using the proposed activity-based costing pools. (Round answers to 2 decimal places, e.g., 15.25.)
- **Product assembly:** $ [Input field] / MH
- **Machine setup and calibration:** $ [Input field] / setup
- **Product inspection:** $ [Input field] / batch
- **Raw materials storage:** $ [Input field] / lb
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Which one is the correct answer?arrow_forwardThe management of Hartman Company is trying to determine the amount of each of two products to produce over the coming planning period. The following information concerns labor availability, labor utilization, and product profitability: Labor-Hours Required(hours/unit) Department Product 1 Product 2 Hours Available A 1.00 0.35 95 B 0.30 0.20 36 C 0.20 0.50 50 Profit contribution/unit $30.00 $15.00 (a) Develop a linear programming model of the Hartman Company problem. Solve the model to determine the optimal production quantities of products 1 and 2. If required, round your answer to two decimal places. Product 1 Product 2 Production (b) In computing the profit contribution per unit, management does not deduct labor costs because they are considered fixed for the upcoming planning period. However, suppose that overtime can be scheduled in some of the departments. Which departments would you recommend scheduling for…arrow_forwardSchoening Corporation is a shipping container refurbishment company that measures its output by the number of containers refurbished. The company has provided the following fixed and variable cost estimates that it uses for budgeting purposes and the actual results of operations for January. Revenue Employee salaries and wages Refurbishing materials Other expenses Fixed Element per Month $ 50,600 $41,200 Variable Element per Actual Total for Container January Refurbished $4,100 $ 1.100 $ 700 $ 158,600 $92,700 $ 27,000 $ 40,800 When the company prepared its planning budget at the beginning of January, it assumed that 40 containers would have been refurbished. However, 38 containers were actually refurbished during January. The activity variance for "Refurbishing materials" for January would have been closest to: $1,000 F $1,400 F $1,000 U $1,400 Uarrow_forward
- Joker Ltd manufactures two products, Normal and Plus. It has recently implemented an activity-based costing system for its manufacturing overhead costs, with the budgeted activity cost and budgeted quantity of activity driver as follows: Activity Budgeted Activity Cost Activity Driver Budgeted Quantity of Activity Driver Labour-related 205,000 Direct labour hours 41,000 Machine setups 227,000 Number of setups 5,000 General factory 340,000 Machine hours 34,000 772,000 The breakdown of the expected consumption of activities by the two products is as follows: Normal Plus Labour-related 25,000 16,000 Machine setups 2,000 3,000 General factory 20,000 14,000 For the next accounting period, the expected production volume of Normal is 4,500 units and Plus is 3,000 units. Required:Calculate the overhead cost per unit of a Plus.arrow_forwardMary Ellis owns a small manufacturing company and would like to develop more accurate estimates for overhead expenses when making planning decisions. She is pretty sure that overhead is a mixed cost that varies with direct labour-hours but she would like to do a proper analysis to determine the variable and fixed components. She collected the following information for the past 12 months on direct labour-hours incurred and total overhead expenses. Total Overhead Costs $44,000 Month January Direct Labour-Hours 1,500 February 1,680 $ 47,200 March 1,000 $ 48,000 April 2,520 $ 51,200. May 2,700 $ 53,600 June 3,300 $ 56,000 July 3,900 $ 59,200 August 4,500 $ 61,600 September 4,200 $ 60,000 October 2,700 $ 54,400 November 1,800 $49,600 December 3,900 $ 58,400 Required: 1. Using the least-squares regression method, estimate the variable overhead cost per direct labour-hour and the total fixed overhead cost per month. (Round Fixed cost to the nearest whole doller amount and the Variable cost…arrow_forwardA company has two products A and B. The budgeted fixed manufacturing overhead is $10,000. It is expected to work in full capacity. It plans to use cost-based pricing by using the absorption method. Assume the company can produce and sell 1,000 units Product A and 1,000 units Product B. Product A Product B Direct Labor $1 $3 Direct Materials $3 $2 Variable Manufacturing Overhead $2 $1 Budgeted labor hours used for each unit product 1 4 Budgeted machine hours used for each unit product 3 1 Sale Demand 1000units 1000units Required ROI Rate 10% 5% Required Investment $5000 $30000 Fixed Selling Expenses $2000 $4000 Unit Variable Selling Expenses $1 $2 If allocating fixed manufacturing overhead based on machine hour basis, calculate the sale price of products A and B and budgeted profit of products A and B.arrow_forward
- Activity-Based Costing Slack Corporation has the following predicted indirect costs and cost drivers for the year for the given activity cost pools: Maintenance Materials handling Machine setups Inspections Machine hours Material moves Machine setups Inspection hours Fabrication Department Finishing Department Cost Driver $50,000 30,000 70,000 $40,000 Machine hours 15,000 Material moves 5,000 Machine setups 25,000 Inspection hours $85,000 The following activity predictions were also made for the year. Fabrication Department Finishing Department Direct materials cost Direct labor cost Machine hours (Fabrication) Machine hours (Finishing) Materials moves Machine setups Inspection hours It is assumed that the cost per unit of activity for a given activity does not vary between departments. Slack's president, Charles Slack, is trying to evaluate the company's product mix strategy regardin two of its five product models, ZX300 and SL500. The company has been using a company-wide overhead…arrow_forwardPanamint Systems Corporation is estimating activity costs associated with producing disk drives, tapes drives, and wire drives. The indirect labor can be traced to four separate activity pools. The budgeted activity cost and activity base data by product are provided below. Procurement Scheduling Materials handling Product development Production Disk drives Tape drives Wire drives Activity Cost Activity Base $392,400 Number of purchase orders 233,100 Number of production orders 409,400 Number of moves 708,700 Number of engineering changes 1,526,300 Machine hours Number of Purchase Orders Number of Number Number of of Moves Engineering Changes 11 7 23 Production Orders 4,090 280 1,800 185 12,000 910 The activity-based cost for each disk drive unit is Oa. $793.58 Ob. $21.93 Oc. $235.34 Od. $191.6 1 1,410 740 4,500 Machine Hours 1,800 8,300 11,500 Number of Units 2,300 4,300 2,400arrow_forward10. Farm, Inc. currently applies overhead using direct labor hours and has an expected capacity of 50,000 direct labor hours. The company has recently identified the activities of maintenance and inspection as the major contributors of manufacturing overhead. The company expects $50,000 in maintenance costs and $75,000 in inspection costs. The following data have been assembled for use in developing a bid for a proposed job: Direct materials $500 Direct labor $2,000 Machine hours 500 Number of inspections 4 Direct labor hours 800 The total expected number of inspections is 1,500, and the total expected number of machine hours for all jobs during the year is 25,000. Using activity-based costing, and the appropriate activity drivers, the total cost of the potential job would be: a. $1,200 b. $4,500 c. $5,700 d. $3,700 e. $2,500 f. $5,000 g. $4,300 h. None of the abovearrow_forward
- Nonearrow_forwardMariposa, Inc., produces machine tools and currently uses a plantwide overhead rate, based on machine hours. Harry Whipple, the plant manager, has heard that departmental overhead rates can offer significantly better cost assignments than can a plantwide rate. Mariposa has the following data for its two departments for the coming year: Department A Department B Overhead costs (expected) $528,000 $132,000 Normal activity (machine hours) 110,000 55,000 Required: 1. Compute a predetermined overhead rate for the plant as a whole based on machine hours.$fill in the blank 1 per machine hour 2. Compute predetermined overhead rates for each department using machine hours. Round your answers to one decimal place. Department A $fill in the blank 2 per machine hour Department B $fill in the blank 3 per machine hour 3. Suppose that a machine tool (Product X75) used 60 machine hours from Department A and 140 machine hours from Department B. A second machine tool (Product Y15)…arrow_forwardalland Manufacturing Company makes two different products, M and N. The company's two departments are named after the products; for example, Product M is made in Department M. Yalland's accountant has identified the following annual costs associated with these two products: Financial data Salary of vice president of production division ................. $160,000 Salary of supervisor Department M .............................. 80,000 Salary Yalland Manufacturing Company makes two different products, M and N. The company's two departments are named after the products; for example, Product M is made in Department M. Yalland's accountant has identified the following annual costs associated with these two products:Financial dataSalary of vice president of production division ................. $160,000Salary of supervisor Department M .............................. 80,000Salary of supervisor Department N ................................. 60,000Direct materials cost Department M…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education