
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:ity College-CHM 101 (Section 90) - Spring20 - MARX > Activities and Due Dates > Ch 7 HW
O Assignment Score:
O Resources Ly Give Up?
50.1%
O Hint
Check Answer
< Question 16 of 28
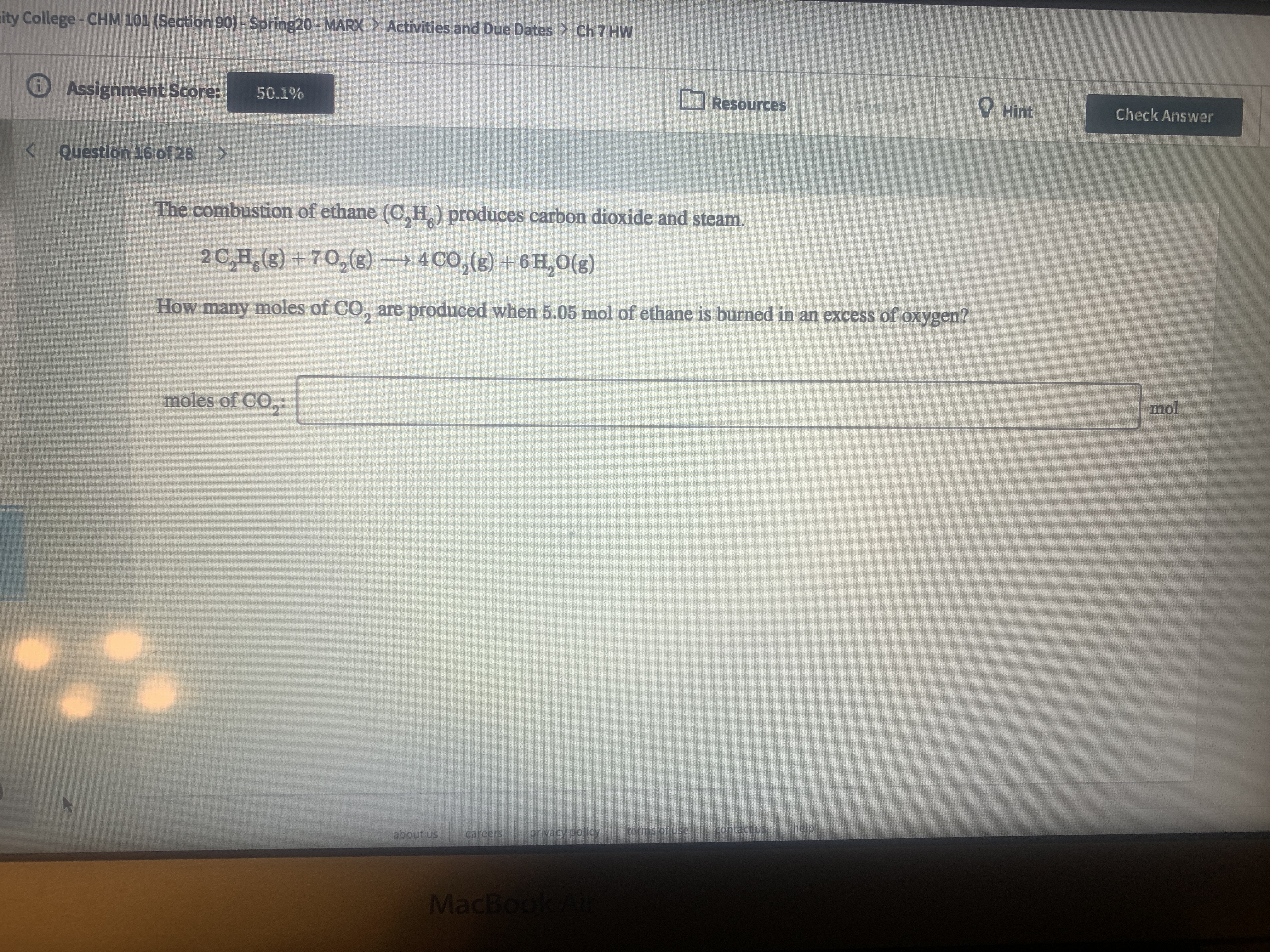
The combustion of ethane (C,H.) produces carbon dioxide and steam.
2 C,H,(s) +70,(g) → 4 CO,(g) + 6 H, O(g)
How many moles of CO, are produced when 5.05 mol of ethane is burned in an excess of oxygen?
moles of CO,:
mol
terms of use
contactus
help
about us
carecrs
privacy policy
MacBook A
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Answer 9 and 10arrow_forwardMail - Scheffel, Reagan - Outlook X ABP I X Submit C R : X x 100 + 11:47 PM 11/4/2022arrow_forward7. Determining the Sign of AH Indicate the sign of the enthalpy change, AH, in these processes carried out under atmospheric pressure and indicate whether each process is endothermic or exothermic: a. an ice cube melts b. 1 g of butane (C4H10) is combusted in sufficient oxygen to give complete combustion to CO2 and H2O.arrow_forward
- Here's a formula for the combustion of ethane: 2 C,H, (g) + 7 O, (g) → 6 H,O (g) + 4 CO2 (g) AH = -5318 kJ/mol a.) How many grams of ethane do I need to burn to generate 50,000 kJ of heat?arrow_forwardIgnition wires heat sample Thermometer Stirrer A bomb calorimeter, or a constant volume calorimeter, is a device often used to determine the heat of combustion of fuels and the energy content of foods. In an experiment, a 0.4059 g sample of 9,10-anthracenedione (C14H30,) is burned completely in a bomb calorimeter. The calorimeter is surounded by 1.116x10³ g of water. During the combustion the temperature increases from 22.76 to 25.09 °C. The heat capacity of water is 4.184 Jgl°c-!. Water The heat capacity of the calorimeter was determined in a previous experiment to be 965.5 J/°C. Assuming that no energy is lost to the surroundings, calculate the molar heat of combustion of 9,10-anthracenedione based on these data. C14HgO2(s) - 1502(g) 4 H20(1) + 14 CO,(g) - Energy Molar Heat of Combustion = kJ/mol Sample dish Burning sample Steel Insulated outside chamber bomb Combustion (bomb) calorimeter.arrow_forwardThe process of flambéing involves pouring liqueur on food for flavor. This addition to desserts adds tons of flavor, (C₂H5OH), which combusts in the presence of immense heat. You may have noticed this in restaurants, chemical equation for the combustion of ethanol as a reference in this assessment. C₂H₂OH (1) +30, (g) 2 CO₂ (g) + 3 H₂0 (g) Use the graph above to explain if the combustion of ethanol is exothermic or endothermicarrow_forward
- Write and balance the reaction for the complete combustion of heptane, C7H16. (Use the lowest possible whole number coefficients. Omit states-of-matter from your answer.)arrow_forwardnot sure what i did wrong says incorrect i need helparrow_forwardThe combustion of methane is CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O ΔH = -802 kJ/molHow much heat is produced when 2 moles of methane is burned?Select one:A. -802 kJ B. -2250 kJ C. -1604 kJ D. -401 kJarrow_forward
- The following table is the data a student recorded after completing the Hess' Law Lab (VCL 3-12). 200.0 ml of water was added the measured amount of solid NaOH in a calorimeter. Parameter Reaction 1 Mass NaOH (g) 4.575 25.00 Initial temperature (°C) 30.05 Final temperature (°C) Using all the steps and procedues of this lab, calculate the energy released (kJ/mol) of NaOH in Reaction 1.arrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardCan you help me solve #4?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY