
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
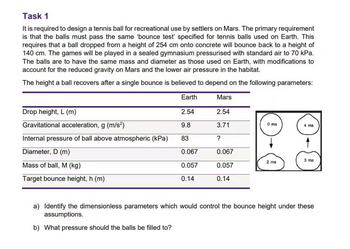
Transcribed Image Text:Task 1
It is required to design a tennis ball for recreational use by settlers on Mars. The primary requirement
is that the balls must pass the same 'bounce test' specified for tennis balls used on Earth. This
requires that a ball dropped from a height of 254 cm onto concrete will bounce back to a height of
140 cm. The games will be played in a sealed gymnasium pressurised with standard air to 70 kPa.
The balls are to have the same mass and diameter as those used on Earth, with modifications to
account for the reduced gravity on Mars and the lower air pressure in the habitat.
The height a ball recovers after a single bounce is believed to depend on the following parameters:
Earth
Drop height, L (m)
Gravitational acceleration, g (m/s²)
Internal pressure of ball above atmospheric (kPa)
Diameter, D (m)
Mass of ball, M (kg)
Target bounce height, h (m)
2.54
9.8
83
0.067
0.057
0.14
b) What pressure should the balls be filled to?
Mars
2.54
3.71
?
0.067
0.057
0.14
0 ms
2 ms
4 ms
3 ms
a) Identify the dimensionless parameters which would control the bounce height under these
assumptions.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 9 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A circular log floating in water is neutrally buoyant. Our ancestors found that by having half a log with semi-circular cross section and hollowing out the interior, it became stable so that they could use it to migrate across oceans. The reasons for it to become stable are: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) It lowers the centre of gravity G so that it is below the centre of buoyancy B. It lowers the centre of gravity G so that it is below the metacentre M. It increases the metacentric radius BM. It enables the shifting of the centre of buoyancy B laterally to produce a restoring moment when it is tilted. (A) (B) (C) (D) (i) and (ii) (ii) and (iii) (iii) and (iv) (iv) and (i)arrow_forwardA child takes a helium balloon on a plane from Denver (with an air pressure of 0.83 atm) on a cool day when the temperature is 20.0oC to Boston (at sea level, with an air pressure of 1.0 atm) where the temperature is 5.0oC. Assume that no gas escapes from the balloon during the flight. What is the volume of the balloon in Boston, relative to its size in Denver? Group of answer choices The volume in Boston is 0.79 times the volume in Denver. The volume in Boston is 0.20 times the volume in Denver. The volume in Boston is 0.87 times the volume in Denver The volume in Boston is 1.3 times the volume in Denver. The volume in Boston is the same as the volume in Denver.arrow_forwardq1barrow_forward
- 2. Calculate the mass of silver initially at 445 °C which would be needed to be dropped into a 435 mL sample of water initially at 23.0 °C in an insulated container to raise the temperature of the water to 33.5 °C. The specific heat capacity of water is 4.184 J K-¹ g¹ and the molar heat capacity of silver is 25.9 J K¹ mol¹¹. 2 Tot 21arrow_forwardQ22. An object is shot straight up from 7 m above ground level, and returns to the ground after 2.3 s. If the effects of the air are neglected, what is the highest position it has reached (as measured from the ground)? Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point, and proper SI unit. Take g = 9.81 m/s². Your Answer: Answer unitsarrow_forwardThermodynamics Question! Please and thank you for all your help! Please make sure the answer is valid and in the correct units!arrow_forward
- Q3. In the image shown below, according to the provided datum line, determine the gravitational potential energy of the 5.9-kg block. The radius r = 2.6 m and the angle 0 = 29°. Negative sign must be included if the energy is negative. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 1 place after the decimal point, and proper SI unit. Take g = 9.81 m/s². Your Answer: Answer Ө units Datumarrow_forwardA boxer delivers a hard blow to the chin of his opponent. The inertia of the boxer's hand (with glove) and forearm is 3.0 kg, and the inertia of the opponent's head is 6.5 kg. You learned in neurobiology class about 10 J of extra internal energy will render an opponent wobbly - kneed, and you guess that about half of the converted energy will end up in the opponent's head. Assuming a coefficient of restitution e = 0.20, with what speed does the boxer's fist have to contact the opponent's head in order to deliver the punch?arrow_forwardProblem Description You are stuck in an elevator with a meter stick, a spring with a spring constant of 30 N/m, and an object with a mass of exactly 0.5 kg. When you suspend the object from the end of the spring, you find that the spring stretches by 18 cm. Determine everything you can about the motion of the elevator from this information. Instructions In a neat and organized fashion, write out a solution which includes the following: 1. A sketch of the physical situation with all given physical quantities clearly labeled. 2. Represent the forces exerted on the object using a force diagram and, after you have made your determinations about the motion of the elevator, construct possible motion diagrams representing the motion of the elevator (if you think there is only one possible motion draw that, if you think there are several possible motions draw motion diagrams for each of them). 3. Determine everything you can about the motion of the elevator. Use your force diagram and…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY