
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Consider the following 3 pieces of the motion for a block that is initially at rest on a floor. (1) The block's velocity is zero at the instant it is given a quick push by a hand. (2) The hand does not touch the block after the quick push. The block slides across the floor, gradually slows down, then comes to rest. In (3), the block is at rest. The next series of questions will pertain to these cases.
In (3), after the block has stopped moving and is at rest, what is the direction of the block’s acceleration?
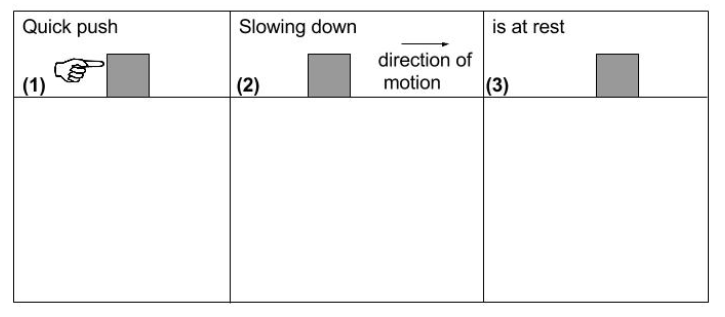
Transcribed Image Text:is at rest
Quick push
Slowing down
direction of
motion
|(3)
|(1)
(2)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A person catches a ball with a mass of 145 g dropped from a height of 60.0 m above his glove. His hand stops the ball in 0.0100 s. What is the force exerted by his glove on the ball? Assume the ball slows down with constant acceleration.arrow_forwardCalculusarrow_forwardWhich of the following statement/s is/are correct regarding the concepts of motion? According to Aristotle, a body that is stationary will continue to be stationary unless a force is applied to it. According to Aristotle, a falling body accelerates because its weight increases as it approaches Earth’s surface. According to Galileo, a body in motion along a frictionless surface does not need an external force to maintain its motion. According to Galileo, objects fall at the same rate even if one object is more massive than the other object. 1 and 2 3 and 4 1,3, and 4 1,2,3 and 4 Which of the following is a correct explanation to one of the consequences of Special Relativity? A. Time Dilation describes that twins would have different age difference if they both travel close to the speed of light. B. Mass-energy Equivalence paved the way for humans to create grenades to be used during wars and political conflicts. C. Relativity of Simultaneity implies that two events would not…arrow_forward
- The figure below shows two blocks connected to each other by a light cable that passes over a pulley with negligible friction. The block of mass m₁ = 3.10 kg lies on a horizontal table with negligible friction, while the block of mass m₂ = 10.4 kg hangs vertically. m₁ 2₁ = a₂ = (a) What is the magnitude of the acceleration of each block (in m/s²)? (Here, a, is the acceleration of m₂, and an is the acceleration of m₂.) m/s² m/s² Ⓡ (b) What is the tension in the cable (in N)?arrow_forwardA semi is traveling down the highway at a velocity of v = 39.5 m/s. The driver observes a wreck ahead, locks his brakes, and begins to slide. The truck has mass m and a coefficient of kinetic friction between the tires and the road of μk = 0.25. Write an expression for the sum of the forces in the x-direction for the truck while braking. Using the results from that input an expression for the trucks acceleration, ax, while braking. What is the magnitude of the acceleration in m/s^2, and how far does the truck travel, d in meters, before stopping?arrow_forwardThe diagram below represents a system consisting of two masses: mi=14 kg and m2=40kg, one of them on an incline and the other one hanging. The pulley is massless and frictionless and the cords joining the masses are ideal. The angle of the incline is 0=35°. The coefficient of kinematic friction is Hk=0.22 and we know the system starts to move from rest. a) Find the system's velocity (magnitude and direction) after moving 25 m along the incline. Solve the problem using the energy approach. m2 b) A cannon on top of a 100 meter tall cliff fires a projectile at 70 m/s at an angle of 25 degrees above the horizon. What is the range of the projectile?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON