
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
(c) Calculate the test statistic.
d) Decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis. Then interpret the decision in the context of the original claim.
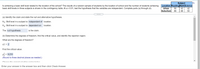
Transcribed Image Text:Subject
Location Reading Math Science
Is achieving a basic skill level related to the location of the school? The results of a random sample of students by the location of school and the number of students achieving
basic skill levels in three subjects is shown in the contingency table. At a = 0.01, test the hypothesis that the variables are independent. Complete parts (a) through (d).
Urban
50
43
42
Suburban
66
68
50
(a) Identify the claim and state the null and alternative hypotheses.
Họ: Skill level in a subject is independent of location.
Ha: Skill level in a subject is dependent on
location.
The null hypothesis
is the claim.
(b) Determine the degrees of freedom, find the critical value, and identify the rejection region.
What are the degrees of freedom?
d.f. = 2
Find the critical value.
x3
= 9.210
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
Chonn tha arrent roinntion rosion holow.
Enter your answer in the answer box and then click Check Answer.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Guilty or Innocent? In the U.S. court system, a defendant is assumed innocent until proven guilty. Suppose that you regard a court trial as a hypothesis test with null and alternative hypotheses H0: Defendant is innocentHa: Defendant is guilty. a. Explain the meaning of a Type I error.b. Explain the meaning of a Type II error.c. If you were the defendant, would you want a to be large or small? Explain your answer.If you were the prosecuting attorney, would you want ß to be large or small? Explain your answer.e. What are the consequences to the court system if you make a = 0? ß = 0?arrow_forwardThe data below were collected to test the effectiveness of a drug to lower systolic blood pressure. Blood pressure (in mm of mercury) was measured before and after treatment for 12 patients; the results are shown. The company claims the drug is effective. Explore this claim through completing the given questions. Assume the population differences is approximately normal and that all conditions for testing are satisfied. Subject A |E F H J G K L Before 200 174 198 170 179 182 193 209 185 155 169 210 After 191 170 177 167 159 151 176 183 159 145 146 177 Before - 9 After 4 21 3 20 31 17 26 26 10 23 33 Blank #1: The individual differences are given because these samples are Fill in the missing parts of the test to show it in its entirety: To explore whether the drug is effective, conduct a significance test using the hypotheses (do before - after as the direction of subtraction) Ho : Hdifference = 0 Ho : Hdifference Blank #2: Determine the correct alternative hypothesis by filling in the…arrow_forwardWhat are the null and alternative hypotheses? A. H0: The two variables, x and y, are associated. Ha: The two variables, x and y, are not associated. B. H0: The variable x is dependent upon y. Ha: The variable y is dependent upon x. C. H0: The two variables, x and y, are not associated. Ha: The two variables, x and y, are associated. The P-value is (Round to three decimal places as needed.) What is the conclusion of the independence test? A. Do not reject H0. The data provide sufficient evidence of an association. B. Reject H0. The data provide sufficient evidence of an association. C. Do not reject H0. The data do not provide sufficient evidence of an association. D. Reject H0. The data do not provide sufficient evidence of an association.arrow_forward
- A hypothesis test is conducted in order to determine the average weight of a Kit Kat bar.using the following null and alternative hypotheses: H0: The average weight of a Kit Kat bar is 1.5 ounces. HA: The average weight of a Kit Kat bar is greater than 1.5 ounces. Using complete sentences, explain what both a Type 1 and Type 2 error would be in context of this hypothesis test.arrow_forward(c) Calculate the test statistic. d) Decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis. Then interpret the decision in the context of the original claim.arrow_forwardWhen conducting a hypothesis test, we hope to avoid commiting a type 1 error, which is: 1. Not as bad as committing a type 2 error 2. rejecting a null hypothesis when it is true 3. rejecting the alternate hypothesis when it is true 4. accepting the null hypothesis when the alternate hypothesis is truearrow_forward
- A researcher wants to test whether there is a difference in test scores between two groups. Which hypothesis should be the null hypothesis? a. There is a difference in test scores between the two groups. Ob. There is no difference in test scores between the two groups. Oc. The test scores of the two groups are positively related. Od. The test scores of the two groups are negatively related.arrow_forwardWhat calculator button would be used to perform a hypothesis test if the null and alternative hypothesis are as follows: Ho: P₁ = P2 H₁ P₁ P2 Select one: O a. Z-Test... O b. 2-SampZTest... O c. T-Test... O d. 2-SampTTest O e. 2-PropZTest...arrow_forward(d) Decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis. O A. Fail to reject H, because the test statistic is in the rejection region(s). O B. Reject H, because the test statistic is not in the rejection region(s). O C. Fail to reject Ho because the test statistic is not in the rejection region(s). D. Reject Ho because the test statistic is in the rejection region(s). (e) Interpret the decision in the context of the original claim. A. At the 5% level of significance, there is sufficient evidence to reject the claim that the mean price is $24,000. B. At the 5% level of significance, there is not sufficient evidence to reject the claim that the mean price is $24,000. C. At the 5% level of significance, there is sufficient evidence to reject the claim that the mean price is not $24,000. O D. At the 5% level of significance, there is not sufficient evidence to reject the claim that the mean price is not $24,000.arrow_forward
- Suppose that you want to perform a hypothesis test for a population mean, μ. a. Express the null hypothesis both in words and in symbolic form. b. Express each of the three possible alternative hypotheses in words and in symbolic form.arrow_forwardWhen using the 4 step hypothesis testing method, the alternative hypothesis __________? a. is symbolized by: H1 b. is symbolized by: H0 c. states that the two population means are equal d. must be directional in nature (must be a one tailed test)arrow_forwardFor the given hypothesis test, explain the meaning of the kind of error, as requested. A statistics student has heard that about 25% of the students on his campus attend sporting events weekly. He wants to know if statistics students attend events in the same proportions as the general student body. Explain what the second type of error would be in this case (where the student fails to reject a null hypothesis that is actually false). O A. The second kind of error would be saying that statistics students attend sporting events in much higher proportions than the student body as a whole, even though they actually have the same attendence proportion. B. The second kind of error would be saying that there is no difference in the attendence of statistics students and the student body as a whole at sporting events, even though there really is. O C. The second kind of error would be saying that there is no difference in the attendence of statistics students and the student body as a whole at…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman