
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
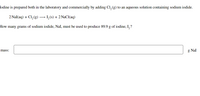
Transcribed Image Text:Iodine is prepared both in the laboratory and commercially by adding Cl, (g) to an aqueous solution containing sodium iodide.
2 Nal(aq) + Cl,(g)
I,(s) + 2 NaCI(aq)
How many grams of sodium iodide, Nal, must be used to produce 89.9 g of iodine, I,?
mass:
g Nal
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1

Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The balanced chemical equation is P₄(s) + 6 Cl₂(g) → 4 PCl₃(g). What is the mass in grams of phosphorus trichloride that can be formed from 226.0 grams of chlorine gas based on the balanced chemical equation?arrow_forwardThe question is in the picture. (There's only one answer)arrow_forwardGiven the following reaction and the amounts of the reactants, determine the mass (in grams) of hydrogen that can be produced: 2 Al (s) + 6 HCI (aq) --> 2 AICI3 (aq) + 3 H2 (g) 5.34 mols of aluminum 1.52 mols of hydrochloric acidarrow_forward
- 11)arrow_forwardOne way the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) tests for chloride contaminants in water is by titrating a sample of silver nitrate solution. Any chloride anions in solution will combine with the silver cations to produce bright white silver chloride precipitate. Suppose an EPA chemist tests a 200. mL sample of groundwater known to be contaminated with copper(II) chloride, which would react with silver nitrate solution like this: CuCl2(aq) + 2 AgNO3(aq) → 2 AgCl(s) + Cu(NO3)2(aq) The chemist adds 75.0 mM silver nitrate solution to the sample until silver chloride stops forming. He then washes, dries, and weighs the precipitate. He finds he has collected 6.3 mg of silver chloride. Calculate the concentration of copper(II) chloride contaminant in the original groundwater sample. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. mg Larrow_forwardWhat mass of precipitate (in g) is formed when 45.5 mL of 0.300 M Na₃PO₄ reacts with 64.0 mL of 0.200 M Cr(NO₃)₃ in the following chemical reaction? Na₃PO₄(aq) + Cr(NO₃)₃(aq) → CrPO₄(s) + 3 NaNO₃(aq)arrow_forward
- Chlorine can be prepared in the laboratory by the reaction of manganese dioxide with hydrochloric acid, HCI(aq), as described by the chemical equation MnO,(s) + 4 HCI(aq) → MnCl, (aq) + 2 H,O(1) + Cl, (g) How much Mn0,(s) should be added to excess HCI(aq) to obtain 125 mL Cl, (g) at 25 °C and 705 Torr? mass of MnO,: Question Source: McQuarrie, Rock, And Gallogly 4e- General Chemsitry Publisher: University Sciencarrow_forwardOne way the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) tests for chloride contaminants in water is by titrating a sample of silver nitrate solution. Any chloride anions in solution will combine with the silver cations to produce bright white silver chloride precipitate. Suppose an EPA chemist tests a 250.mL sample of groundwater known to be contaminated with iron(III) chloride, which would react with silver nitrate solution like this: FeCl3 (aq) + 3AgNO3 (aq) → 3AgCl (s) + FeNO33 (aq)The chemist adds 86.0m M silver nitrate solution to the sample until silver chloride stops forming. He then washes, dries, and weighs the precipitate. He finds he has collected 7.5mg of silver chloride. Calculate the concentration of iron(III) chloride contaminant in the original groundwater sample. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits.arrow_forwardLead ions can be precipitated from solution with KCl according to the following reaction: Pb2+(aq)+2KCl(aq)→PbCl2(s)+2K+(aq) When 28.6 g KCl is added to a solution containing 25.5 gPb2+, a PbCl2 precipitate forms. The precipitate is filtered and dried and found to have a mass of 29.0 g . Determine the limiting reactant.arrow_forward
- One way the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) tests for chloride contaminants in water is by titrating a sample of silver nitrate solution. Any chloride anions in solution will combine with the silver cations to produce bright white silver chloride precipitate.Suppose an EPA chemist tests a 250.mL sample of groundwater known to be contaminated with cadmium chloride, which would react with silver nitrate solution like this: CdCl2(aq)+2AgNO3(aq)→2AgCl(s)+CdNO32(aq). The chemist adds 51.0mM silver nitrate solution to the sample until silver chloride stops forming. She then washes, dries, and weighs the precipitate. She finds she has collected 8.9mg of silver chloride. Calculate the concentration of cadmium chloride contaminant in the original groundwater sample. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits.arrow_forwardIodine is prepared both in the laboratory and commercially by adding Cl, (g) to an aqueous solution containing sodium iodide. 2 Nal(aq) + Cl, (g) - L(s) + 2 NaCl(aq) How many grams of sodium iodide, Nal, must be used to produce 89.4 g of iodine, I,? mass: g Nal Enter numeric valuearrow_forwardOne way the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) tests for chloride contaminants in water is by titrating a sample of silver nitrate solution. Any chloride anions in solution will combine with the silver cations to produce bright white silver chloride precipitate. Suppose an EPA chemist tests a 200.mL sample of groundwater known to be contaminated with iron(III) chloride, which would react with silver nitrate solution like this: FeCl3 (aq) + 3AgNO3 (aq) →3AgCl (s) + (FeNO3)3 (aq) The chemist adds 48.0mM silver nitrate solution to the sample until silver chloride stops forming. She then washes, dries, and weighs the precipitate. She finds she has collected 7.5mg of silver chloride. Calculate the concentration of iron(III) chloride contaminant in the original groundwater sample. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY