
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
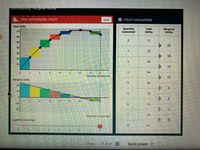
Transcribed Image Text:DmISIIng Margifal Otmty
n. TOTAL AND MARGINAL UTILITY
Reset
E UTILITY CALCULATIONS
Total Utility
Quantity
Consumed
Total
Marginal
Utility
70
Utility
60
50
22
40
1
22
30
18
20
40
10
14
2
3
4
54
Quantity Consumed
10
Marginal Utility
4
64
20
6.
10
70
3.
6.
-10
6.
72
-20
-2
7
70
Quantity Consumed
Quantity Consumed
-6
8.
64
8
Prev
1 of 3
Score answer >
...
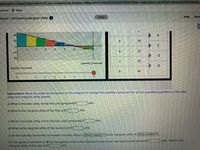
Transcribed Image Text:nheducation.com/ext/map/index.html?_con%3Dcon&external_browser3D0&launchUrl=https%253A%252F%252Flearn.wallacestate.edu%252Fwebapps%252Fblackbo.
YouTube
O Maps
Saved
Help
Save
Graphs - Diminishing Marginal Utility 6
20
6.
10
70
5.
6.
72
-10
-2
-20
7
70
Quantity Consumed
-6
Quantity Consumed
8
64
0.
1
6.
Instructions: Move the slider at the bottom of the diagram to change the quantity consumed for all the available quantities on the total
utility and marginal utility graphs.
a) What is the total utility of the first unit consumed?
utils.
b) What is the marginal utility of the first unit? utils.
c) What is the total utility of the first two units consumed?
utils.
d) What is the marginal utility of the second unit?
utils.
e) As the quantity consumed increases, the total utility is (Click to select) v while marginal utility is (Click to select) ♥
f) If this good is available for $0 (a free good), what is the maximum amount an individual would consume?
marginal utility of this last unit?
units. What is the
utils.
6,
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- . TOTAL AND MARGINAL UTILITY E UTILITY CALCULATIONS Reset Total Utility Quantity Consumed Total Marginal Utility 70 Utility 60 50 22 40 1 22 30 18 20 2 40 10 14 3 4 6 8 3 54 Quantity Consumed Marginal Utility 10 20 4 64 6. 10 70 4 6. -10 72 -20 -2 Quantity Consumed 70 Quantity Consumed -6 8 64 2. 4 6 8arrow_forwardSuppose you go to Trader Joe's to buy fruit for the week. You only like apples (A) and bananas (B) and your weekly fruit budget is $11. When you arrive at Trader Joe's you notice that the price of an apple is $1.00 and the price of a banana is $0.25. QUESTION #1: How many apples and bananas should you buy? QUESTION #2: When you have found the answer, draw a diagram that shows the outcome. Step #1. Determine your preferences. Let's suppose that your preferences can be represented by the following utility function: U(A, B) = AªBß = A0.40 B0.60 FYI: This utility function is known as a Cobb-Douglas utility function. It is the most commonly used function used in economics! The reason we like it so much is that it has: 1. Constant returns (double your consumption of A and B and your utility doubles); a + B = 1 2. Diminishing marginal utility (the extra utility gained from consuming A (or B) decreases as you consume more of the A good (or B good); a 0.40); B > a. Step #2: Determine your…arrow_forwardInfo in imagesarrow_forward
- CS 11 Economicsarrow_forward36arrow_forwardSuppose that with a budget of $210, Fatima spends $126 on sushi and $84 on bagels when sushi costs $2 per piece and bagels cost $2 per bagel. Then, after the price of bagels falls to $1 per bagel. Instructions: Enter your answers as a whole number. How many pieces of sushi and how many bagels did Fatima consume before the price change? pieces of sushi and bagels At the new prices, how much money would it have cost Fatima to buy those same quantities (that is, the quantities that she consumed before the price change)? Given that it used to take Fatima's entire $210 to buy those quantities, how big is the income effect caused by the lower price of bagels?arrow_forward
- Refer to the following table. Suppose strawberries cost $1 and apples cost $2. SHow all the formulas used and your calculations. What is marginal utility (MU) of the 3rd apple? What is marginal utility (MU) of 6th strawberry? What is the marginal utility per dollar spent on the 3th apple? What is the marginal utility per dollar spent on the 6th strawberry? Which of the combinations of strawberries and apples satisfies the following rule? How do you know?arrow_forward6arrow_forwardThe following table reflects the utility one receives from consuming a given product. Units Consumed Total Utility (TU) Marginal Utility (MU) 0 0 ------- 1 60 60 2 ____ 50 3 150 ____ 4 175 ____ 5 ____ 20 6 210 ____ Complete the table solving for the missing total utility or marginal utility values in each row. Total utility increases throughout the table. What rate does total utility increase? In other words, is it rising at an increasing rate, a…arrow_forward
- Only typed answer and please don't use chat gpt and don't use tablearrow_forwards) Using the indifference curves, a budget line and a price change, show how we can derive an individual's demand curve for a product..arrow_forwardECON Questions 5, 6, 7, and 8 How to solve and answer these economics questions showed in the screenshot?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education