
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
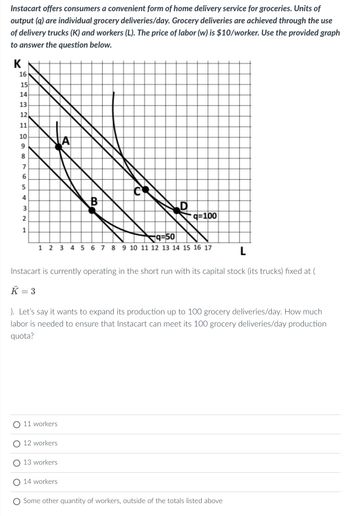
Transcribed Image Text:Instacart offers consumers a convenient form of home delivery service for groceries. Units of
output (q) are individual grocery deliveries/day. Grocery deliveries are achieved through the use
of delivery trucks (K) and workers (L). The price of labor (w) is $10/worker. Use the provided graph
to answer the question below.
K
16
15
14
13
21
12
11
10
9
32 DS18
7
6
5
4
2
1
11 workers
A
q=50
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
12 workers
B
L
Instacart is currently operating in the short run with its capital stock (its trucks) fixed at (
K = 3
13 workers
C
). Let's say it wants to expand its production up to 100 grocery deliveries/day. How much
labor is needed to ensure that Instacart can meet its 100 grocery deliveries/day production
quota?
14 workers
q=100
Some other quantity of workers, outside of the totals listed above
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The fast food company Schnabb uses labor and capital to produce its product. Holding the production fixed, what is the effect of a lower price of capital on the ratio between the number of workers and the amount of capital used? Explain using isocosts and an isoquant.arrow_forwardFor a decrease in the price of capital (K), construct a table AND explain the scale and substitution effects for a producer.arrow_forwardA baker uses labor (L) and raw materials (M) to produce mini Muhlenberg Mule sugar figurines (q). The process is fairly simple as workers only must make the sugar mixture and pour the mixture into the mule molds. The baker’s production function is as follows f(L, M) = L 0.50M. Let wL and wM denote the prices of a unit of L and M, respectively. (a) Write the firm’s cost minimization problem if it wants to produce q units of output. (b) Write the Lagrangian function that describes the cost minimization problem. (c) Derive the long run conditional factor input demands for L and M as a function of wL, wM, and q; L ∗ (wL, wM, q) and M∗ (wL, wM, q). (d) Suppose wL = $25 and wM = $2. Determine the cost-minimizing combination of inputs if the baker wants to produce 200 mules. (e) Using wL = $25 and wM = $2 and the demand functions from part (c), write the firm’s long run cost function CLR(q).arrow_forward
- Suppose that Maria is starting a food ordering and delivery company. Customers order meals online. Employees prepare the meals and deliver them to customers. Maintenance of the online platform for ordering meals costs the company $5 per day. The company also rents space where orders are prepared. Rent costs $50 per day. To make the deliveries, the business also rents two delivery cars that cost $10 each per day. The costs of ingredients for preparing different numbers of meals are provided in the table below. Maria also has to hire between 0 and 10 workers (depending on the number of meals she chooses to make) to buy ingredients, prepare meals, and deliver the orders. She will pay each employee $120 per day. The first two columns of the table below show how many meals different number of workers can prepare and deliver. Price per meal $50 Workers (Labor L) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Meals (Output Q) ol- 30 42 52 60 67 73 79 85 90 95 MPL FC Cost of ingredients $10 $75 $100 $121 $138 $152…arrow_forwardB. Suppose that your production process is characterized by the production function x = f(e) = 100 In ( + 1). For purposes of this problem, assume w > 1 and p > 0.01. a. Set up your profit-maximization problem. b. Derive the labor demand function. C. The labor demand curve is the inverse of the labor demand function with p held fixed. Can you demonstrate what happens to this labor demand curve when p changes? d. Derive the output supply function. e. The supply curve is the inverse of the supply function with w held fixed. What happens to this supply curve as w changes? (Hint: Recall that In x = y implies e' = x, where e ≈ 2.7183 is the base of the natural log.) f. Suppose p = 2 and w profit will you make? = 10. What is your profit-maximizing production plan, and how mucharrow_forwardThe table below describes the hourly cost Sam faces as he washes more cars. Sam's Car Wash Costs Cars Washed per Hour Total Cost (dollars) Marginal Cost (dollars) 1 $2 $2 2 4 3 12 4 8 5 10 6 42 Instructions: Enter your answers as a whole number. Complete the missing values in the table.arrow_forward
- The short run is a time period that is A) long enough to change the size of the firm's plant. B) too short to change the size of the firm's plant. C) too short to change the amount of ANY resource the firm employs. D) too short to change the amount of labor hired.arrow_forwardTim is a baker who produces doughnuts. He can access labour at a rate of $2 per hour, and capital at a rate of $0.25 per machine hour. He produces doughnuts according to Q = L+ K0.5. If the bakery is operating with an optimal factor allocation, and producing 40 doughnuts per day, determine the average total cost of a doughnut. The bakery employs one worker, Anil, who consumes doughnuts (d) and other goods (y) with utility U(d,y) = edy. (Assume y is the Marshallian good, with Py=$1). %3D Sketch Anil's utility curve, and his budget, which is the pay he receives from his job. Do Anil's preferences satisfy the rules of preference ordering? Are there any constraints on his consumption of either good? Derive the supply and demand curves based on Anil's individual demand, and Tim's costs of production.arrow_forwardKnown function is the production of a commodityQ = 40X + 12X2 - 1.2X3a. Calculate how many units of input X in order to achieve maximum total productb. Calculate how many units of input X in order to achieve maximum marginal productc. Calculate how many units of input X in order to achieve maximum average productarrow_forward
- If you increase the total amount of labor, the labor constraints curve becomes flatter. true or falsearrow_forwardMaria's Umbrellas has a production function given by Q = L0.5K0.5. The wage (W) is $80 per day and the rental per unit of capital (R) is $5 per day. In the long run, how many units of capital will Maria want to buy for each unit of labor?arrow_forwardEach of the following examples reflect some labour cost faced by an employer. Select all of those which are considered quasi-fixed labour costs. Select one or more: a. Harpreet spent $1,000 advertising a recent job opening b. Denise pays her entry-level employees an hourly wage of $20 c. John recently laid off five workers and gave them each $20,000 in severance pay d. Ahmed's sales employees earn an average annual commission of $50,000 e. Amanda spends $5,000 per year on supplemental health insurance for each of her employeesarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education