
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
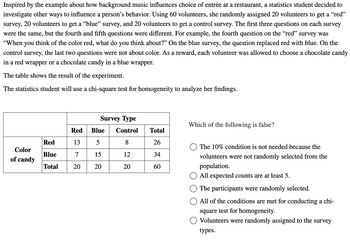
Transcribed Image Text:Inspired by the example about how background music influences choice of entrée at a restaurant, a statistics student decided to
investigate other ways to influence a person's behavior. Using 60 volunteers, she randomly assigned 20 volunteers to get a "red"
survey, 20 volunteers to get a “blue” survey, and 20 volunteers to get a control survey. The first three questions on each survey
were the same, but the fourth and fifth questions were different. For example, the fourth question on the "red" survey was
"When you think of the color red, what do you think about?" On the blue survey, the question replaced red with blue. On the
control survey, the last two questions were not about color. As a reward, each volunteer was allowed to choose a chocolate candy
in a red wrapper or a chocolate candy in a blue wrapper.
The table shows the result of the experiment.
The statistics student will use a chi-square test for homogeneity to analyze her findings.
Color
of candy
Red
Red
13
Blue
7
Total 20
Survey Type
Control
8
12
20
Blue
5
15
20
Total
26
34
60
Which of the following is false?
The 10% condition is not needed because the
volunteers were not randomly selected from the
population.
All expected counts are at least 5.
The participants were randomly selected.
All of the conditions are met for conducting a chi-
square test for homogeneity.
Volunteers were randomly assigned to the survey
types.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- please answer a, b, carrow_forwardHow often do you go out dancing? This question was asked by a professional survey group on behalf of the National Arts Survey. A random sample of 95 single men showed that 24% went out dancing occasionally. Another random sample of 92 single women showed that 21% went out dancing occasionally. Is the proportion of single men who go out dancing occasionally higher than the proportion of single women? Use a 5% level of significance. If men are group 1 and women are group 2, what is the p-value for this hypothesis test? 0.656 0.688 0.344 0.217 0.242arrow_forwardCreate a Study For this discussion, you will come up with an example of a situation in which two means would need to be compared, and describe which test would be the most appropriate. Develop a main response in which you address the following: Describe a possible study that could be conducted to compare two groups means. What would the main topic be? What groups would be compared? What data would be collected? Identify the test that would be the best choice to compare the group means. Explain why this test is the most appropriate for your example.arrow_forward
- A small university was looking to recruit students for their golf program during Freshman orientation. Each organization would be allotted 10 minutes to give a small presentation about their program. The golf coach wants to discuss the programs golf over the past five years during his presentation. To do this, he plans to take samples of the scores from both practice rounds and games. He has recruited students from Statistics class to help him determine which statistic would be best to use to display the scores. The students have narrowed it down to four different statistics. For each statistic, the coach has taken 100 random samples of golf scores over the past five years and the statistic is calculated for each sample. Suppose the value for the population parameter he is trying to estimate is a score of 75. ALL GRAPHS ARE IN THE ATTACHED PICTURE!! THANK YOU!! a) For each graph above, identify whether the statistic appears to have a biased or unbiased estimator of the population…arrow_forwardIf your height is at 58th percentile in your age group, which of the following statement is TRUE ? Group of answer choices There are 58% people whose heights are the same. There are other 42% people whose height are at or below your height. Your height is 5 feet and 8 inches. There are other 58% people with height at or above your height. There are other 42% people with height at or above your height.arrow_forwardImportant: This question continues from the previous two questions and onto the following two questions. A Rasmussen Reports national survey of 1000 random adult Americans found that 6% felt that Saint Patrick's Day was one of our nation's most important holidays. From the previous question, input the calculated number of successes and number of failures. Show your work on your scratch paper. The number of successes is The number of failures is .Write your answer as a whole number. . Write your answer as a whole number.arrow_forward
- In a statistics activity, students are asked to spin a penny and a dime and determine the proportion of times that each lands with tails up. The students believe that since a dime is lighter, it will have a lower proportion of times landing tails up compared with the penny. The students are instructed to spin the penny and the dime 30 times and record the number of times each lands tails up. For one student, the penny lands tails side up 18 times, and the dime lands tails side up 20 times. Let pp = the true proportion of times a dime will land tails up and pp = the true proportion of times a penny will land tails up. The P-value for this significance test is 0.296. Which of the following is the correct conclusion for this test of the hypotheses H Pp-Pp=0 and H, Po-Pp 0.05. There is sufficient evidence that the true proportion of times a dime will land tails up is significantly less than the penny. O The student should reject the null hypothesis since 0.296 > 0.05. There is insufficient…arrow_forwardIndiana has a population of about 7 million people and Ohio about 12 million. Is it possible for there to be a poll where over 50% of Hoosiers say "yes", over 50% of Ohioans say "yes", but over 50% of all residents of both states say "no"? If no, explain why not. If yes, give an example of how that could happen.arrow_forwardA survey asked participants if they liked vanilla ice cream, chocolate ice cream, both, or neither. Of those surveyed, 44% liked vanilla, 68% liked chocolate, and 19% liked neither. What percentage of the students liked both vanilla and chocolate? (1) 17% (3) 27% (2) 22% (4) 31%arrow_forward
- A statistics instructor would like to know whether it is worthwhile to require students to do weekly homework assignments. For one section of the statistics course, homework is assigned, collected and graded each week. For another section, the same problems are suggested each week, but the students are not required to turn in their homework. At the end of the semester, all students take the same final exam. The score distribution for the two sections are as follows: With Homework 12 15 17 5 10 No Homework 12 21 28 25 14 Do these data indicate a significant difference between the score distributions for students with homework versus students with no homework? Test at the 5% level of significance.arrow_forwardInspired by the example about how background music influences choice of entrée at a restaurant, a statistics student decided to investigate other ways to influence a person's behavior. Using 60 volunteers, she randomly assigned 20 volunteers to get a "red" survey, 20 volunteers to get a "blue" survey, and 20 volunteers to get a control survey. The first three questions on each survey were the same, but the fourth and fifth questions were different. For example, the fourth question on the "red" survey was "When you think of the color red, what do you think about?" On the blue survey, the question replaced red with blue. On the control survey, the last two questions were not about color. As a reward, each volunteer was allowed to choose a chocolate candy in a red wrapper or a chocolate candy in a blue wrapper. The table shows the result of the experiment. We want to test Ho: The distribution of candy choice is the same for subjects like these who receive the red survey, the blue survey,…arrow_forwardA recent report On the evening news stated that things watched an average of 13 hours of TV per week. A teacher that I'm skeptical high school believe that the student in her school actually watch more than 13 hours per week. She randomly selected 25 students from our school and direct him to record the TV watching for one week in a diary. The students record of the following data: 5,5,6,18,23,13,0,28,20,5,23,11,0,25,22,13,24,6,14,20,23,20,11,22,11. Is there enough evidence to support teacher claim ? Quesitons : what is the null hypothesis (Ho) and what is the alternative hypothesis (Ha)? What is the test statistics ? Wrote formula and value 3 times decimal place What is the p value ? what's the conclusion based on the result ?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman