
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
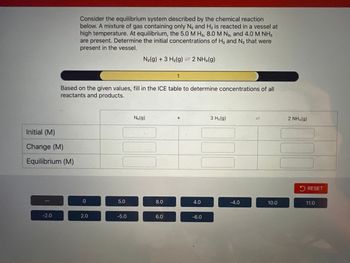
Transcribed Image Text:Initial (M)
Change (M)
Equilibrium (M)
-2.0
Consider the equilibrium system described by the chemical reaction
below. A mixture of gas containing only N₂ and H₂ is reacted in a vessel at
high temperature. At equilibrium, the 5.0 M H2, 8.0 M N₂, and 4.0 M NH3
are present. Determine the initial concentrations of H₂ and N₂ that were
present in the vessel.
Based on the given values, fill in the ICE table to determine concentrations of all
reactants and products.
0
2.0
5.0
N₂(g) + 3 H₂(g) = 2 NH3(g)
-5.0
N₂(g)
Ssivestit
8.0
1
6.0
+
4.0
-6.0
3 H₂(g)
ઇસ્કો અને કોની
-4.0
10
10.0
2 NH3(g)
RESET
11.0
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Given data is
Molarity of N2 at equilibrium= 8 M
Molarity of H2 at equilibrium= 5 M
Molarity of NH3 at equilibrium = 4M
N2(g) + 3H2(g) <===> 2NH3(g)
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- An equilibrium mixture contains 0.500 mol of each of the products (carbon dioxide and hydrogen gas) and 0.200 mol of each of the reactants (carbon monoxide and water vapor) in a 1.00 L container. CO(g) + H₂O(g) CO₂(g) + H₂(g) How many moles of carbon dioxide would have to be added at constant temperature and volume to increase the amount of carbon monoxide to 0.300 mol once equilibrium has been reestablished? moles of CO₂: 0.054 Incorrect molarrow_forwardConsider the following equilibrium system: N2O4(g) + ?????? ↔ 2NO2(g). How will the equilibrium shift if the following disturbances occur? Draw the diagram to show the initial change and final state when new equilibrium's re-established. a) increase in container volumeb) addition of Argon gas and increase in temperaturearrow_forwardDefine chemical equilibrium. Must amounts of reactants and products be equal at the equilibrium?arrow_forward
- Consider the following equilibrium system: PCI5(9) PC13 (9) + Cl₂(g) A 10.00 L evacuated flask filled with 0.4163 mol PCI5 (9) at 297.5 K. The temperature is then raised to 503.5 K, where the decomposition of PCIs gas takes place to an appreciable extent. When equilibrium is established, the total pressure in the flask atm. What is the value of the equilbrium constant in terms of concentrations, Ko at 503.5 K? Kc =arrow_forwardA mixture of water and graphite is heated to 600 K. When the system comes to equilibrium it contains 0.13 mol of H2, 0.13 mol of CO, 0.43 mol of H2O, and some graphite. Some O2 is added to the system and a spark is applied so that the H2 reacts completely with the O2. Find the amount of CO in the flask when the system returns to equilibrium.arrow_forwardThe equilibrium constant, K, for the following reaction is 3.78E-2 at 530 K. PCI5(9) PCI3(g) + Cl₂(g) An equilibrium mixture of the three gases in a 9.30 L container at 530 K contains 0.252 M PCI5, 9.77E-2 M PCI3 and 9.77E-2 M Cl₂- What will be the concentrations of the three gases once equilibrium has been reestablished, if the volume of the container is increased to 16.6 L? [PC15] = [PC13] = [Cl₂] = M M M CHECK ANSWERarrow_forward
- Calculating an equilibrium constant from a heterogeneous equilibrium... Iron and water react to form iron(III) oxide and hydrogen, like this: 2 Fe(s)+3 H₂O(g) →Fe2O3(s)+3 H2(g) At a certain temperature, a chemist finds that a 2.5 L reaction vessel containing a mixture of iron, water, iron(III) oxide, and hydrogen at equilibrium has the following composition: compound amount Fe 2.86 g Н20 2.70 g Fe2O3 2.61 g H₂ 2.34 g Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant K for this reaction. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. K = 1 C ☐ x10 ☑ 5 ? 18 Ar New Chrome available :arrow_forwardFor the chemical equation so, (g) + NO, (g) SO, (g) + NO(g) the equilibrium constant at a certain temperature is 2.70. At this temperature, calculate the number of moles of NO, (g) that must be added to 2.31 mol SO, (g) in order to form 1.10 mol SO, (g) at equilibrium. moles of NO, (g): molarrow_forwardInitial (M) Change (M) Equilibrium (M) -0.00875 0.0209 Consider the reaction of SO2 and O₂ described by the chemical reaction below. Determine the equilibrium constant for this reaction by constructing an ICE table, writing the equilibrium constant expression, and solving it. Complete Parts 1-2 before submitting your answer. 2 SO2(g) + O₂(g) = 2 SO3(g) NEXT > A 2.00 L reaction vessel was filled 0.0432 mol SO₂ and 0.0296 mol O₂2 at 900 K and allowed to react. At equilibrium, the concentration of SO3 was found to be 0.0175 M. Fill in the ICE table with the appropriate value for each involved species to determine concentrations of all reactants and products. 0 0.00875 re or pull up for additional resources 2.00 1 2SO2(g) 0.0216 2.00 0.0432 0.0148 + 0.0296 2 0.0041 O₂(g) 0.0175 0.0129 11 -0.0175 0.0061 2SO3(g) RESET 0.0350 0.0257arrow_forward
- For the generalized chemical reaction A(g) + B(g) C(g) + D(g) determine whether the concentration of D in an equilibrium mixture will (1) increase, (2) decrease, or (3) not change when each of the following changes is effected. a) concentration of C is increased [ Select ] ["increase", "decrease", "no change"] b) concentration of C is decreased [ Select ] ["increase", "decrease", "no change"]arrow_forwardhelparrow_forward"Synthesis gas" is a mixture of carbon monoxide and water vapor. At high temperature synthesis gas will form carbon dioxide and hydrogen, and in fact this reaction is one of the ways hydrogen is made industrially. A chemical engineer studying this reaction fills a 1.5 1. flask with 0.88 atm of carbon monoxide gas and 4.0 atm of water vapor. When the mixture has come to equilibrium he determines that it contains 0.33 atm of carbon monoxide gas, 3.45 atm of water vapor and 0.55 atm of hydrogen gas. The engineer then adds another 0.22 atm of carbon monoxide, and allows the mixture to come to equilibrium again. Calculate the pressure of carbon dioxide after equilibrium is reached the second time. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. atm D.P Aarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY