
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
For the reaction A + B -> what is m and n?
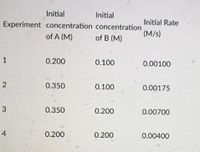
Transcribed Image Text:Initial
Initial
Initial Rate
Experiment concentration concentration
(M/s)
of A (M)
of B (M)
0.200
0.100
0.00100
0.350
0.100
0.00175
0.350
0.200
0.00700
4
0.200
0.200
0.00400
1.
2.
3.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In the reaction N2 + 3H2 = 2NH3, increasing the pressure will: a) increase the concentration of NH3 b) increase the concentration of N2 c) increase the concentration of H2 d) cause no changes in concentration It was found that aluminum oxide functions as a catalyst for the reaction described in the question . If one adds aluminum oxide to the mixture after it has reached equilibrium, this addition will: a) increase the concentration of NH3 b) increase the concentration of N2 c) increase the concentration of H2 d) cause no changes in concentrationarrow_forwardOpen the photoarrow_forward6) For a given equilibrium system, 2X = Y, use the graph to the right to determine which statement(s) below is/are true. Circle all that apply. 7). anonsuma Lopinated wahallo) ob Concentration (M) 0.12 0.1 0.08 0.06 0.04 0.12 0.02 0 00 0 0.08 0.015 a. The reaction has reached equilibrium at 60 seconds. b. There are more reactants than products at equilibrium. c. K> 1 for this reaction. d. The value of K, is 3. 0.055 -0.028 20 0.038 0.049 0.028 2X = Y 0.057 0.06 0.06 0.06 0.06 0.06 ad 0.022 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 40 Time (seconds) 60 80 100 Which one of the following statements about the equilibrium constant, K₂, is false? a. An is equal to the sum of the coefficients of the gaseous products minus the sum of the coefficients of the gaseous reactants. An b. The relationship between K, and K. is: K₂= K. (RT) LES GE с c. No units are reported with K, values. d. K. is usually larger than K₂.arrow_forward
- !! FULL DETAILS PLSarrow_forwardBased on a Ke value of 0.150 and the initial concentrations given in the table, determine in which direction the net reaction will proceed to attain equilibrium. Initial concentrations (M) Mixture XY [X] [Y] A 0 0.100 0 0.500 0.100 0.100 B с 0.200 0.300 0.300arrow_forwardFor a reaction A+B 2 AB, if the initial concentration of A is 2.00 M, B is 1.80 M and AB is OM and the equilibrium concentration of AB is 0.02 M. Select all statements that are TRUE. O The concentration of A at equilibrium is 2.00 M. O To calculate the Keg for this reaction, we can use (A]=2.00 M, [B]= 1.80 M and (AB]=0.02 M to solve for it. O The concentration of B at equilibrium is 1.78 M. O The Keq will be much larger than 1 and this reaction favor the formation of the product. O The change in concentration, x, is equal to 0.02 M.arrow_forward
- G.269.arrow_forwardConsider the following graphical representation of concentration versus time for the equilibrium system: COC1₂(g) = Cl₂(g) + CO(g) AH = + 108 kJ 0.14 0.12- -C1₂ 0.10- CO 0.08 0.06- COCI₂ 0.04 0.02- 0.00 0 2 8 10 16 Time (min) a) What change was imposed at time = 4 minutes? Be specific. b) What change was imposed at time = 10 minutes? Be specific. c) What change was imposed at time = 14 minutes? Be specific. d) Using the data for the 12 minute mark, calculate the value of Keq at the temperature concerned. Show your work. Concentration (mol L-¹) 12 18arrow_forward7. (1 Consider the reaction: N₂(g) + O₂(g) = 2NO(g); Kc 1.0x10-6. Suppose a sample of air 08) contains initially [N₂]=0.80M and [0₂]=0.20M. Use the neglect x approach to calculate the equilibrium concentration of all reactants and products at equilibrium. As part of your answer show that neglect x is valid. ausdi noitulos senisinoo vilsitini erudsteamet nisheo s is sutxim notlosen MEP1.0 of IH to noite insonoo eri bnuol esw mundilupe how Tuoy wor12 slab bebivo1q erit ritiw eldst 301 ne we10 sarrow_forward
- 9) Consider the reaction below at a certain temperature and pressure. The reaction begins with only [CO,] of 0.200 M and the equilibrium constant (Kc) is 9.81 X 10“, what is the equilibrium concentration of H' and HCO,? CO, (g) + H,O (1) H* (aq) + HCO3° (aq)arrow_forwardFrom the following reaction, as A decreases, what happens: to B A -->B Increases O Decreases O Stays the same O No way to tellarrow_forwardWriting the concentration equilibrium expression for a.. Write the concentration equilibrium constant expression for this reaction. CH3CO,H(aq)+C,H,OH(aq)→CH;CO,C,H,(aq)+H,0(1)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY