Introduction
“Mother’s Milk” is packed with proteins, fats and carbohydrates that support the
growth, development and survival of baby mammals. The sugar lactose is the
main carbohydrate in milk. Lactose can be cleaved into two simpler sugars,
glucose and galactose, by lactase, an enzyme produced in the small intestine. The
two smaller sugars are readily absorbed through the intestinal wall into the
bloodstream for delivery to the cells of the body, where they are used for energy.
After infant mammals are weaned from their mother’s milk, lactase production
shuts down, presumably because it is no longer needed. This condition is called
lactase nonpersistence – meaning the production of lactase enzyme does not
persist into adulthood. The general condition for mammals is not to consume
milk after weaning and to be lactase non persistent. Some populations of
humans are unusual in that adults continue to consume milk form other
mammals, such as cows.
If a person who is lactase nonpersistent drinks milk, undigested lactose passes
from the small intestine to the large intestine where it is fermented by bacteria.
Fermentation produces various gasses in the large intestine, which cause
abdominal pain, bloating, flatulence and diarrhea – all symptoms of lactose
intolerance. Worldwide, most adults are lactose intolerant, although some
people may not know it because their symptoms are mild. Only a minority of
human adults (about 35% of the global human population) continues to produce
lactase into adulthood and can drink milk without any problems. These
individuals are said to be lactase persistent or lactose tolerant.
There are several ways to test whether someone is lactase persistent. In the short
film, Got Lactase? The Co-evolution of Genes and Culture, the narrator, Dr.
Spencer Wells, takes a blood glucose test to deduce his lactase status.what im asking you to do is
examine the results of the blood tests conducted on six different
adults to determine who is lactase persistent (lactose tolerant) or lactase
nonpersistent (lactose intolerant).
Procedure
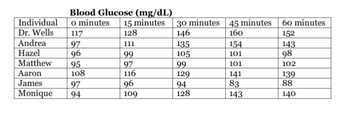
STEP 1: Examine the data in the table below. It shows the blood glucose levels of six
individuals tested in Dr. Sarah Tishkoff’s laboratory. After baseline (i.e. time 0
minutes) blood glucose levels of six individuals were measured and recorded,
Each person drank a liter of milk. Blood glucose levels were again measured at
15, 30, 45 and 60 minutes after drinking the milk. Glucose levels were measured
using glucose strips and a glucose reader.
(table is posted belo)
Step 2. Plot the results from the seven individuals on a graph.
Label your axes with units; provide a legend and a title.
STEP 3: Identify the dependent and independent variables.
(The two main variables in an experiment are the independent and dependent
variable. An independent variable is the variable that is changed or controlled
in a scientific experiment to test the effects on the dependent variable.
A dependent variable is the variable being tested and measured in a scientific
experiment.
When results are plotted in graphs, the convention is to use the independent
variable as the x-axis and the dependent variable as the y-axis.)
Step 4: (answer questions)
1. Identify the time interval when blood glucose levels of participants are highest.
2. Calculate the difference in Andrea’s blood sugar from her baseline to the 30
minute interval.
3. Based on these results, make a prediction about the lactase persistence and
nonpersistence of the participants.
Organize the participants into two groups in a table – persistence and
nonpersistence.
4. Identify the group that you predict the Maasai population of Kenya would fall
into. Justify your choice.
Step by stepSolved in 7 steps with 5 images

- An animal cell is capable of converting alanine into serine. What is the shortest pathway using known enzymes by which this conversion could be accomplished? Show intermediates and cofactors; no enzyme names are required. (Hint: the first step is the removal of the nitrogen by transamination.)arrow_forwardPart II - Lactase Catalyzes the Hydrolysis of Lactose II.i-Enzymes and Sugars The group of college students is on their way to the ice-cream shop and Sanjeet has offered Xiao-Ma Lactaid so that she could go with the group and also eat ice cream despite her lactose intolerance. Xiao-Ma: I've never taken Lactaid. What is it? Sanjeet: Chris: Sanjeet: My mom told me that you become intolerant to dairy because you don't have the enzyme that can digest lactose, which is the sugar found in milk products. Lactaid is a dietary supplement that contains the lactase enzyme. Uh, Sanjeet, remember-I'm a literature major. What's an enzyme? I don't remember what that word really means. Also, is the sugar in the milk different from the other sugar in my food? Finally my biochem class comes in handy in real life! An enzyme is a protein which catalyzes a reaction in the cell. There are tons of different enzymes in your body. The lactase enzyme catalyzes the degrada- tion of lactose into its subunits.…arrow_forwardWhen did some Africans gain the ability to process lactose? Describe how the evolutionary force of mutation changed the gene structure in these human populations, allowing adults to be able to process dairy.arrow_forward
- plz answer all.arrow_forwardAfter a meal that contains carbohydrates, blood glucose levels usually rise gradually as carbohydrates are digested and the resulting monosaccharides are absorbed into the bloodstream. Suppose you run a test on a human with no lactase production. You would provide a dose (e.g., 25 grams) of lactose and measure changes in blood glucose levels over the next three hours. Predict how blood glucose levels would change from fasting to three hours. Justify your response using the results from the above simulation.arrow_forwardon a molecular level explain what enables the interaction of salivary amylase and starch in potatoarrow_forward
- 12.arrow_forwardIn the lactase enzyme simulation you conducted in Part 1 of this Nutrition Lab, you found that enzyme activity is dependent upon the pH of the environment. Coffee has a pH of approximately 5.0. Suppose you added lactase to a cup of coffee with milk. Would glucose be produced? Addition of lactase to a mixture of coffee and milk would yield ______ glucose than addition of lactase to plain milk. more the same amount of lessarrow_forwardWhy is liver used as a source of glycogen in experiments even that there is a greater percentage of glycogen found in animal muscle?arrow_forward
- Discuss the mismatch between amino acid patterns in modern humans and the food they typically consume. What is the cause of this mismatch? Etc.arrow_forwardThe primary complexes for protein synthesis and very long chain fatty acid degradation in eukaryotes are A O ribosomes and proteasomes O ribosomes and peroxisomes O proteases and lysosomes proteases and proteasomes O ribosomes and mRNA and respectivelyarrow_forward