
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Individual and Market Demand - End of Chapter Problem
Suppose that, holding prices constant, Alice has preferences over the number of books she purchases, illustrated in the
accompanying table.
a. In the diagram below, move the points to plot Alice's Engel curve for books.
Income (thousands of dollars)
55
50
45
40
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
0
5
Alice's Engel Curve
10
15
20
25
Optimal number of books purchased
30
35
Income
(thousands of
dollars)
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
Optimal number of books
purchased
5
6
20
25
26
10
9
8
7
6
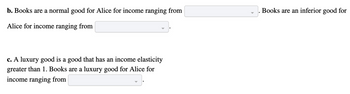
Transcribed Image Text:b. Books are a normal good for Alice for income ranging from
Alice for income ranging from
c. A luxury good is a good that has an income elasticity
greater than 1. Books are a luxury good for Alice for
income ranging from
. Books are an inferior good for
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 36arrow_forwardPlease help awnsering the following question. Thank youarrow_forwardUnits of the Good 0 1 5678AWN2 3 4 Total Utility Total Utility of X of Y 0 0 620 1740 1120 3030 1500 3960 1820 4710 2080 5280 2300 5730 2460 6060 2580 6300 For the next 3 questions, assume that an individual consumes two goods X and Y. The total utility (assumed measurable) of each good is independent of the rate of consumption of other goods. The prices of X and Y are, respectively, $20 and $30. If the consumer buys the fourth unit of X the Marginal Utility per Dollar Spent on X is 16 I If the consumer has $210 to spend on X and Y, the utility-maximizing bundle is The minimum budget necessary to move to a higher equilibrium consumption of X and Y is $ unit(s) of X and unit(s) of Y.arrow_forward
- Figure: Demand for Coconuts Price of coconuts E A D3 B D1 C D2 Quantity of coconuts Use Figure: Demand for Coconuts. If coconuts are a normal good and the income level of consumers falls, it will be represented in the figure as a: shift from D1 to D2 movement from point B to point C shift from D1 to D3 movement from point A to pointarrow_forward6. Part a and Part Barrow_forwardWhich of the following equations correctly represents solving Q = 140 - 4P for P? O P 35-4Q O P = 140 - Q OP 140 - 4Q OP=35-1Q O P = 140+ Q Plot the relationship between P and Q on the following graph. Note: Price (P) is on the vertical axis and quantity (Q) is on the horizontal axis. PRICE 40 35 30 25 20 15 л 10 ?arrow_forward
- quantity of bread 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 B 10 20 30 40 50 60 7080 quantity of apples Juan is a consumer of apples and bread. Juan shifts his consumption bundle from point B to point A. Which of the following is true? Juan's demand curve for apples shifted left and demand curve for bread shifted right. Juan's demand curve for both apples and bread shifted right. Juan's demand curve for apples shifted left and demand curve for bread shifted left. Juan's demand curve for apples shifted right and demand curve for bread shifted left.arrow_forwardMario and Chris are the only two consumers in a particular market for train tickets. The following table displays the relationship between the price of bus tickets for each consumer and quantity of train tickets demanded per week when the price of train tickets is $4.00 each. $2.00 $3.00 $4.00 $5.00 Price of bus tickets Mario's demand for train tickets 8 6. 4 2 Chris' demand for train tickets 1 2 3 a) Suppose the price of bus tickets is $4. The market demand of train tickets per day isarrow_forwardplease solve C by midpoint method Suppose that the demand schedule for rice for a Saudi family is as follows:PriceQuantity DemandedOf Rice Per Month(income = SR 10,000)Quantity DemandedOf Rice Per Month(income = SR 15,000)SR 5 60 70SR 4 80 95SR 3 100 120SR 2 120 145SR 1 140 170a. Given the table above, draw the demand curve of rice using Excel.b. Show what will happen to your graph if this family like now less rice as they are eatingmore outside.c. Use the midpoint method to calculate the price elasticity of demand as the price of riceincreases from SR 4 to SR 5 if (i) family’s income is SR 10,000 and (ii) family’s income is SR15,000.arrow_forward
- Problem 1 In the following scenarios, is the good described a normal good, an inferior good, or is there not enough information to say? Briefly justify your answer. a) Richard's income doubles and he goes from buying 4 apples per week to buying 5 apples per week. The prices of apples and any related goods do not change. b) Terri's income goes down by 50% and she goes from buying a bottle of tequila every week to buying one every month. At the same time, the price of tequila doubles. c) The price of potatoes goes up by 20% and Seamus buys 10% more potatoes. His income and the prices of related goods do not change. Hint: think about this one in the context of another topic you learned about this week.arrow_forward5. Leila currently buys 6 trips using public transportation with a marginal utility of 2, and 4 trips using ride-share with a marginal utility of 8. Suppose that the price of a trip through public transport is 12 and the price of a trip through ride share is 56. Is Leila currently maximizing her utility? Explain why or why not. If not, what is the optimal action to improve her utility?arrow_forwardRefer to the graph below. Assume that the initial equilibrium in the market for bus rides is point A (30 rides per week). The price of bus rides increases and the equilibrium shifts to point B (20 rides per week). The income effect of the change in consumer behavior is the $ of other consumption 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 T T T T T T L B C A 5 10 15 20 25; 30 35 40 45 26 # of bus rides per week decrease of consumption by 4 decrease of consumption by 6 increase of consumption by 6arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education