
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
In the three cases above are wires forming a
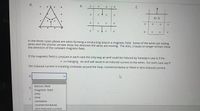
Transcribed Image Text:е.
f.
B=0
In the three cases above are wires forming a conducting loop in a magnetic field. Some of the wires are sliding
wires and the shorter arrows show the direction the wires are moving. The dots, crosses or longer arrows show
the direction of the constant magnetic field.
If the magnetic field is constant in each case the only way an emf could be induced by Faraday's Law is if the
v is changing. An emf will result in an induced current in the wires. For each case say if
the induced current is traveling clockwise around the loop, counterclockwise or there is zero induced current.
d.
electric field
е.
magnetic field
area
time
f.
clockwise
counterclockwise
zero induced current
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Which direction does the magnetic field due to the bottom wire point in?arrow_forwardAn electromagnet is the most powerful type of magnet there is. It is a magnet with a current running through it that can be turned on and off. Why might it be useful to be able to turn the electromagnet on and off?arrow_forwardWhy do parallel currents attract? Include a diagram that shows the magnetic field and magnetic force of the first wire on the second wire.arrow_forward
- what is the magnitude of force on an electron traveling east at 8.78 x106 m/s within a 78 T magnetic field directed in the west direction? Remember that the charge of an electron is 1.6e-19 Carrow_forwardThe figure below indicates that I and I2 are in opposite direction. they have magnitude of 3A and 5A consecutively. they are also at radiuses 2m and 4m consecutively. What is the magnetic field magnitude? of I2 ENG 4) G 7/TVarrow_forwardMagnetic field lines point from the north to the south pole. O True O Falsearrow_forward
- In the sketches, crosses represent the magnetic field into the page (or screen) and arrows represent the motion of the charges on the plane of the page (or screen). Negative or positive sign inside circle represent the sign of the charge. Speed and value of all charges are same. Rank the strength of magnetic force on each charge in the uniform magnetic field. A В C D +) A = B > C = D C A = C хх X х хarrow_forwardWhat is the largest force that the Earth’s magnetic field (here in Vancouver) could exert on an electron moving at a walking speed? Explain what direction the electron would have to move in to get the largest possible force.arrow_forward* Maps O Advertisement 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Io tne iert 14 A magnetic field strength of 4.3 µT is measured at 80.0 mm from a wire. How much current is being carried by the wire? (3 significant figures and scientific notation if appropriate) The two wires shown are separated by 2 cm. Each wire produces a magnetic field of strength 3 T at a distance of 2 cm. What is the magnitude of the net magnetic field strength at a point P, which is 2 cm to the left of the 15 1 1,? La tv MacBook Pro G Search or type URL #3 2$ & 3 7 8. W Y U P D F G H J K L ...- く O %24arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON