
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780133923605
Author: Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
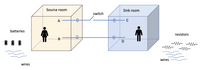
Transcribed Image Text:The diagram illustrates a basic electrical circuit model featuring two rooms: a "Source room" and a "Sink room."
### Components:
1. **Source Room**:
- Contains a figure labeled as 'A.'
- Designated as the starting point of the electrical flow.
- Connected to two wires, labeled as points 'A' and 'B.'
2. **Sink Room**:
- Contains a figure labeled as 'C.'
- Designated as the endpoint of the electrical flow.
- Connected to two wires, labeled as points 'C' and 'D.'
3. **Switch**:
- Positioned between the two rooms, controls the flow of electricity from the source to the sink.
4. **Batteries**:
- Represented outside the source room on the left, indicating the power source for the circuit.
5. **Wires**:
- Illustrated connecting the rooms, providing pathways for electrical current.
6. **Resistors**:
- Depicted outside the sink room on the right, showing components that impede the flow of electricity.
### Connections:
- **From Source to Sink**:
- Wire from point 'A' in the Source room runs through a switch to point 'C' in the Sink room.
- Wire from point 'B' in the Source room runs directly to point 'D' in the Sink room.
### Purpose:
This diagram serves as a simplified representation of an electrical circuit, showing how electricity flows from a power source (batteries) through a switch and resistors, explaining concepts like current direction, circuit control, and resistance.

Transcribed Image Text:**Source Room Setup:**
- A 20V battery is connected to terminals A and B, with A being the point of higher potential.
- The battery has an internal resistance of 0.25 ohms, which can be modeled as a resistor of 0.25 ohms in series with a perfect 20V source.
**Sink Room Setup:**
- A friend connects one resistor at a time to take measurements. The sequence of resistors used in the sink room are:
1. 100 ohms
2. 10 ohms
3. 1 ohm
4. 0.1 ohm
- Both you and the friend perform measurements for each resistor.
**Questions:**
a) What do you and your friend observe with the measurements?
b) What is the circuit like in the other room, and why?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 7 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Two resistors, of resistance 3 ohm and 6 ohm, are connected in parallel across a battery having a voltage of 12V. Determine the total circuit resistance and the current flowing in the 3 ohm resistor.arrow_forwardPlease explain correctly in detail. I will upvote. Thank you.arrow_forwardו 1 רץ:ר Z WhatsApp Image 2. -> loV 42 V. 4V 2V R2 El E3 Eu 19 p= 2W V--9V Fig -W For the Circuit of Fig-), determine R, and R2 then find V ,f Pen= 2W, Va=-9Varrow_forward
- 6. You have a circuit with two resistors, labeled Alpha and Beta, in parallel connected to a battery. (The same type of circuit we tested in our previous lab.) The voltage drop across resistor Alpha is 9.50 V. Alpha has a resistance of 235.0 2 and resistor Beta has a resistance of 518.0 2, What is the voltage drop across resistor Beta?" a. b. What is the total voltage drop across the entire circuit?? c. What is the equivalent resistance for the entire circuit? 10dioarrow_forward2. A parallel circuit has 3 resistors each on different paths connected to a 120 V potential difference. The resistors have resistances of 5.0 0. 7.5 Q. and 9.8 Q. Draw a schematic diagram of the circuit. Create a table for this circuit. INCLUDE DIAGRAMS AND TABLE ON THE SOLUTION. THANK YOUarrow_forwardWhat resistance must be connected in series with a 100-N resistor for the 100-0 resistor to produce heat at the rate of 30 W when the combination is connected to a 120-V source?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,